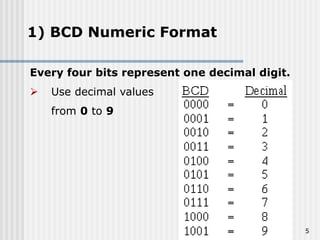
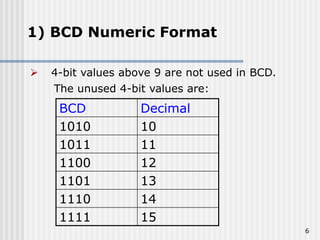
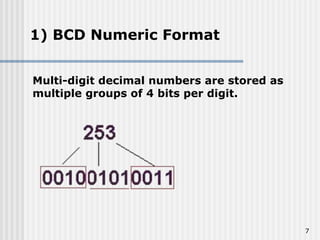
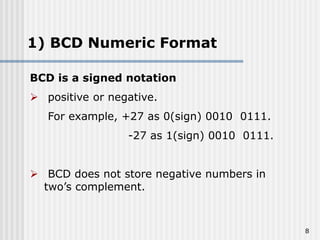
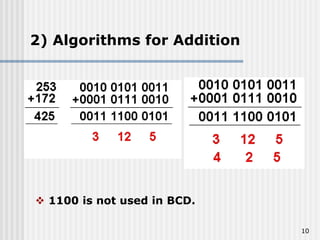
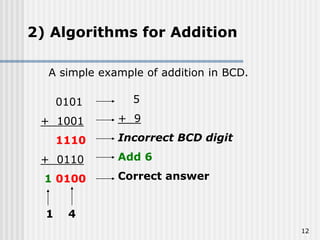
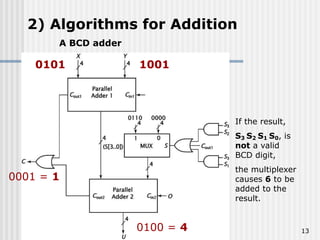
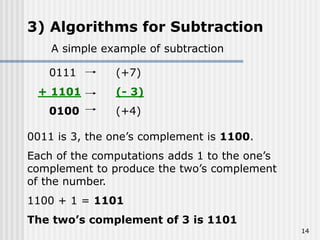
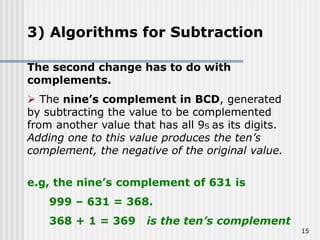
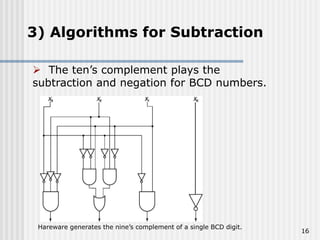
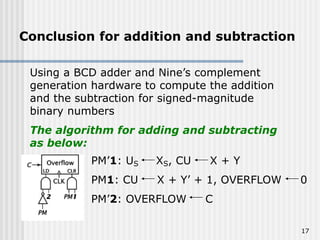
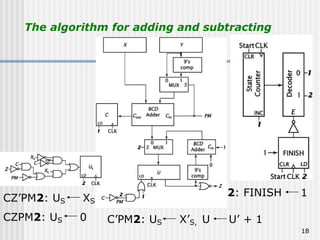
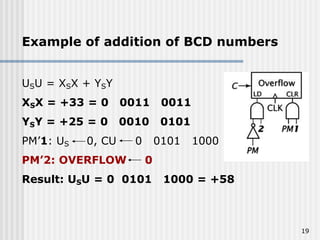
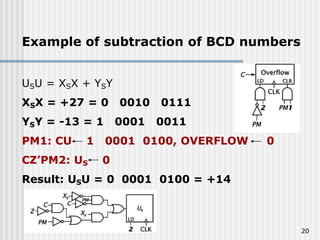
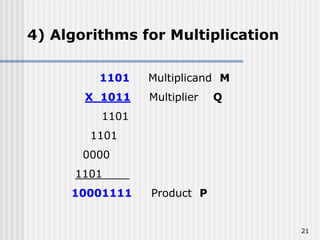
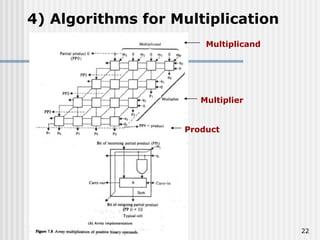
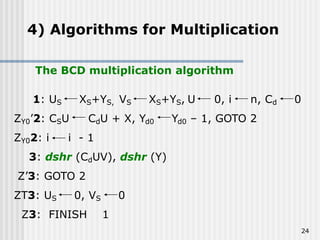
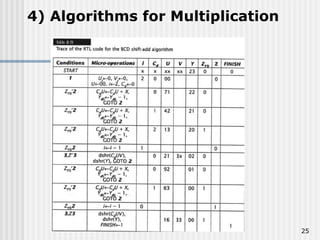
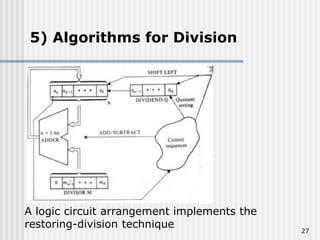
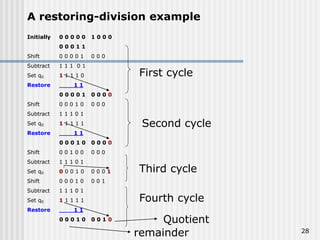
Binary coded decimal (BCD) is a method for representing decimal digits in binary form, with each decimal digit being represented by a 4-bit binary number. BCD is commonly used in digital clocks and calculators to store and display numbers in a human-readable decimal format. Algorithms are required for BCD addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division since standard binary arithmetic can produce invalid results. Addition and subtraction use BCD adders along with 9's complement generation, while multiplication uses an inner loop to perform multiple additions and decimal shifts. Division can be implemented with restoring or non-restoring algorithms using an inner loop for repeated subtraction and shifting.