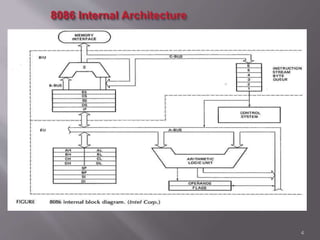
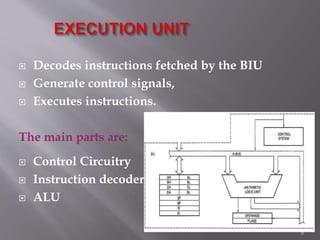
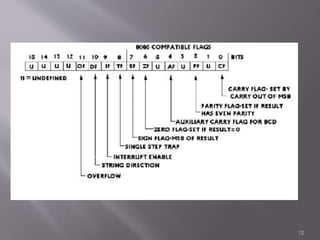
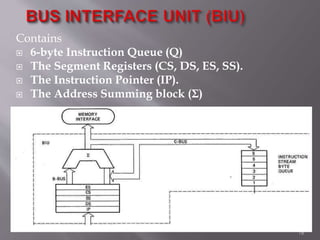
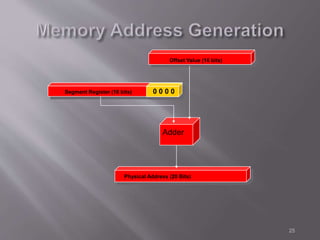
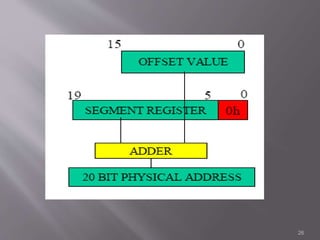
The 8086 microprocessor is a 16-bit CPU with a 20-bit address bus that can access up to 1 MB of memory. It has two main components: the Bus Interface Unit (BIU) and Execution Unit (EU). The BIU handles fetching instructions and reading/writing memory/I/O, while the EU decodes and executes instructions. The 8086 uses segmented memory addressing across four 16-bit segment registers - code, data, stack, and extra. It has 16-bit registers including general purpose, index, pointer and flag registers. The flags register indicates results like carry, zero from arithmetic instructions.