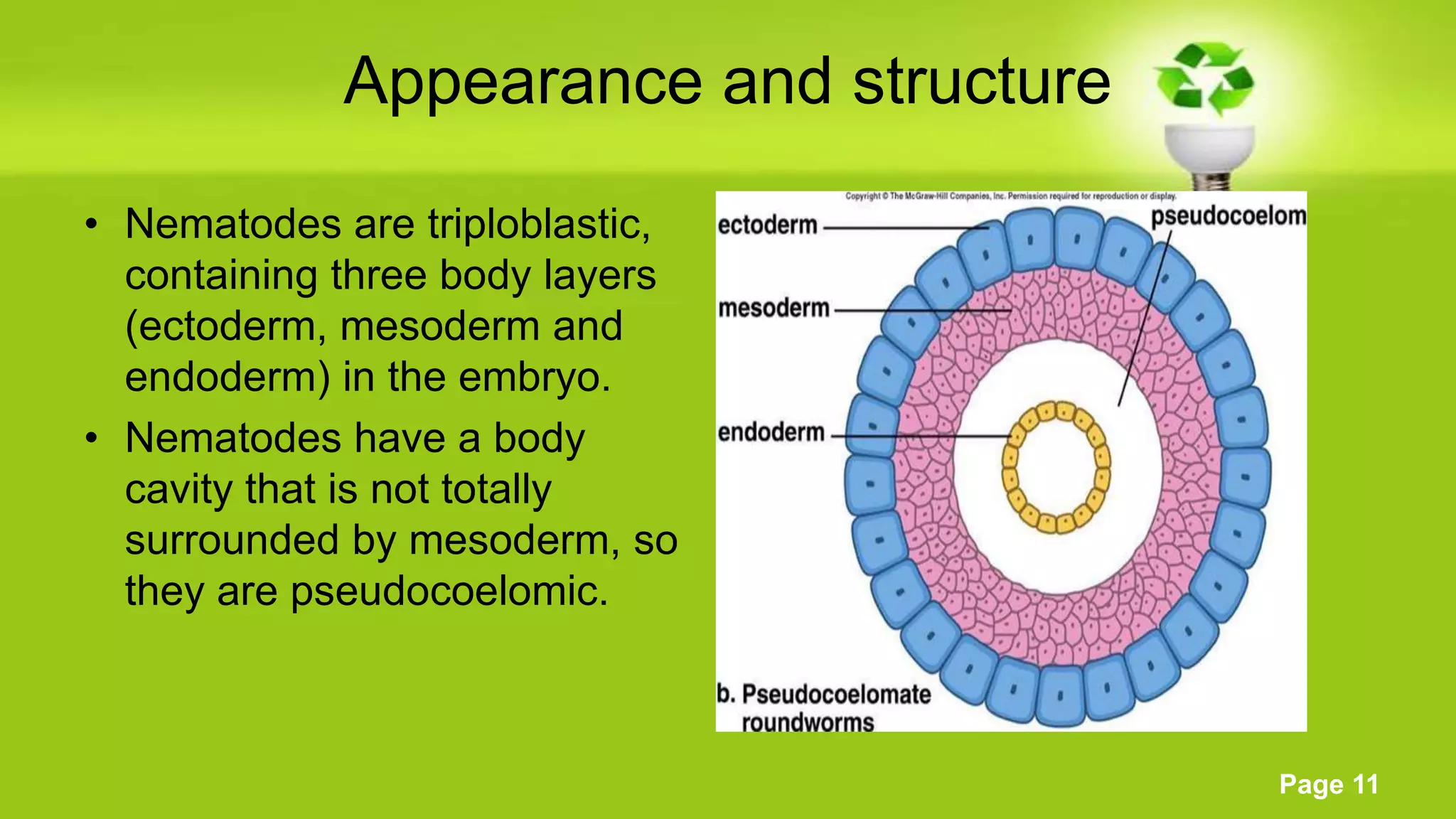
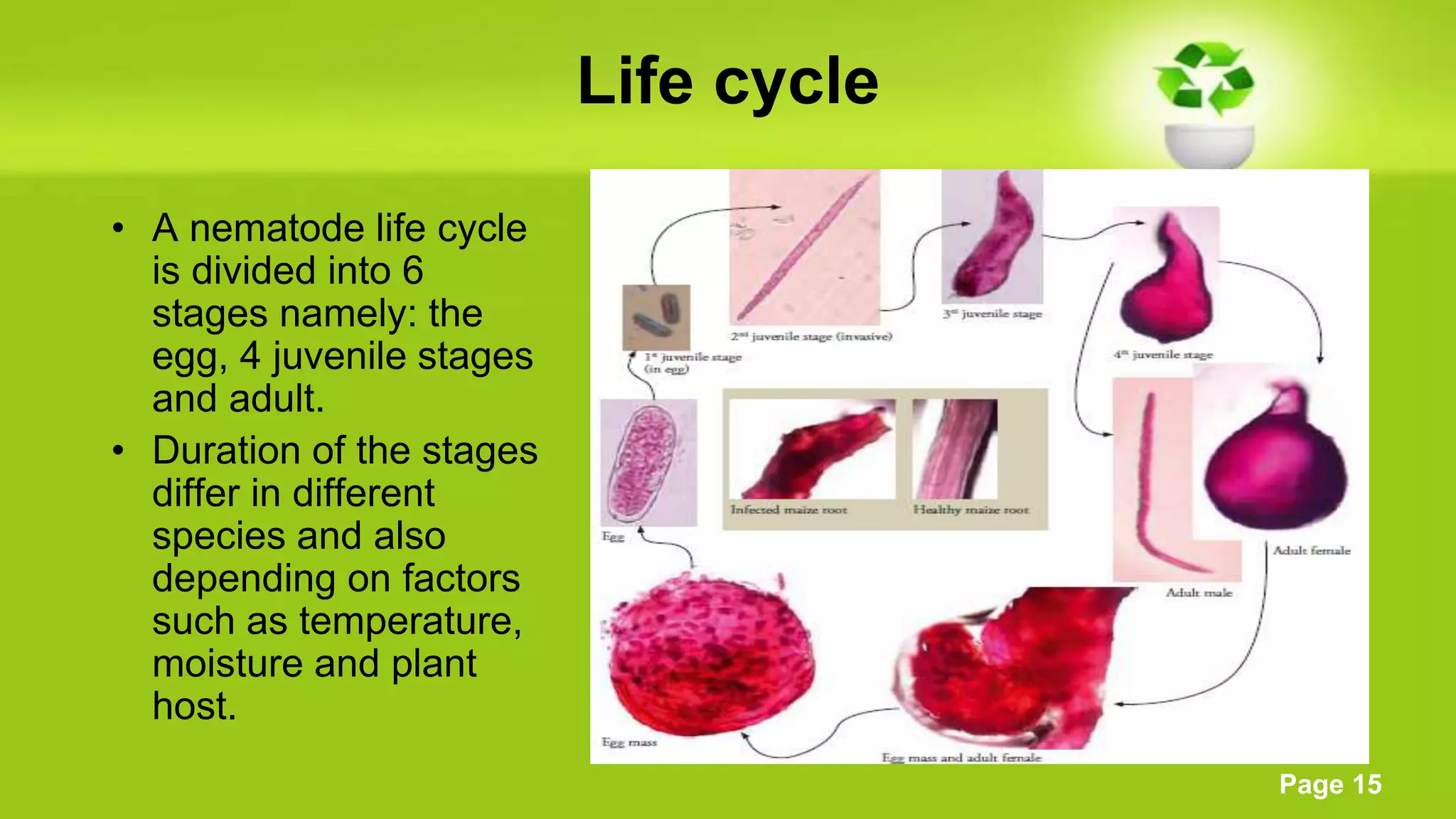
The document discusses the biology of nematodes. It describes their appearance and structure, including their stylets and life cycles. It notes that nematodes live virtually everywhere as parasites or free-living organisms. The document categorizes nematodes into types including migratory endoparasites, sedentary endoparasites, and ectoparasites. It provides examples of nematodes in each category and describes their feeding behaviors and effects on plants.