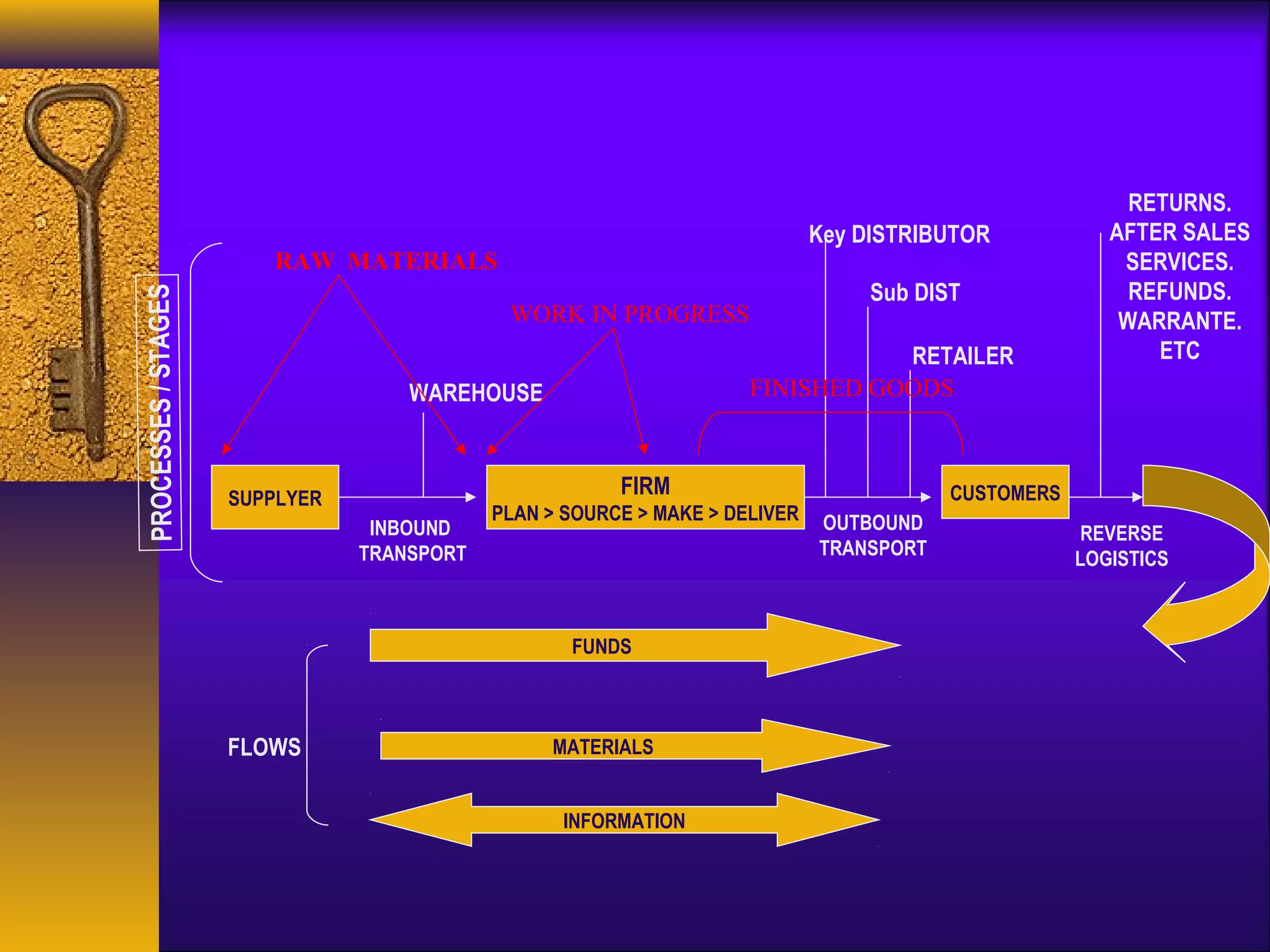
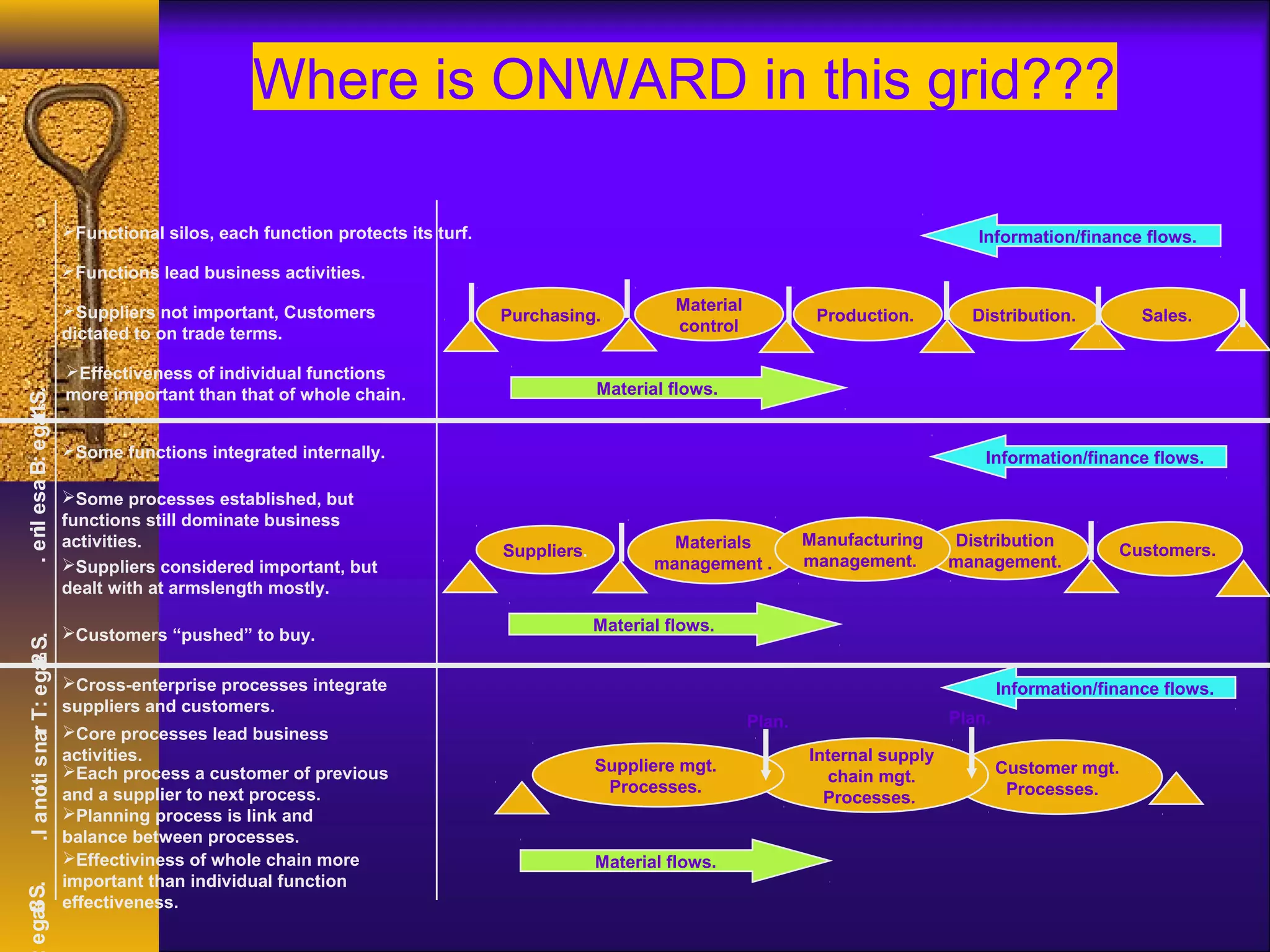
This document discusses 21st century logistics and supply chain management. It defines logistics as planning and controlling the flow of goods and services, and defines supply chain management as coordinating the flow of information, materials, and services from suppliers to customers. The document outlines the strategic, tactical, and operational levels of supply chain decisions. Key challenges include integrating different partners and the dynamic nature of supply chains over time. Benefits of supply chain management include reducing costs, improving customer service, and mitigating the bullwhip effect.