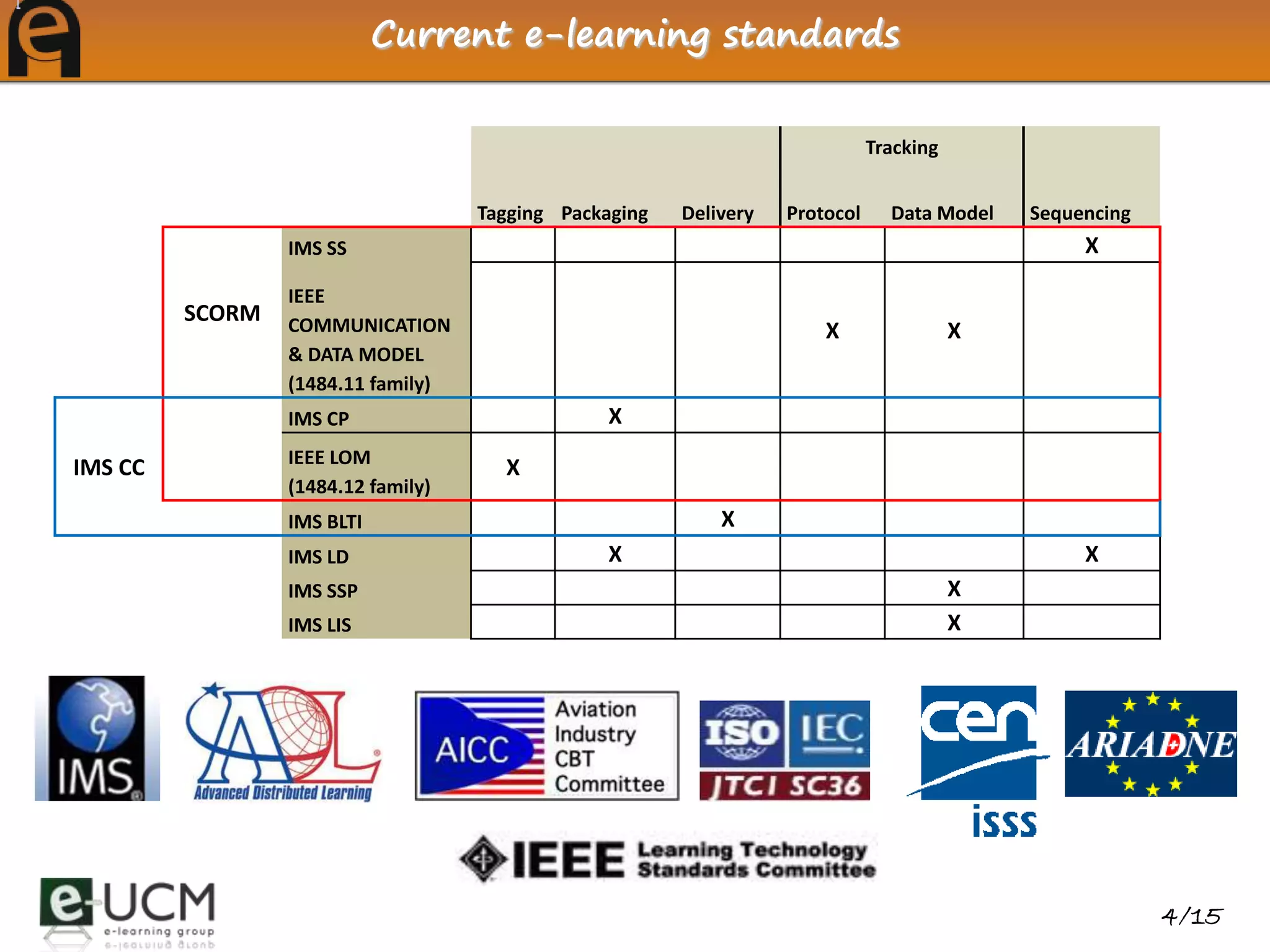
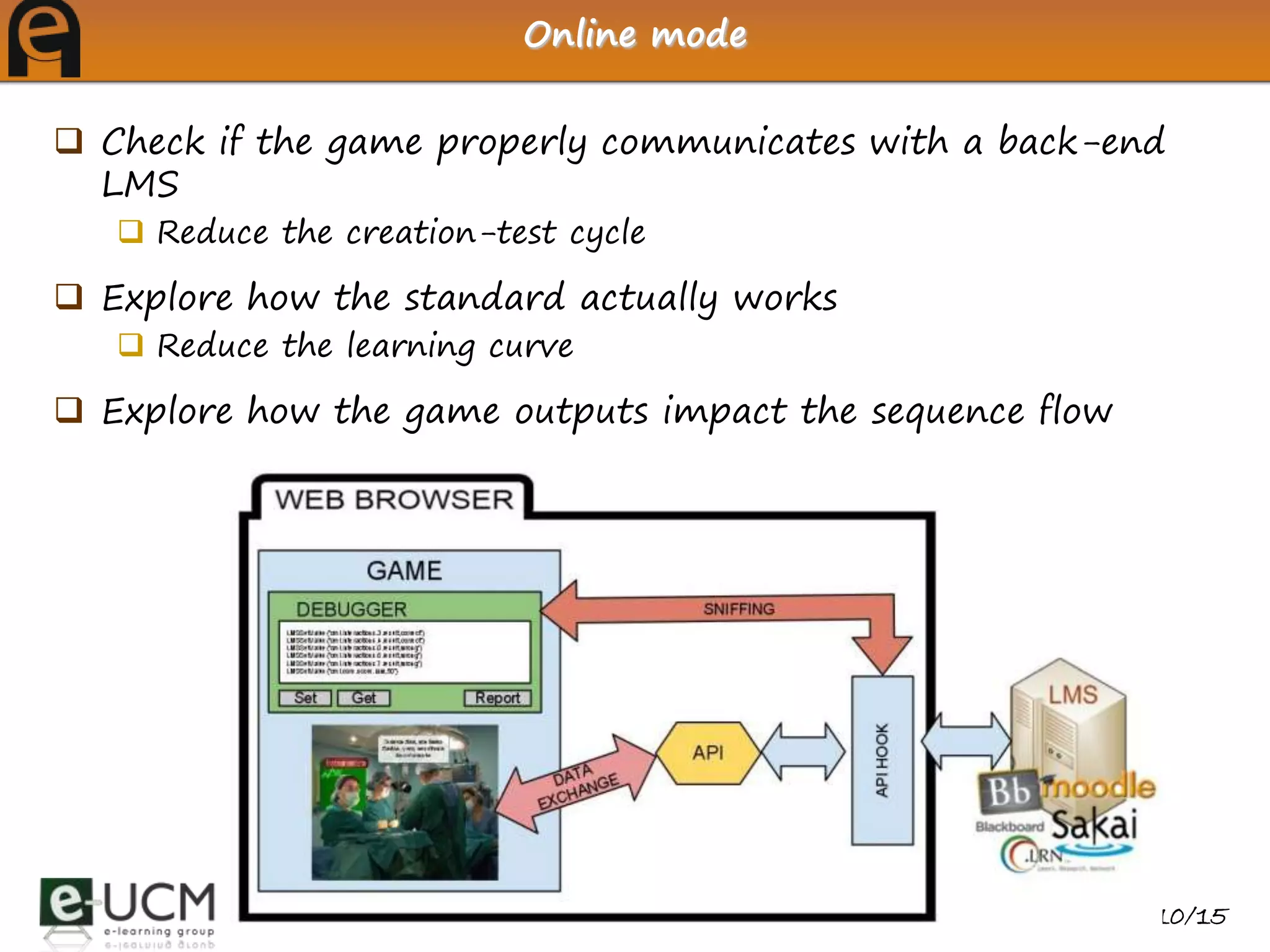
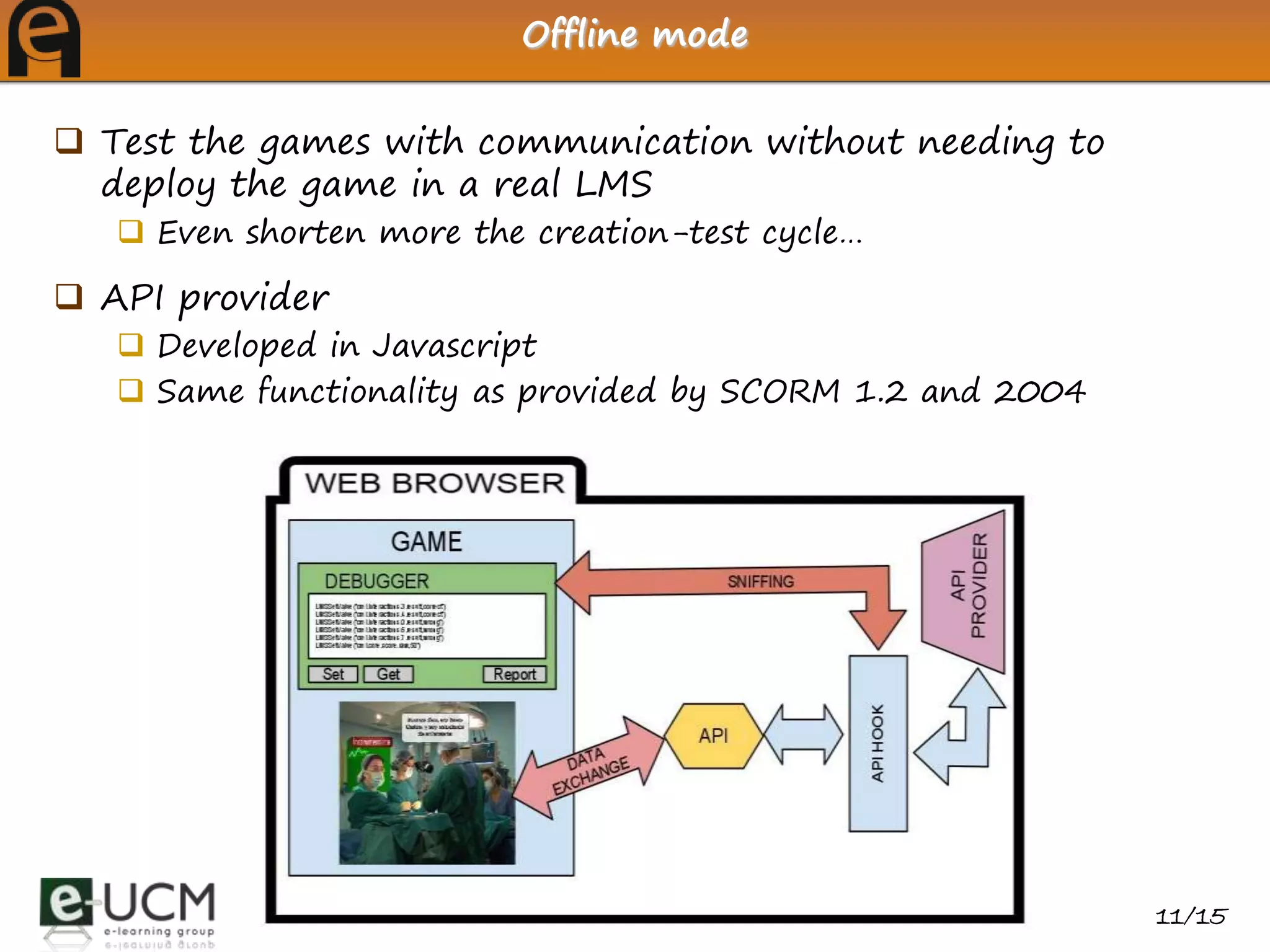
This document discusses deploying and debugging educational games using e-learning standards. It explains how using standards improves reusability and interoperability. The eAdventure platform helps educators create games, add metadata for learning object standards, and debug communication with learning management systems. Educators can test games' standard compliance without a real LMS using eAdventure's offline debugging mode.