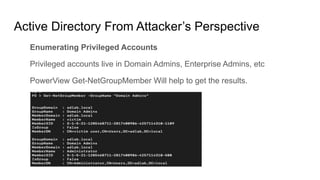
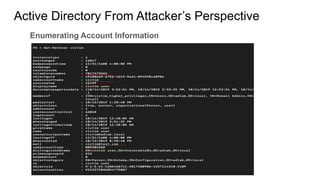
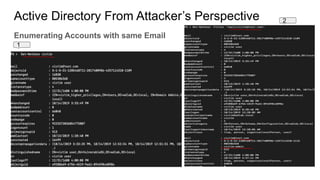
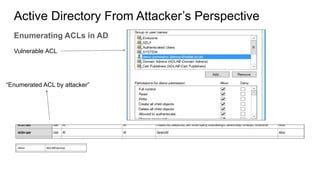
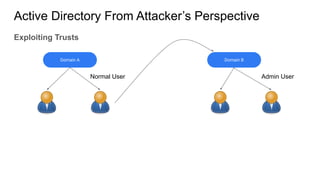
Active Directory is a centralized directory service that stores objects like users, groups, computers, and policies. It provides security and simplifies administration. Groups contain users/computers and help apply policies. Group policies centrally manage settings. Organizational units logically organize objects and delegate administration. Trusts allow access between domains. From an attacker's perspective, they would get an initial foothold, enumerate privileged accounts and permissions, and exploit any misconfigurations to escalate privileges like taking over accounts. They could also use trusts to access other domains.









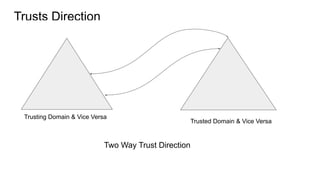
![Trusts Direction
One Way Trust Direction
Trusting Domain [domainA.com] Trusted Domain [domainB.com]
Direction Of Trust
Direction Of Access](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activedirectory101-191107153546/85/Active-directory-101-10-320.jpg)