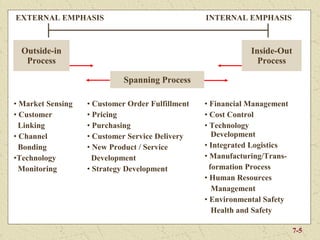
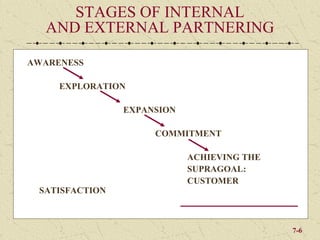
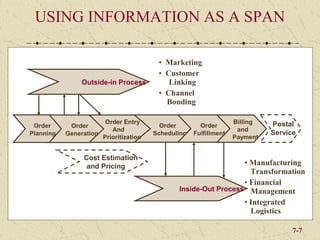
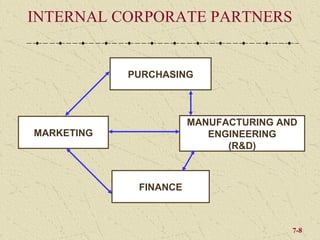
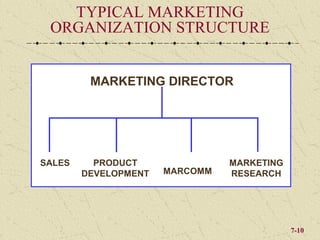
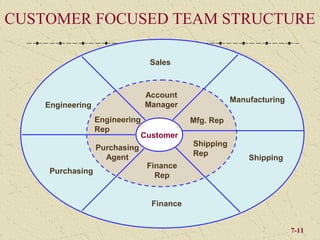
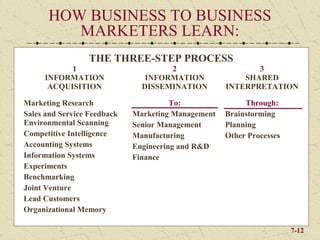
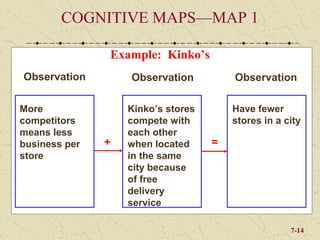
The document discusses integrating marketing into business operations. It provides examples of how companies can establish a customer-focused corporate culture through various initiatives. These include listening to customer feedback, aligning customer needs with company capabilities, and encouraging collaboration across departments. The text also outlines different models for marketing organization and processes that bring together internal partners to learn about customers and share information.