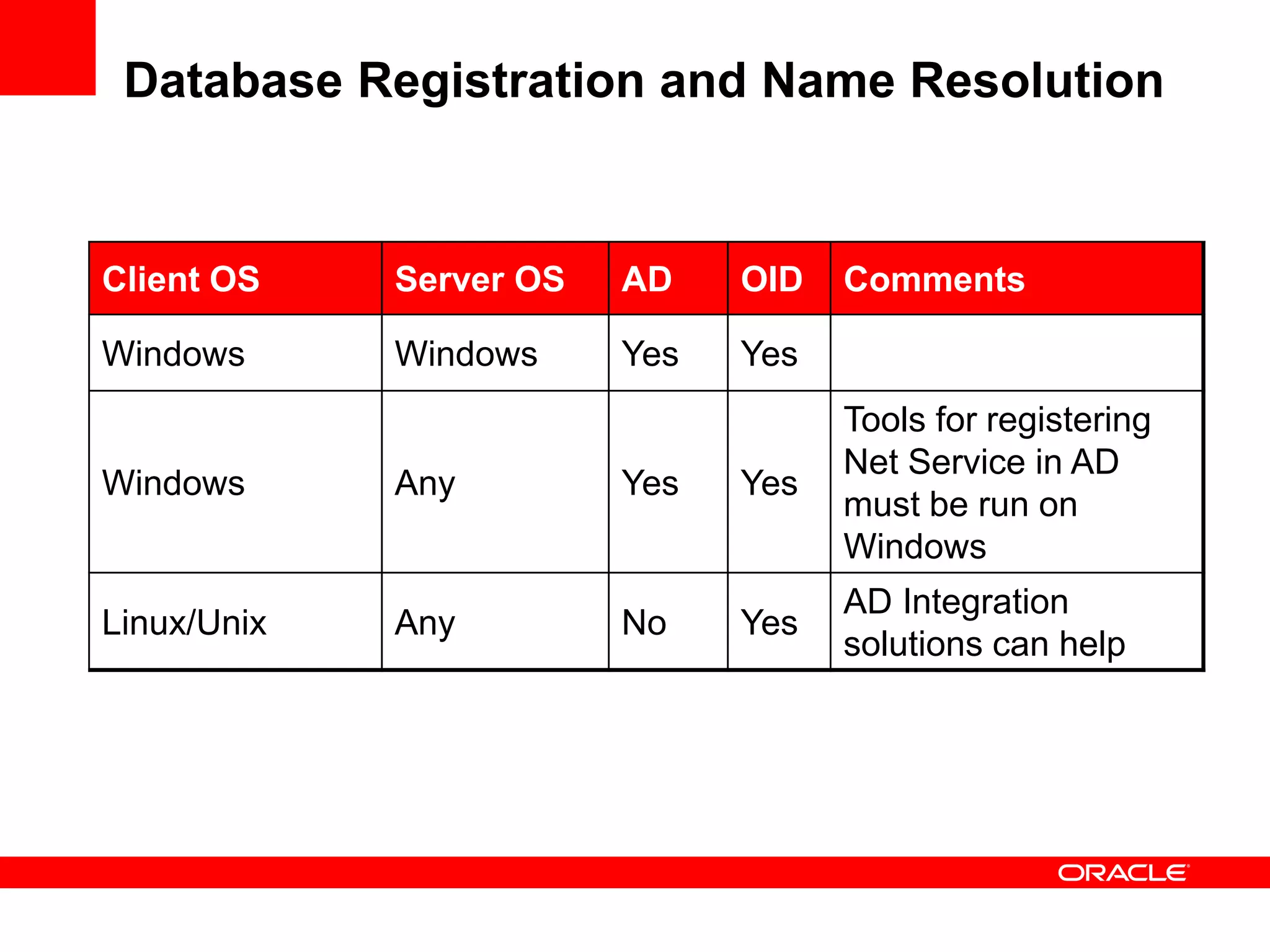
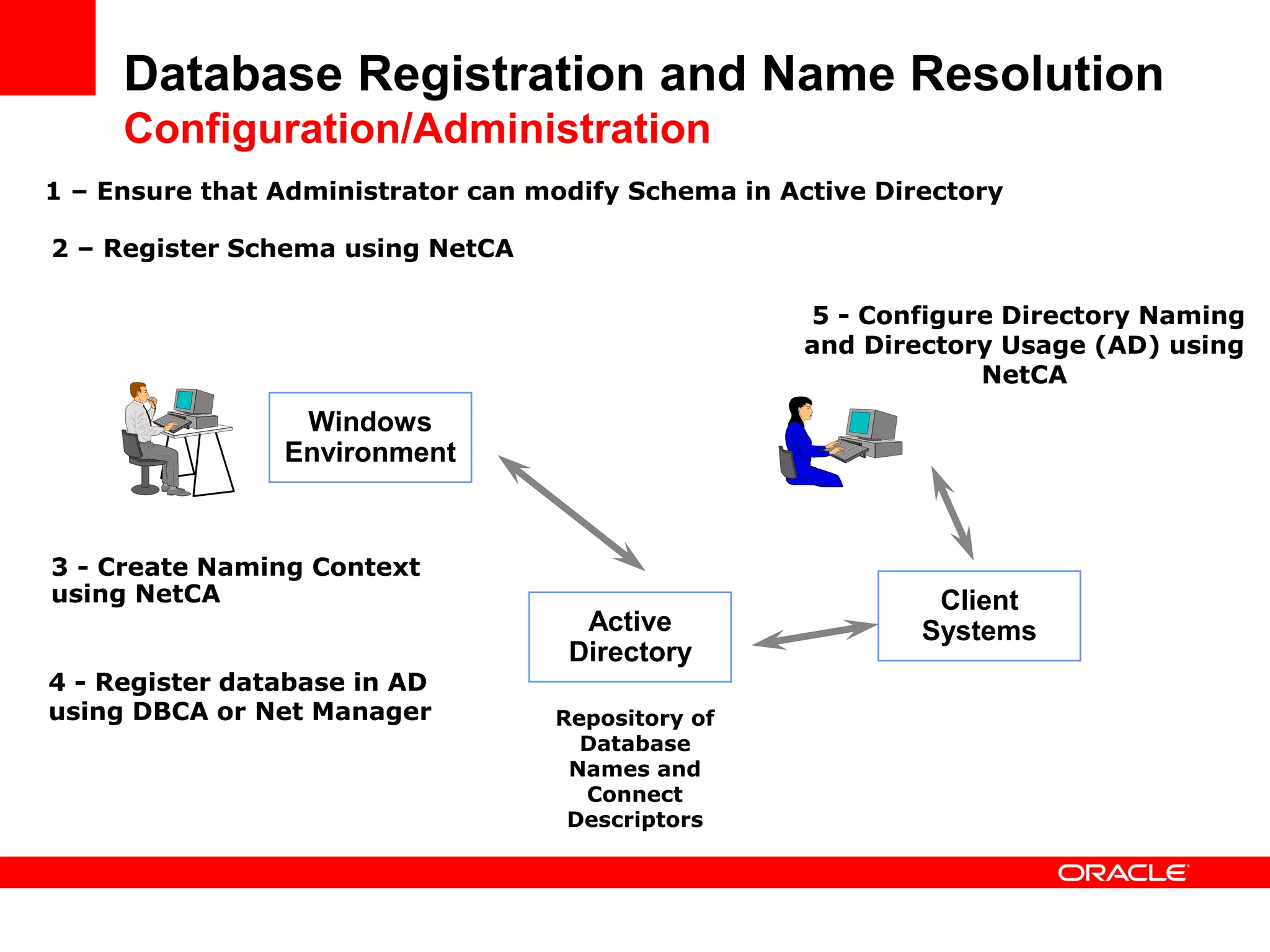
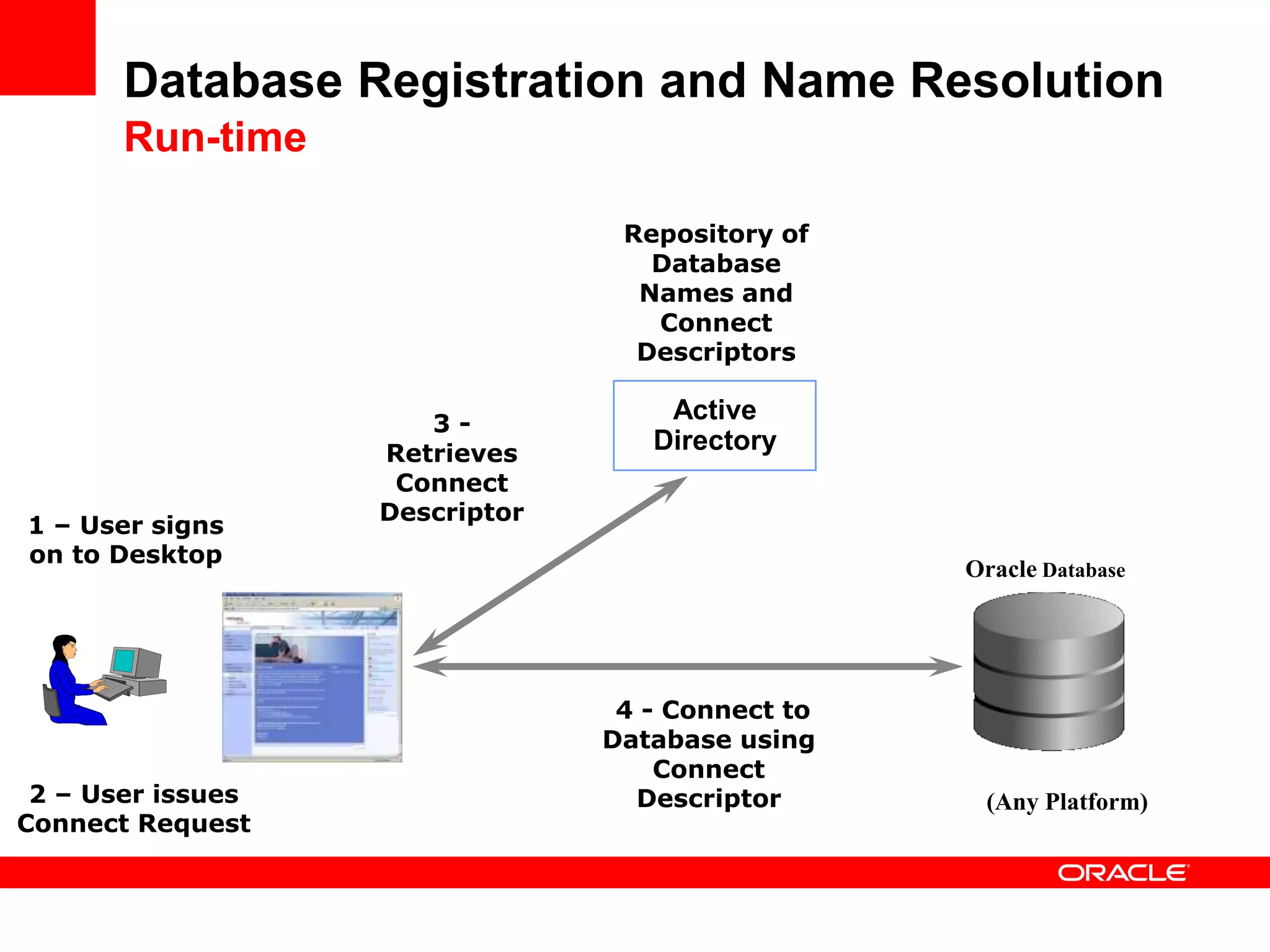
