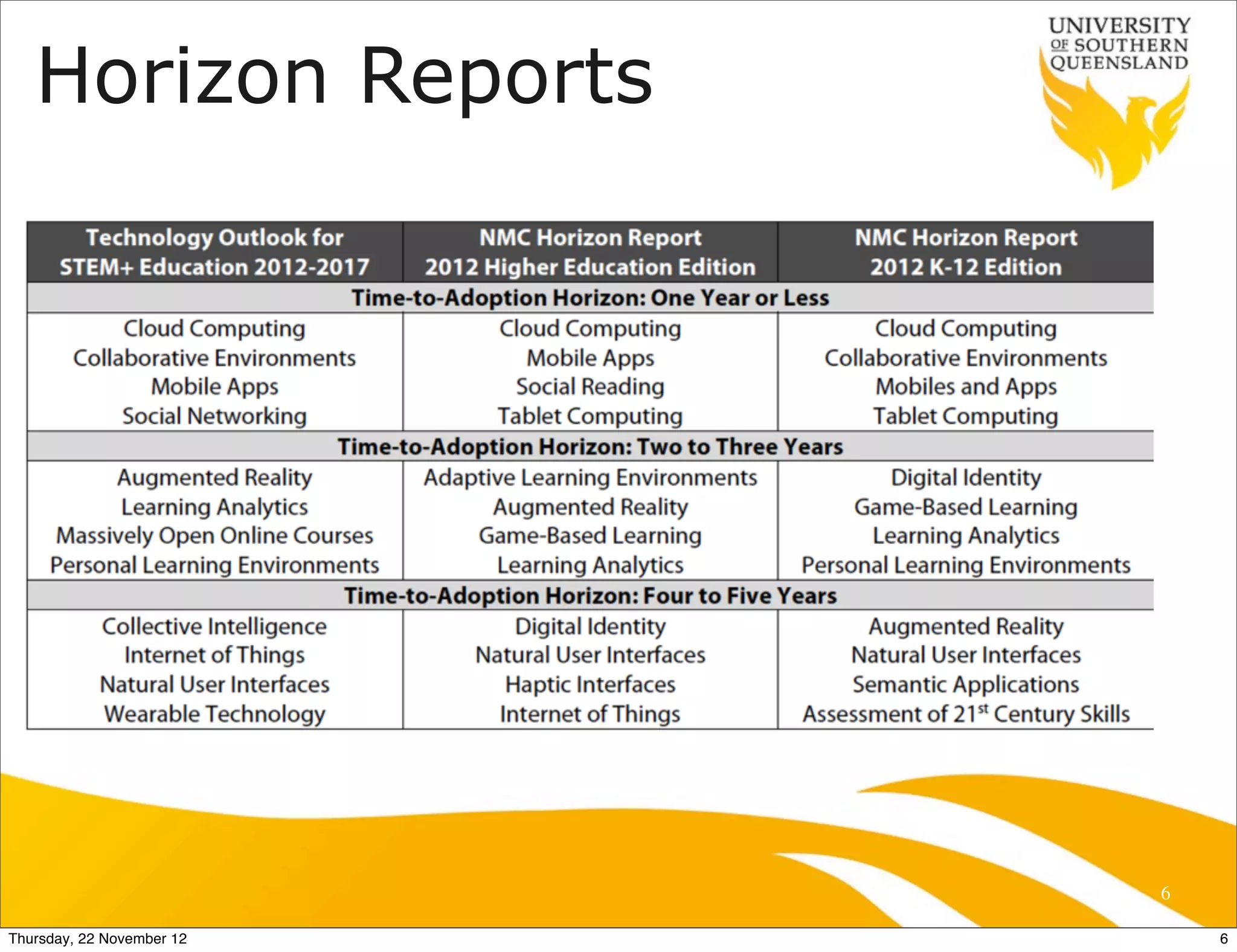
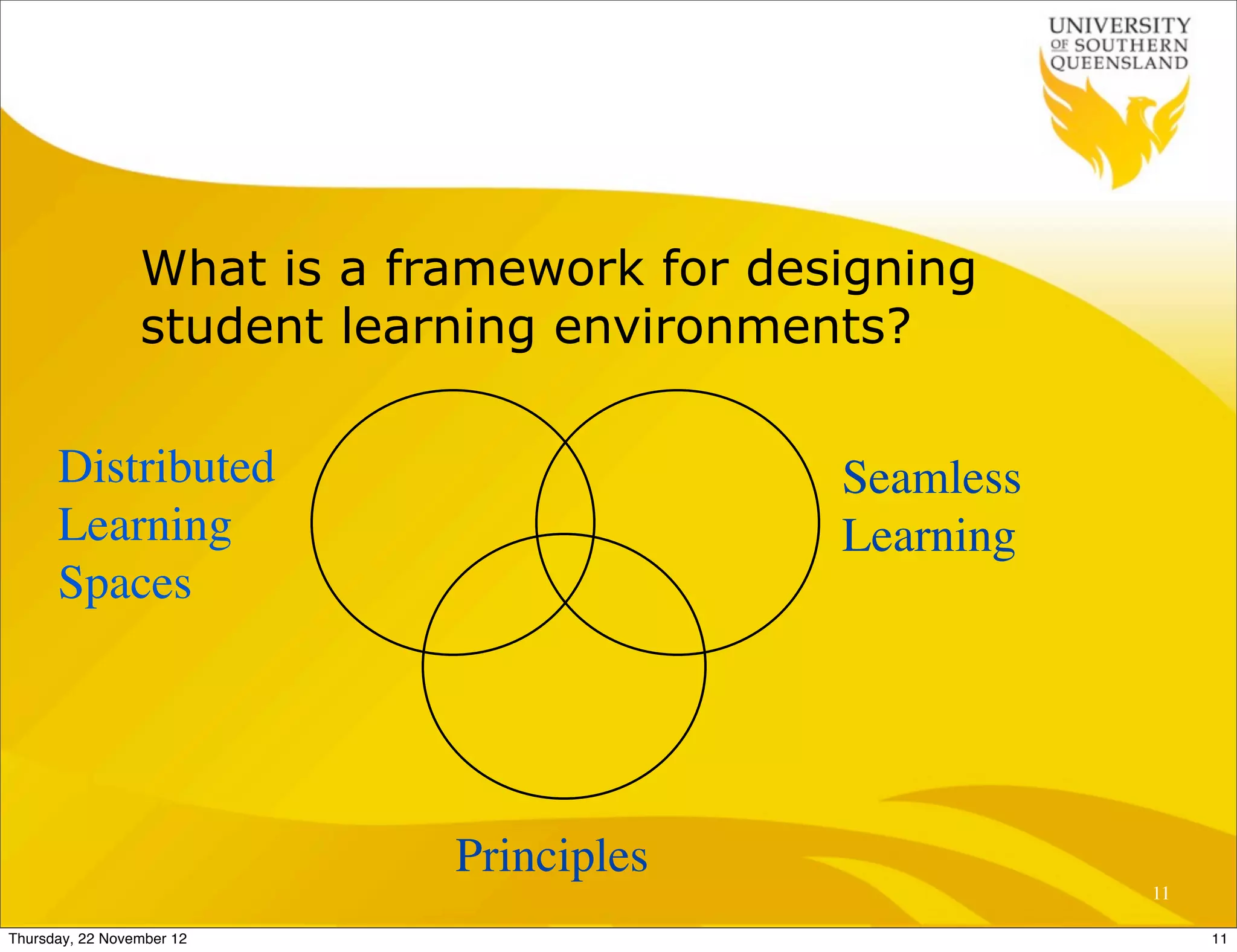
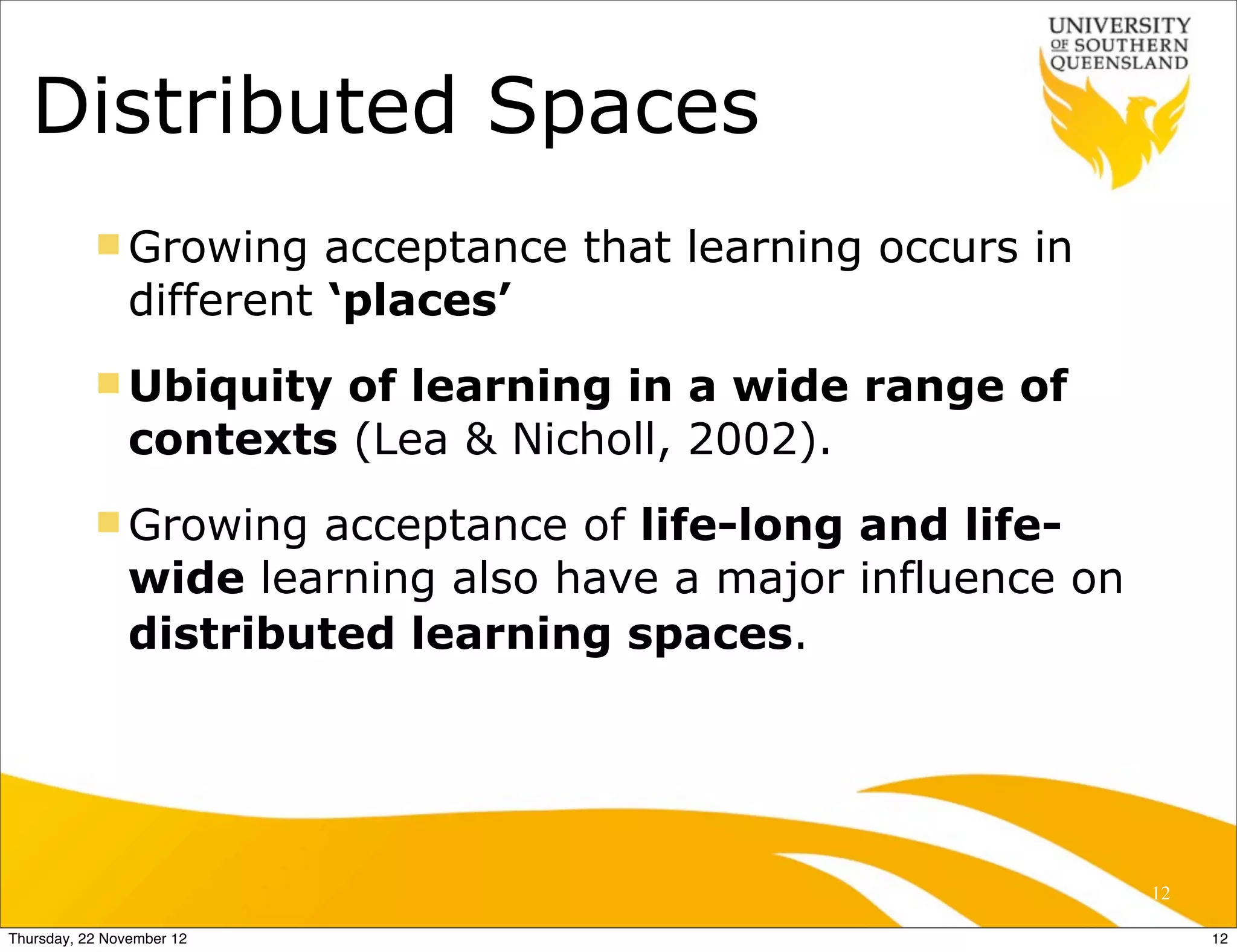
