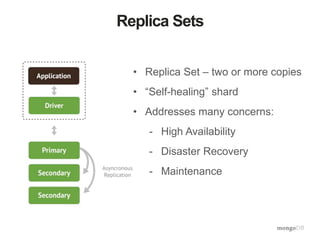
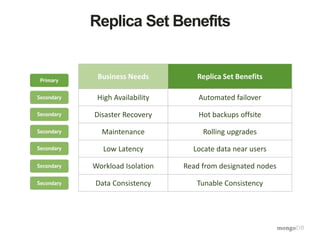
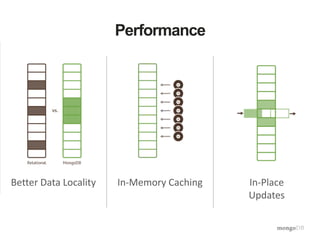
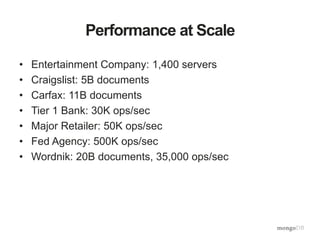
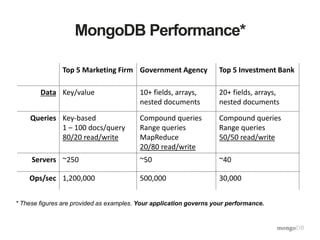
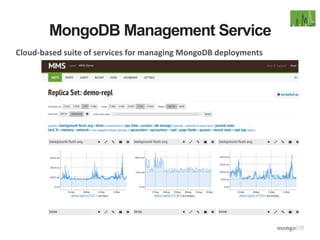
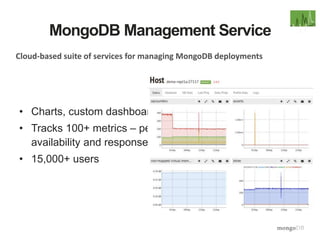
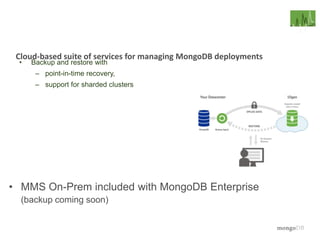
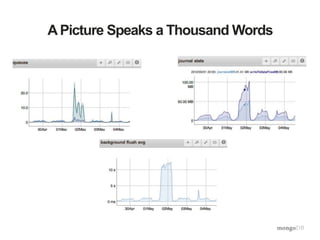
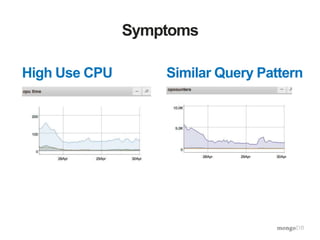
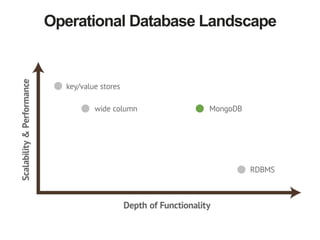
The document discusses the operational benefits and features of MongoDB as a modern database solution, highlighting its agility, flexibility, and automatic sharding capabilities. It emphasizes the importance of high availability, disaster recovery, and performance scaling through replica sets and monitoring tools. Additionally, it mentions the MongoDB Management Service, which provides cloud-based management for deployments with comprehensive performance tracking and support for backups.

![RDBMS
Agility
MongoDB
{
_id : ObjectId("4c4ba5e5e8aabf3"),
employee_name: "Dunham, Justin",
department : "Marketing",
title : "Product Manager, Web",
report_up: "Neray, Graham",
pay_band: “C",
benefits : [
{ type : "Health",
plan : "PPO Plus" },
{ type : "Dental",
plan : "Standard" }
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014fallops101-141024105243-conversion-gate01/85/Ops-Jumpstart-MongoDB-Administration-101-3-320.jpg)
![Document Data Model
Relational MongoDB
{
first_name: ‘Paul’,
surname: ‘Miller’,
city: ‘London’,
location:
[45.123,47.232],
cars: [
{ model: ‘Bentley’,
year: 1973,
value: 100000, … },
{ model: ‘Rolls Royce’,
year: 1965,
value: 330000, … }
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014fallops101-141024105243-conversion-gate01/85/Ops-Jumpstart-MongoDB-Administration-101-4-320.jpg)