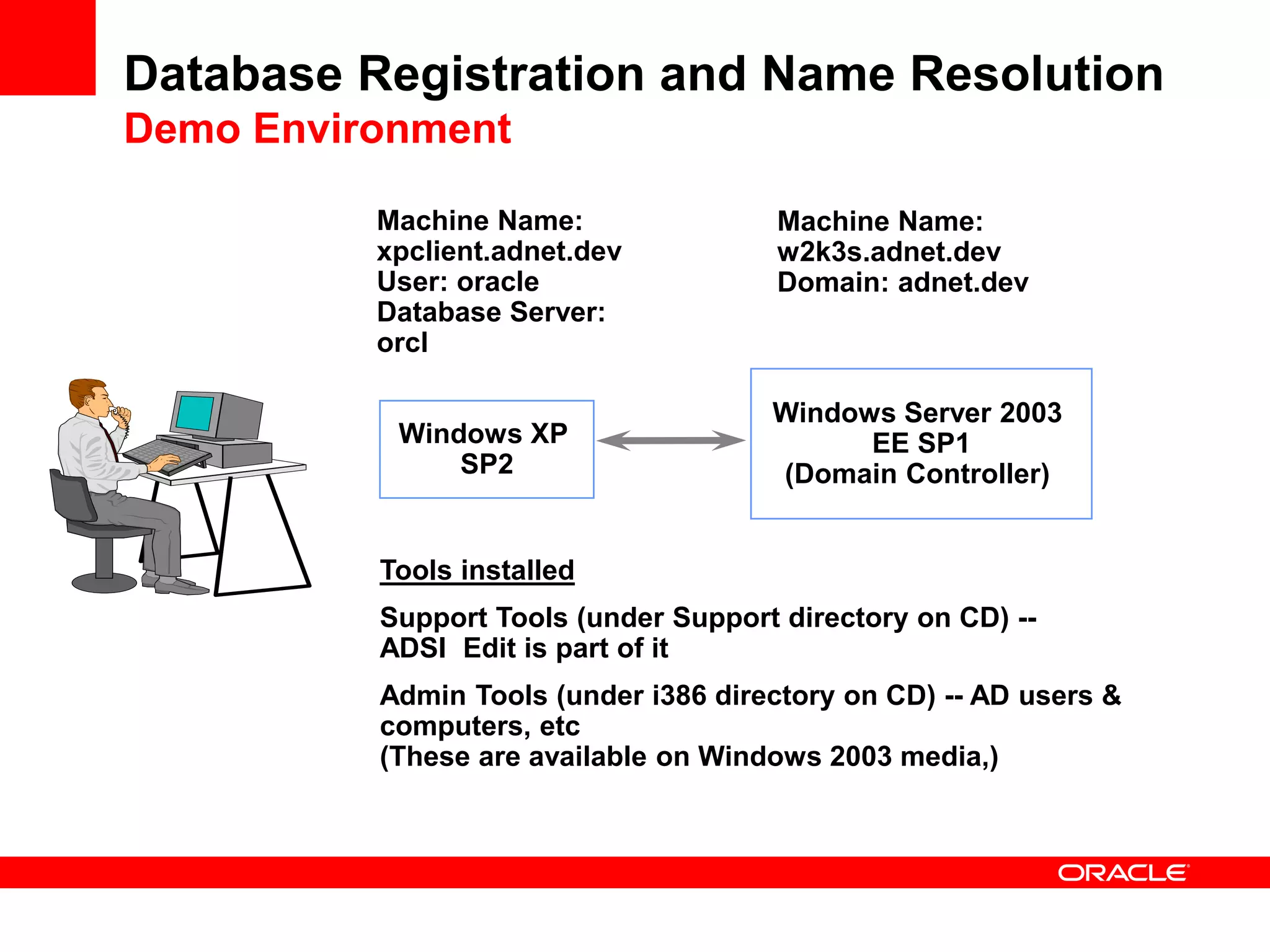
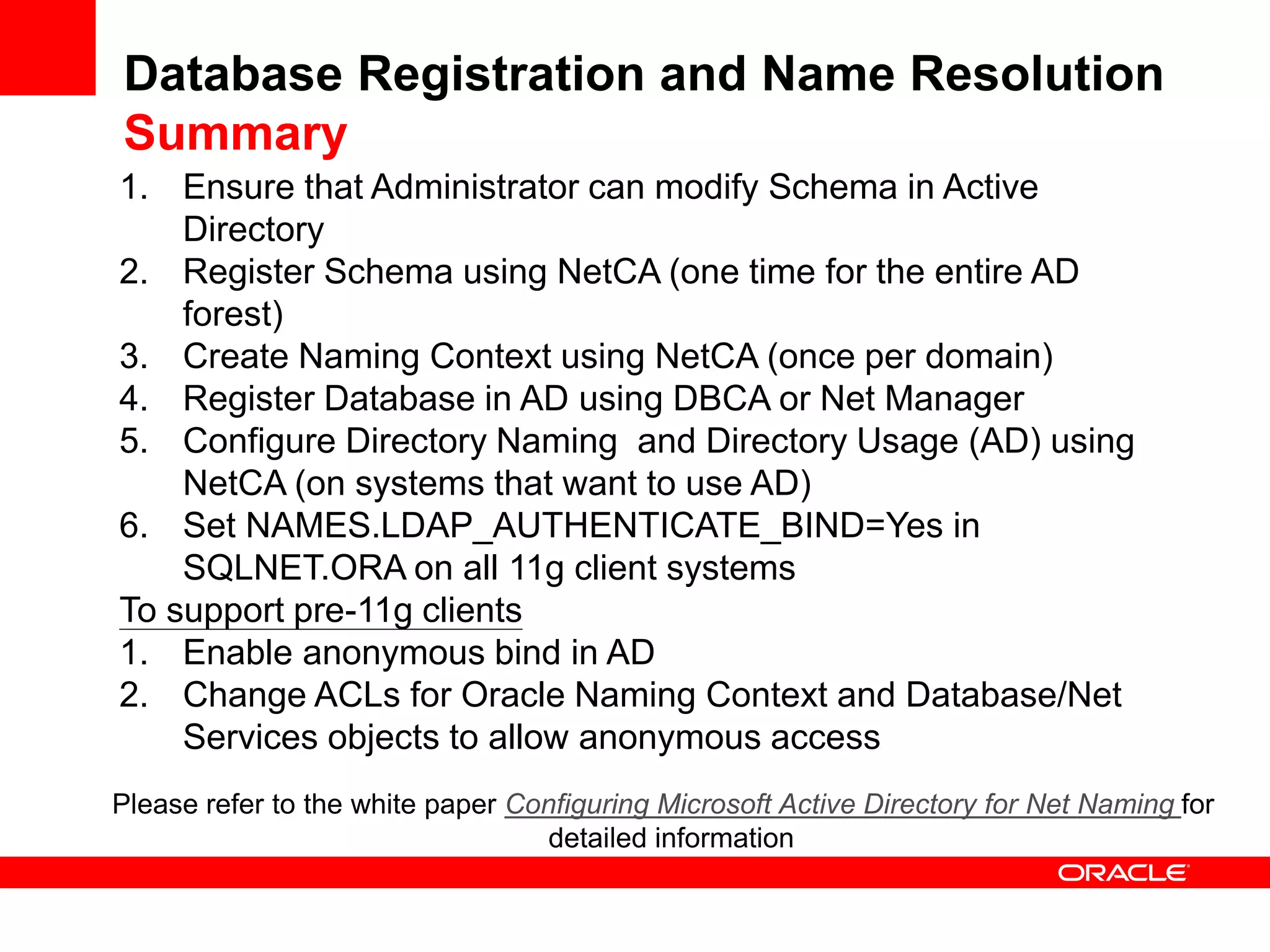
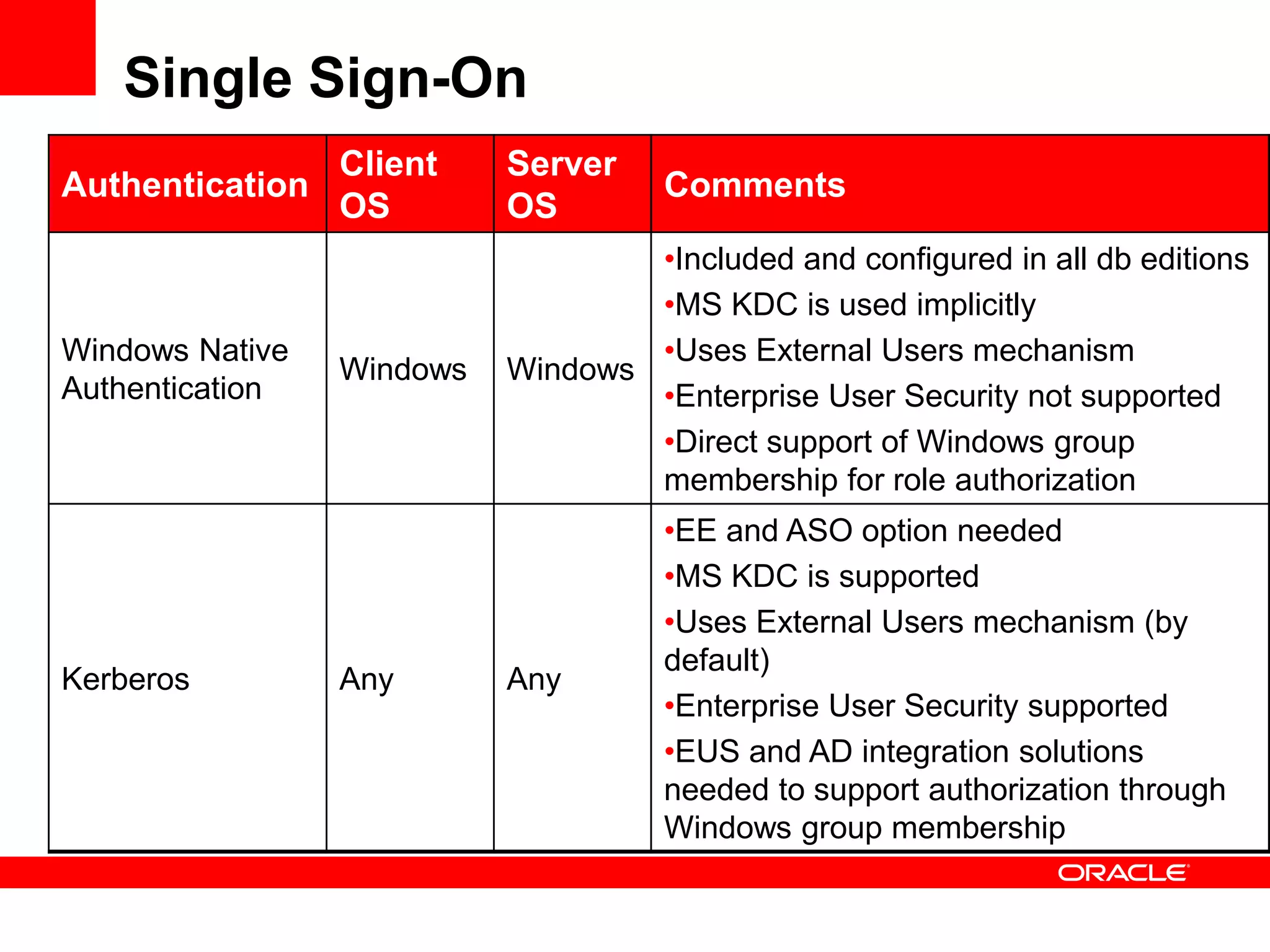