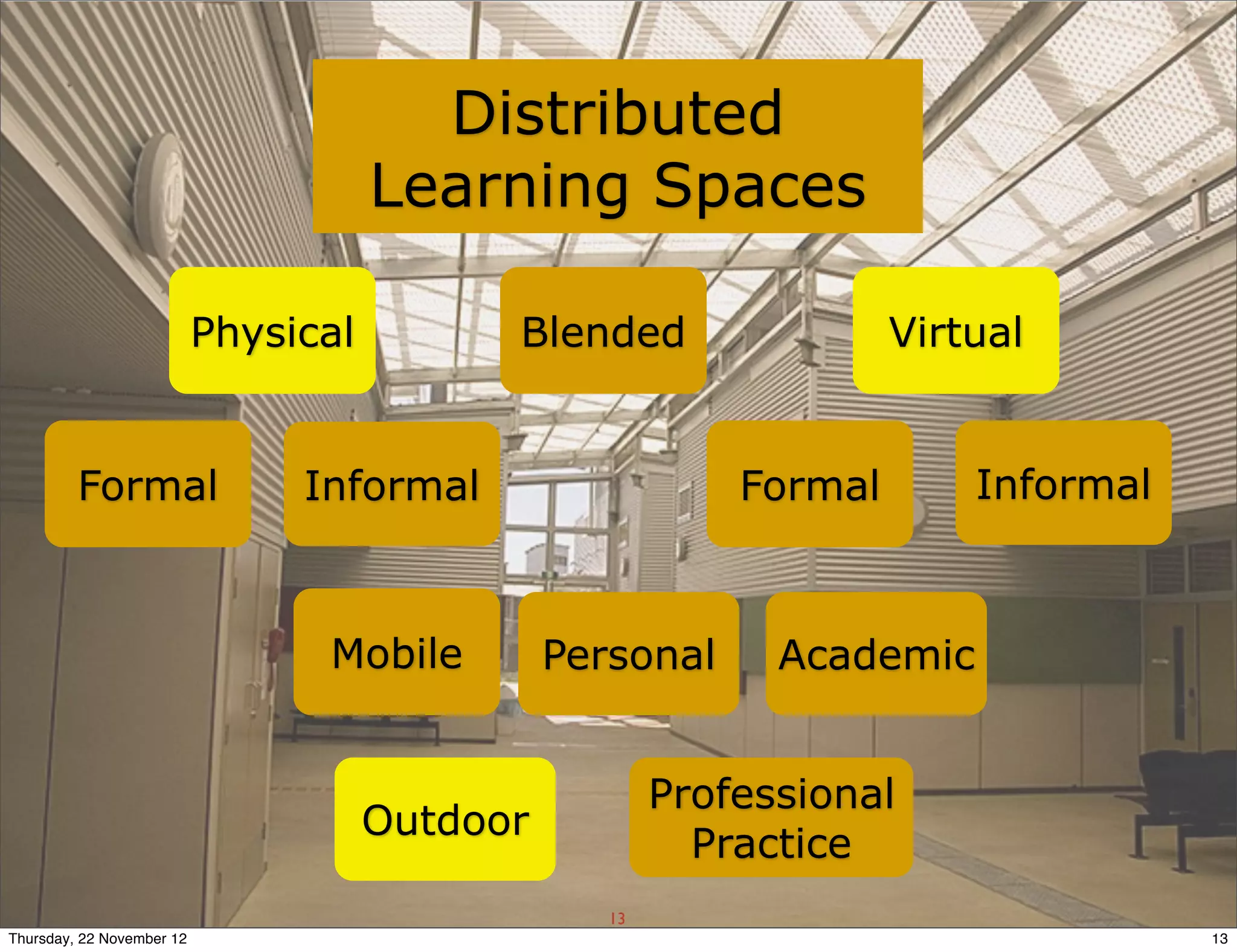
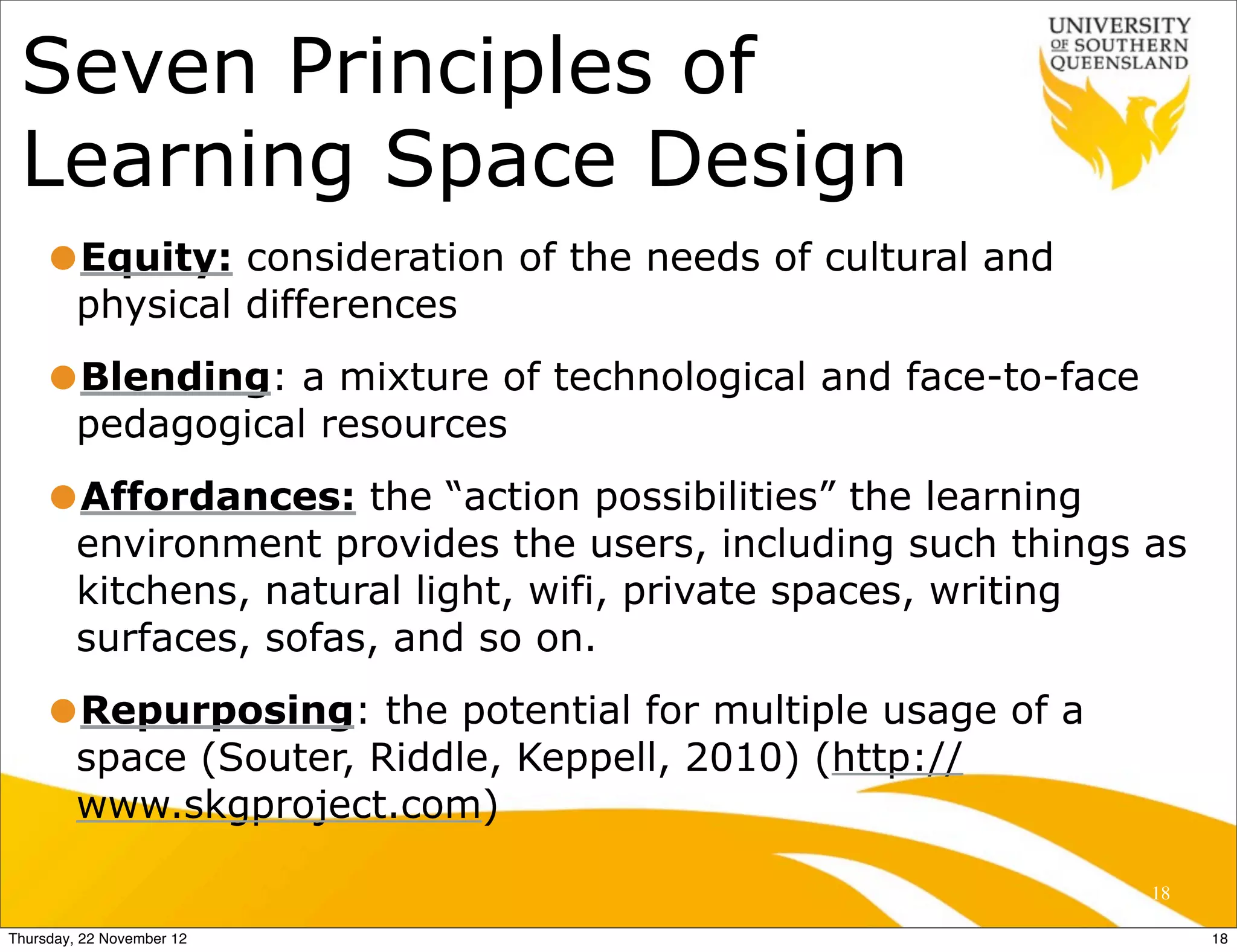
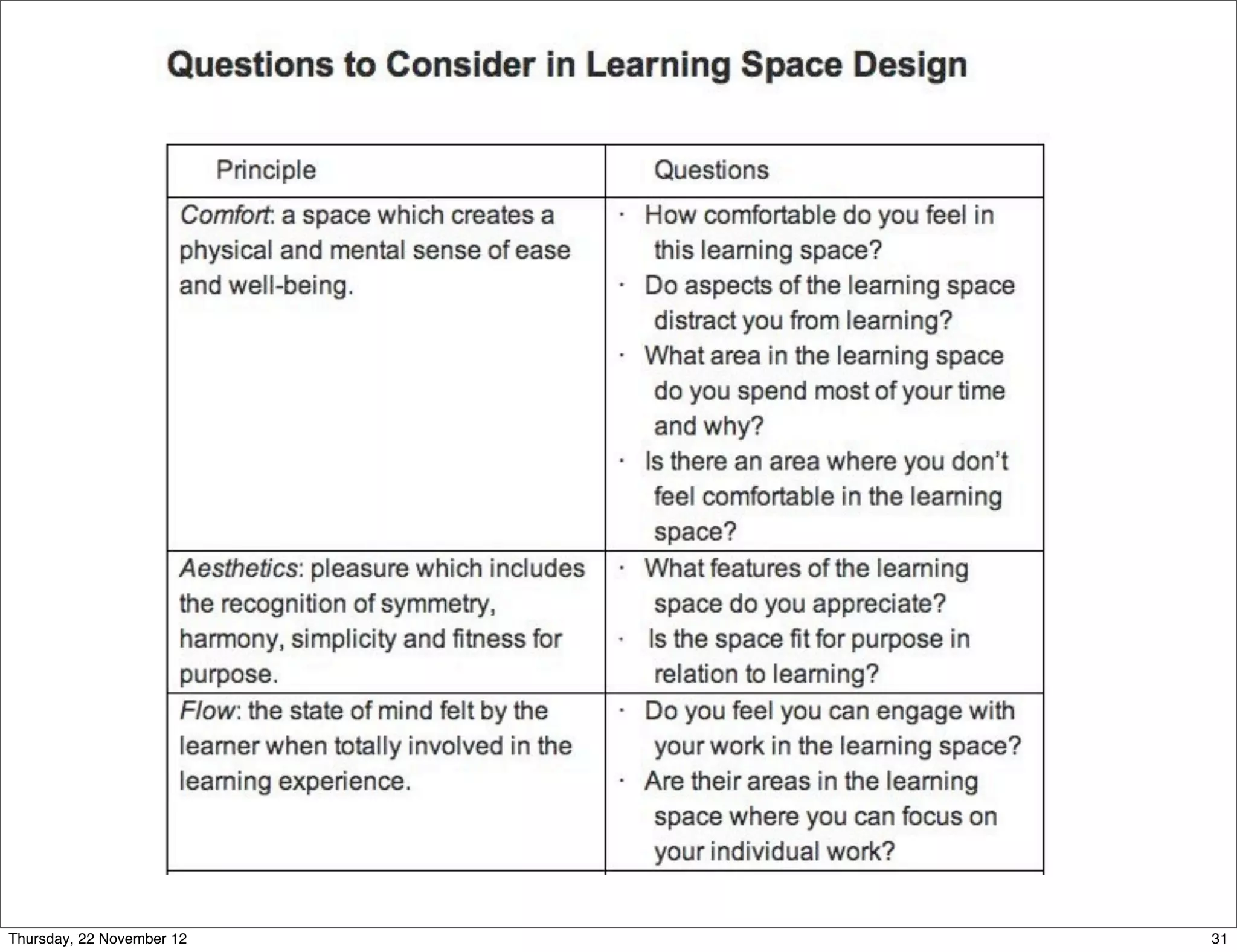
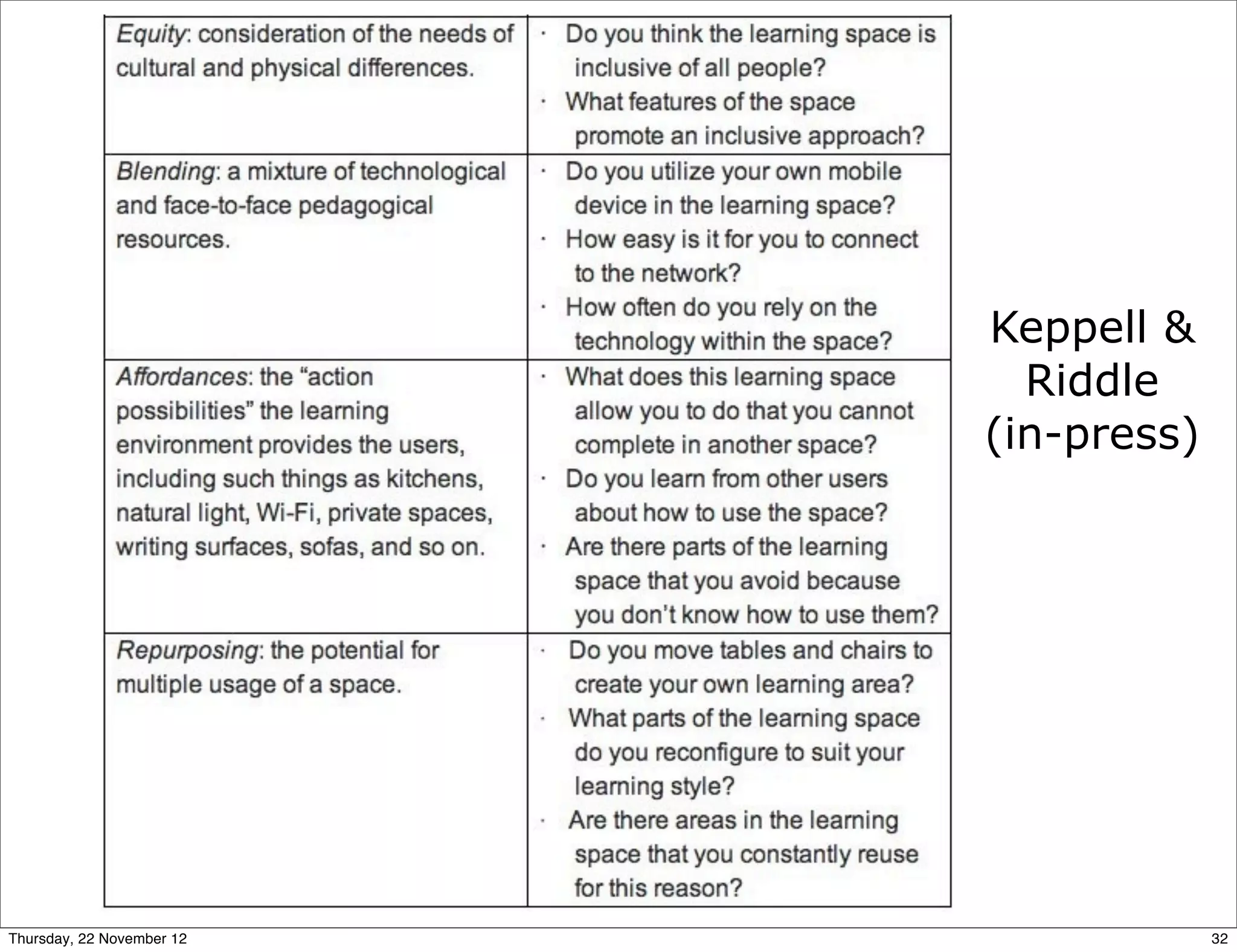
This document presents a framework for designing student learning environments called "spaces for knowledge generation." It discusses trends like the expectation of seamless learning anywhere and anytime, and challenges like developing digital literacies. The framework includes distributed learning spaces that can be physical, blended, or virtual. It also emphasizes seamless learning across different spaces and technologies. The framework is based on seven design principles for learning spaces including comfort, aesthetics, and allowing for multiple uses of a space. Examples are given of how these principles have been applied in various learning environments.