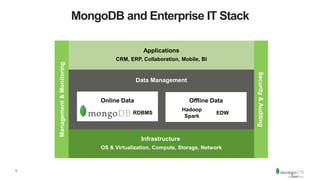
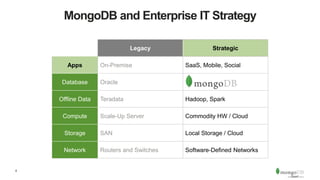
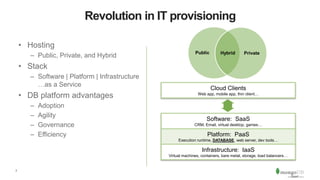
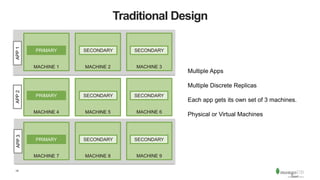
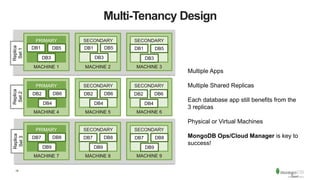
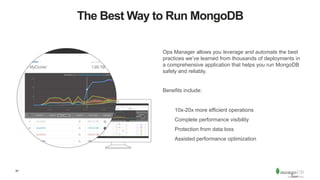
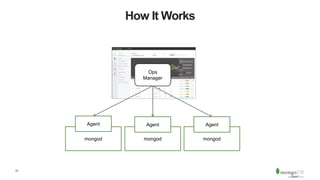
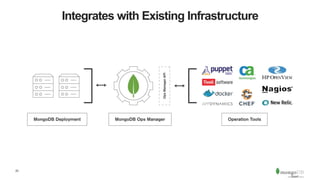
The document discusses the advantages and implementation of Database as a Service (DBaaS) in enterprise architecture, particularly focusing on MongoDB as a service. It highlights the benefits of agility, scalability, and efficiency while addressing risks and best practices for successful adoption. The document also presents case studies from organizations like the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and Goldman Sachs that utilize MongoDB services.