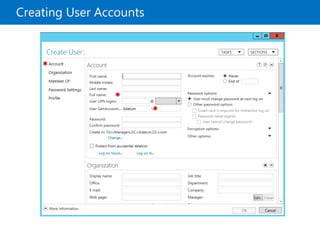
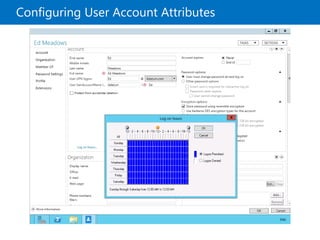
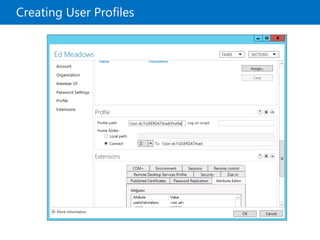
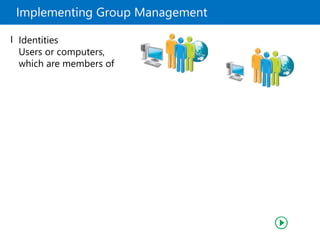
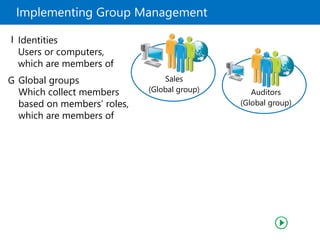
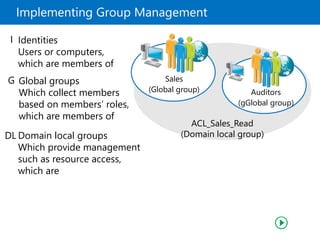
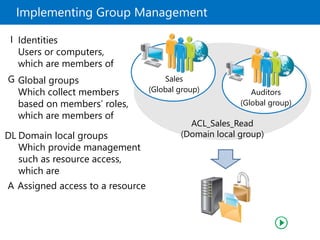
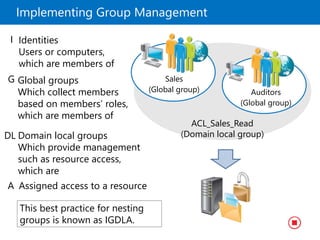
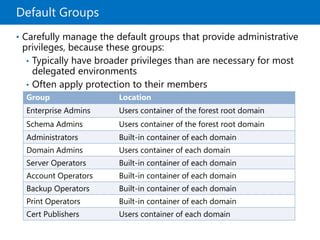
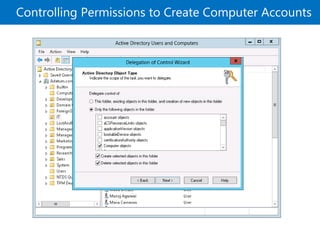
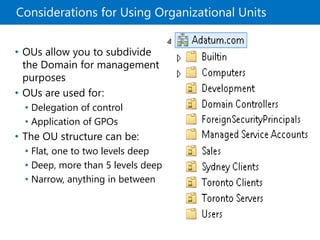
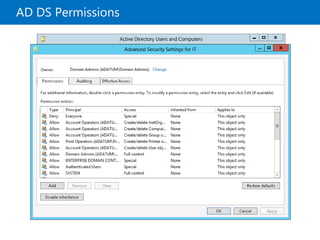
This document provides an overview of a Microsoft course module on managing Active Directory Domain Services objects. The module includes lessons on managing user accounts, groups, computer accounts, and delegating administration. It demonstrates how to perform tasks like creating users and groups, managing computer objects, and delegating administrative permissions to organizational units. The goal is to prepare students to configure Active Directory infrastructure for a new branch office by creating and managing required objects and delegating permissions.