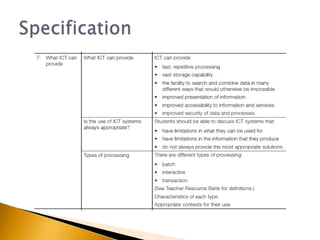
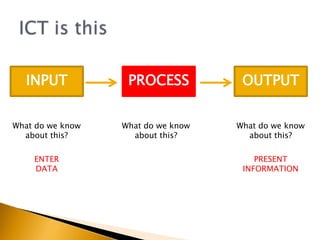
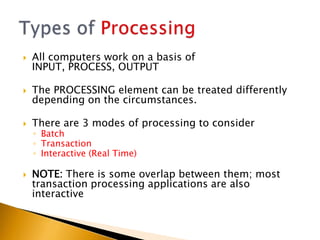
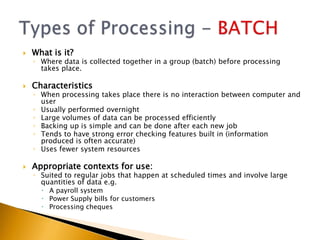
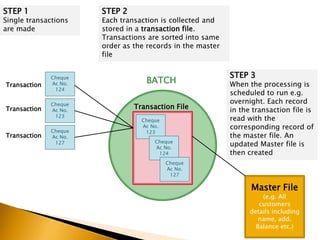
This document provides information about what ICT can provide and different types of processing. It discusses the 6 key features ICT provides: fast repetitive processing, vast storage capacity, improved search facilities, improved presentation of information, improved accessibility of information and services, and improved security of data and processes. It also discusses 3 types of processing - batch processing, interactive processing, and transaction processing - and provides examples of when each might be used. Limitations of ICT and situations when it may not provide the best solution are also addressed. Students are assigned reading and questions to complete for the next lesson.