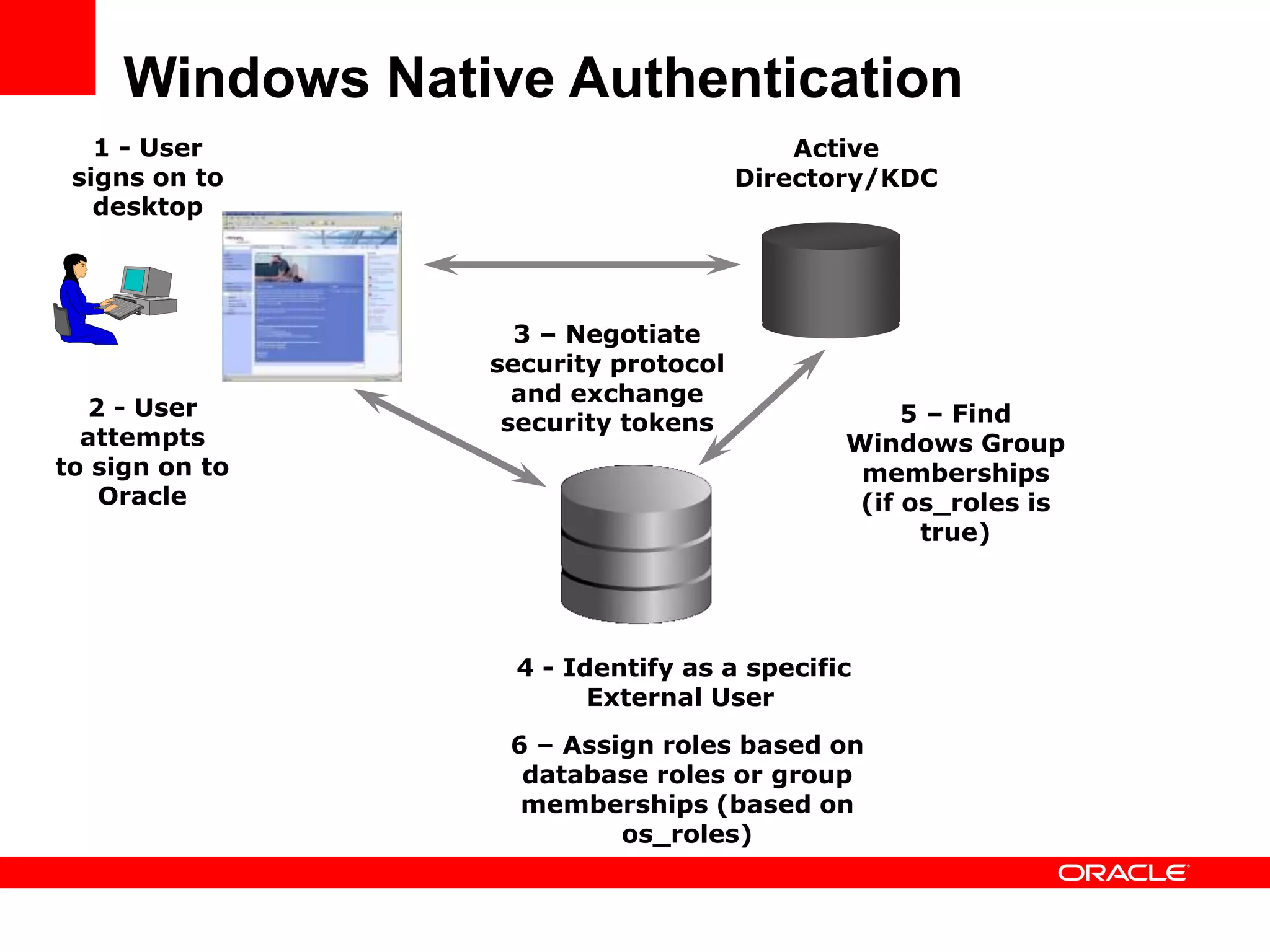
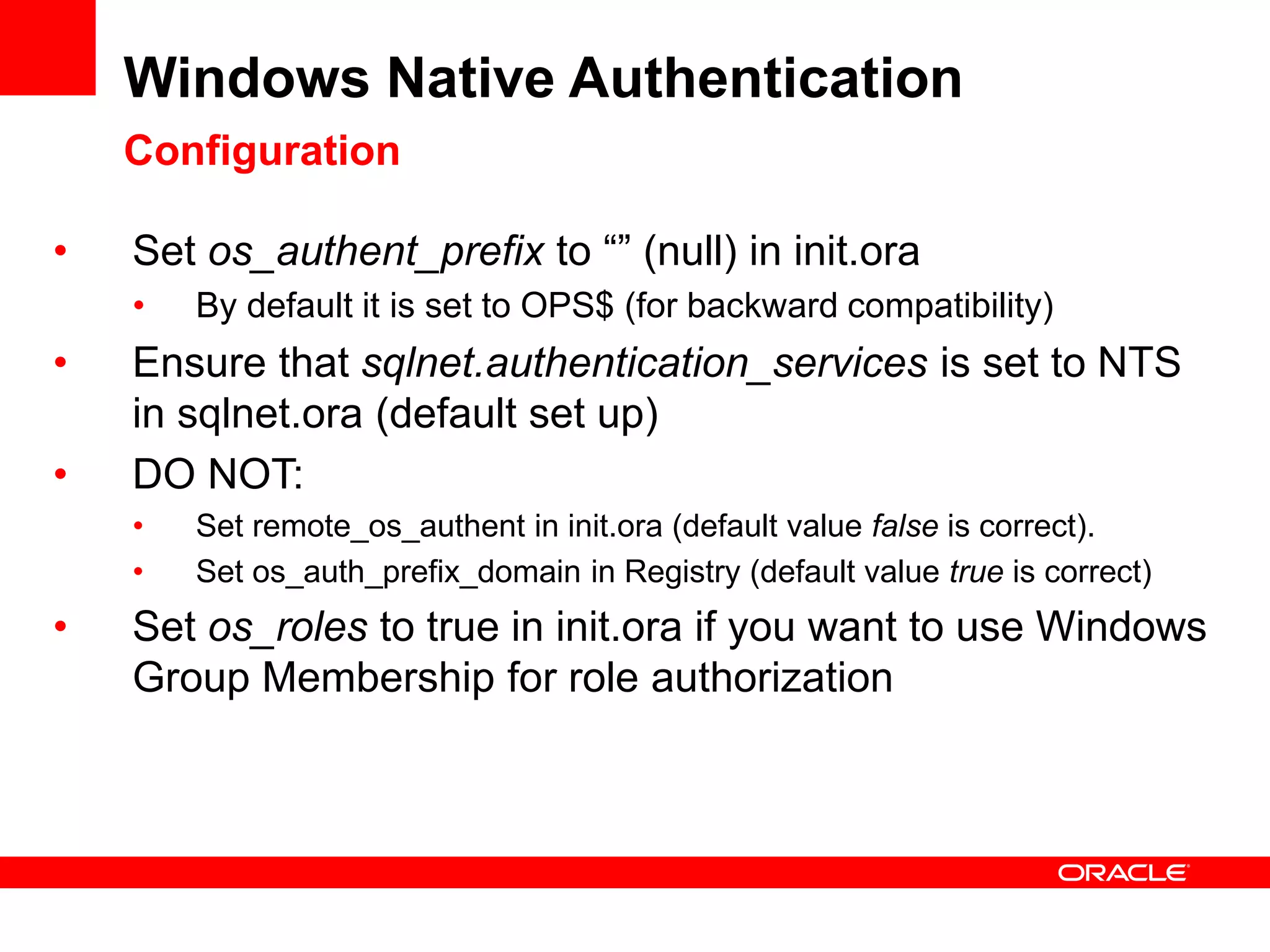
The document provides an overview of Oracle Database integration with Active Directory and Windows security. It discusses features such as database registration and name resolution in Active Directory, single sign-on using Windows native authentication and Kerberos, security integration for .NET applications, and using Oracle Virtual Directory for centralized enterprise user security and management. Configuration details are provided for each feature along with demos. The presentation is intended for informational purposes only and Oracle retains sole discretion over product features and release timing.