Embed presentation
Downloaded 227 times





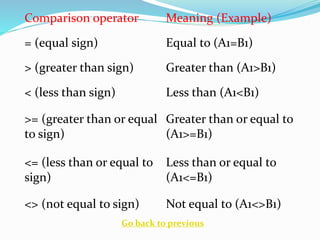





The document outlines different types of operators used in calculations, including arithmetic, comparison, text concatenation, and reference operators. Arithmetic operators perform mathematical operations, comparison operators evaluate logical conditions, text concatenation operators join text strings, and reference operators handle cell ranges in calculations. Each operator is explained with its symbol and usage examples.









