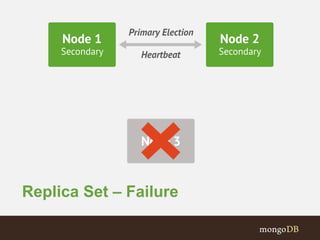
The document discusses MongoDB operations for developers, including its data model, use of replication for high availability, and sharding for scalability. It also covers deployment architectures, security features, and operational resources for MongoDB.





![Document Data Model
Relational MongoDB
7
{
first_name: ‘Paul’,
surname: ‘Miller’,
city: ‘London’,
location:
[45.123,47.232],
cars: [
{ model: ‘Bentley’,
year: 1973,
value: 100000, … },
{ model: ‘Rolls Royce’,
year: 1965,
value: 330000, … }
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20140911admin101webinar-141004191644-conversion-gate02/85/Ops-Jumpstart-MongoDB-Administration-101-7-320.jpg)
![Documents are Rich Data Structures
8
{
first_name: ‘Paul’,
surname: ‘Miller’,
cell: ‘+447557505611’
city: ‘London’,
location: [45.123,47.232],
Profession: [banking, finance, trader],
cars: [
{ model: ‘Bentley’,
year: 1973,
value: 100000, … },
{ model: ‘Rolls Royce’,
year: 1965,
value: 330000, … }
}
}
Fields can contain an array of
sub-documents
Fields
Typed field values
Fields can
contain arrays](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20140911admin101webinar-141004191644-conversion-gate02/85/Ops-Jumpstart-MongoDB-Administration-101-8-320.jpg)