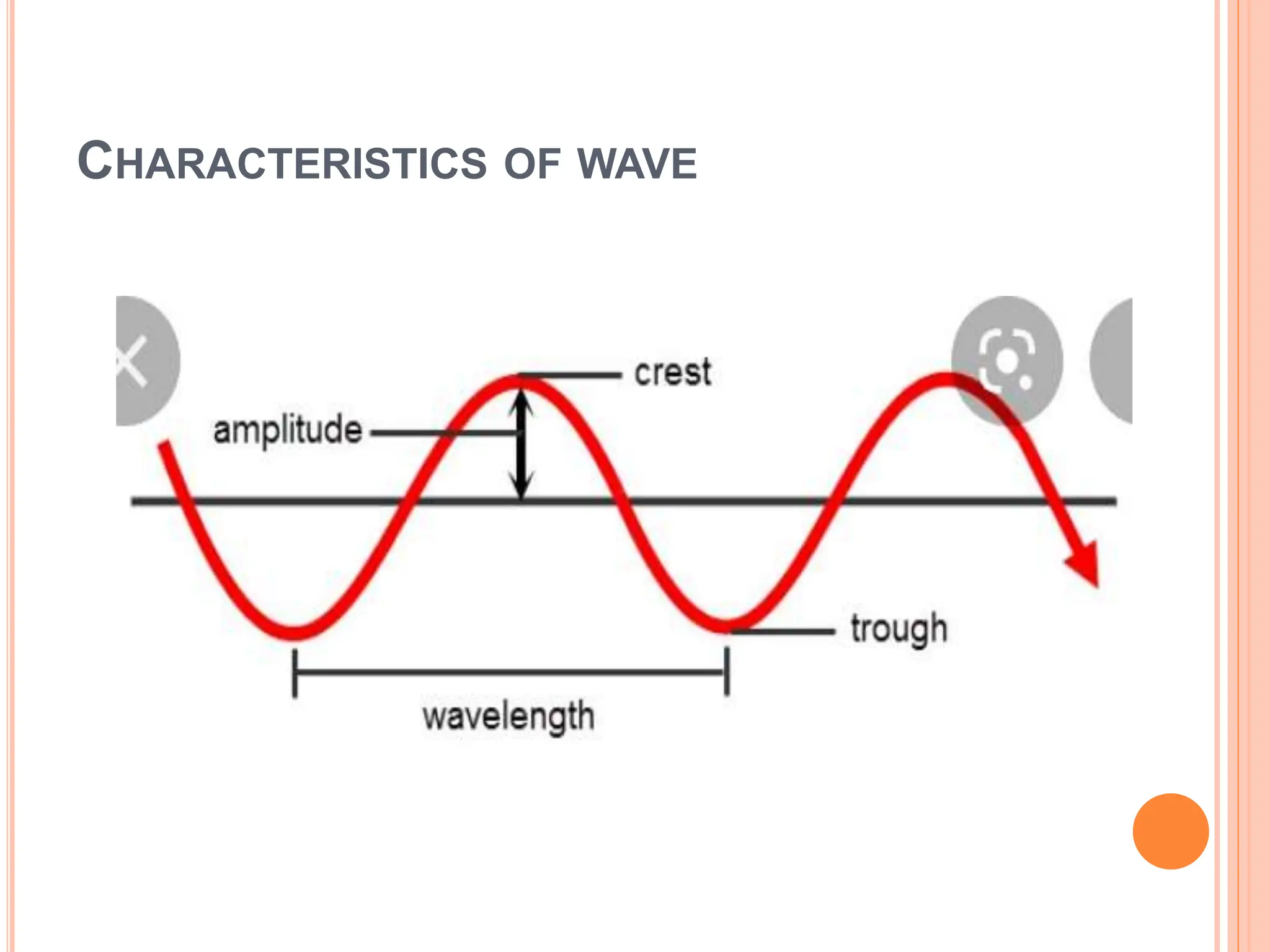
The document explains the differences between transverse and longitudinal waves, detailing how they travel and their required mediums. It also covers important wave characteristics such as amplitude, wavelength, speed, and frequency, providing formulas for calculations. An example demonstrates how to calculate various properties of a wave traveling along a rope.