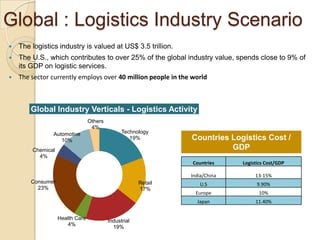
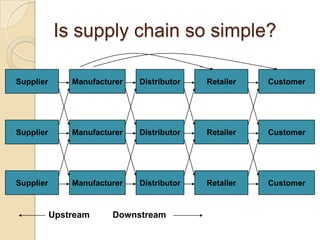
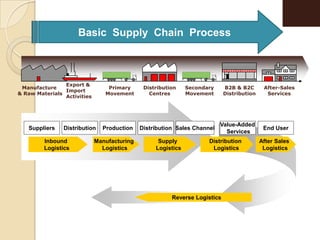
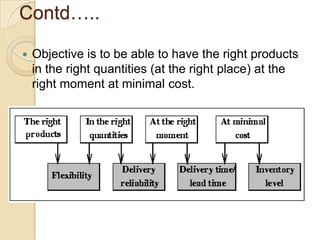
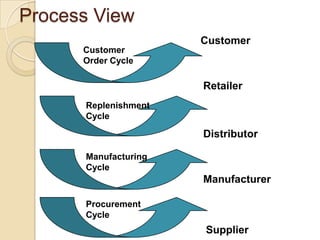
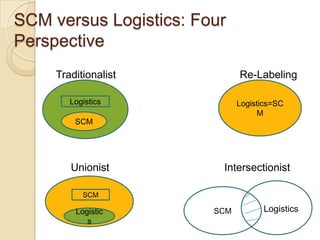
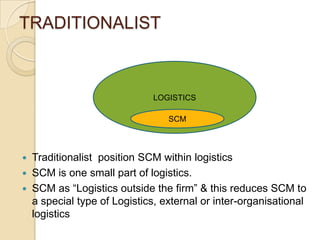
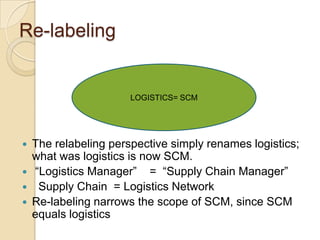
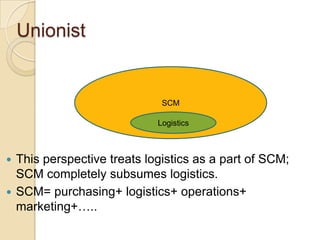
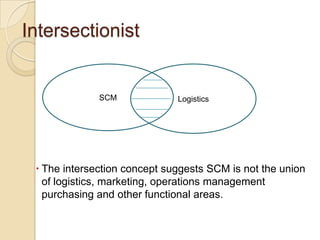
This document discusses logistics and supply chain management. It defines logistics as the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient flow of goods, services, and information from origin to consumption according to customer demands. Supply chain management involves planning and coordination across organizations to deliver value to customers. The document outlines key aspects of logistics like transportation and warehousing as well as objectives like reducing costs and inventory. It also discusses supply chain drivers, processes, and the relationship between logistics and supply chain management.