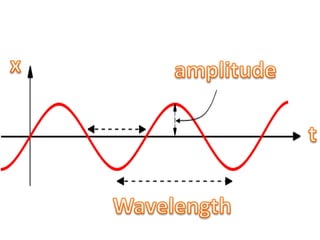
This document defines key terms related to waves, including displacement, oscillation, amplitude, frequency, wavelength, and wave speed. It explains that a wave is a disturbance that moves through a medium, caused by something vibrating in that medium. The key properties of waves - amplitude, frequency, wavelength, and wave speed - are defined and their relationships are shown in the equation that relates wavelength, frequency and wave speed. Examples are given of how changing wavelength would affect a wave.