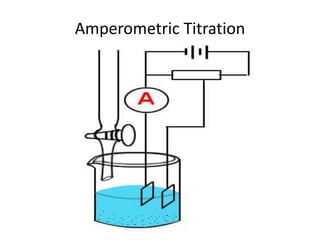
Amperometry is a type of voltammetric analysis that measures current over time while maintaining a constant potential at the working electrode. It can determine both the total elemental content and nature of dissolved species. A typical setup involves a working, reference, and auxiliary electrode in a measuring chamber. Current is measured as a function of the applied potential to generate a voltammogram. Amperometric titrations use this principle to locate the equivalence point from the intersection of current vs volume curves before and after the endpoint. Amperometry has advantages over other methods as it can analyze very dilute solutions and is unaffected by soluble or hydrolyzing products near the endpoint.


![A voltammetric analyses is done by using a certain setup of a measuring chamber
which contains three electrodes.
Working electrode (microelectrode)
Reference electrode
Auxiliary electrode
Apart from these electrodes, there is a voltage source and a devices for measuring
current and voltage – voltmeters and ammeter.
1. The method is based on the principle that the measurements of changes in time (τ) in
the current (I) flowing through the system of electrodes in relation to potential (E)
applied to the working electrode.
2. The change registered in the current allow drawing the I(τ) = f[E(τ)] relationship
which is known the voltammogram.
3. If the same measurements of the current are carried out at constant potential, then it
becomes a classical amperometric system.
4. Amperometric measurements completed in stirred solution or with rotating electrode
which is also termed as hydrodynamic amperometry.
5. The best use of Amperometry apparatus is to detected dissolved oxygen which is
reduced at the measuring electrode.
6. By using a micro- potentiotat the potential of the measuring electrode is kept at a
constant which is main characteristic for the oxygen reduction in Amperometry
technique.
7. Hence, the diffusion limited current is directly proportional to the oxygen
concentration.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/284684363-amperometry-240227161057-9b95944a/85/284684363-Amperometry-ppt284684363-Amperometry-5-320.jpg)
![DIFFERENT ELECTRODES USED IN
AMPEROMETRY
• Though the traditional D.C. amperometric titrations are performed
with D.M.E. as the indicator electrode
• Other electrodes have also been used for the purpose like Platinum
wire electrode, rotated at constant speed of 600 r.p.m. or more, has
been used on a large scale. [Latinen and Kolthoff, 1941] .
• Mechanical mixing help in bringing the electroactive species to the
electrode surface, besides diffusion.
• Consequently, limiting currents are much higher, about twenty
times, in comparison to those obtained with D.M.E.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/284684363-amperometry-240227161057-9b95944a/85/284684363-Amperometry-ppt284684363-Amperometry-7-320.jpg)

![Other Electrodes
• Vibrating platinum electrode [by Harris and Lindsey, 1948] .
• Rotating microelectrode of gold, graphite and aluminium, tantalum
and certain other material have also been used at times.
• Stationary glassy carbon disc electrode has also found application.
• However, all these solid electrodes suffer from one or the other
serious drawback.
• In amperometric titrations DME is used as an indicator electrode.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/284684363-amperometry-240227161057-9b95944a/85/284684363-Amperometry-ppt284684363-Amperometry-9-320.jpg)





