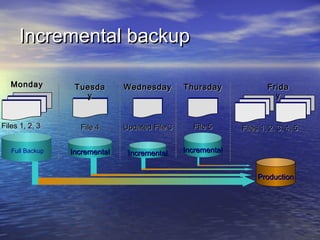
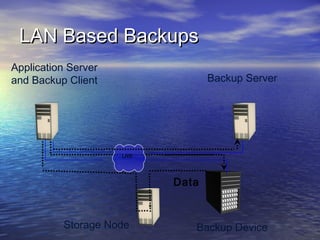
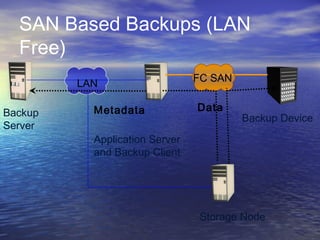
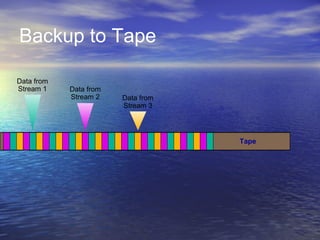
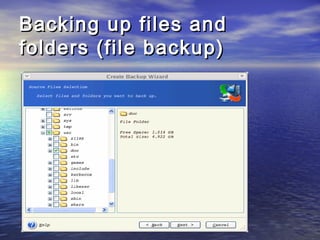
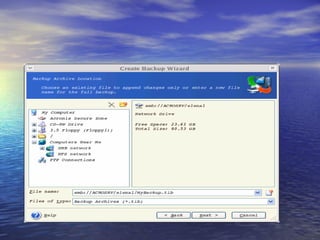
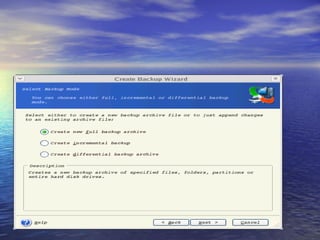
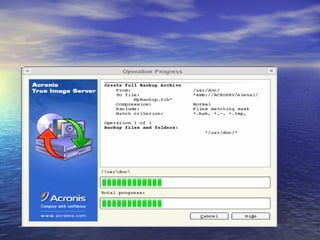
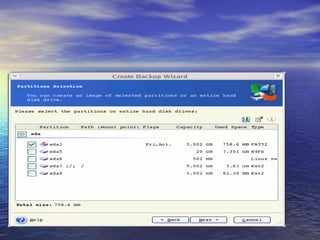
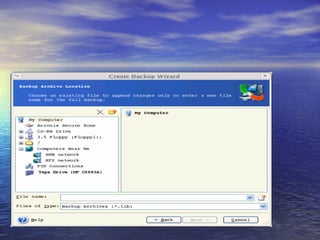
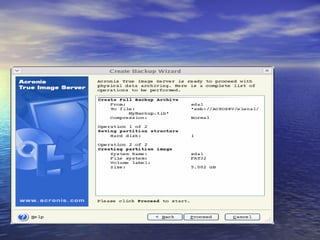
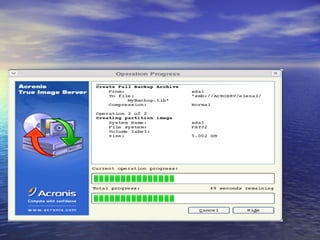
The document provides an overview of backup strategies and technologies. It discusses different types of backups including full, differential, and incremental backups. It covers backup architecture including backup clients, servers, and storage nodes. Key aspects of the backup process and restore process are outlined. Different backup topologies of direct attached, LAN-based, and SAN-based backups are described. Options for backup technology include backing up to tape or disk. Features of Acronis backup software are briefly mentioned.