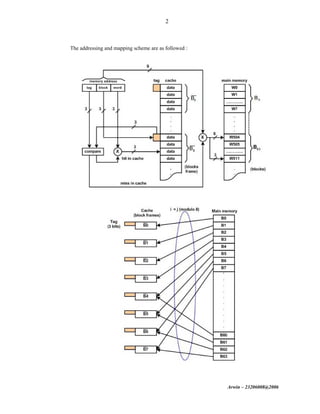
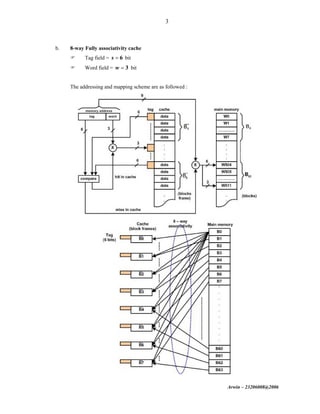
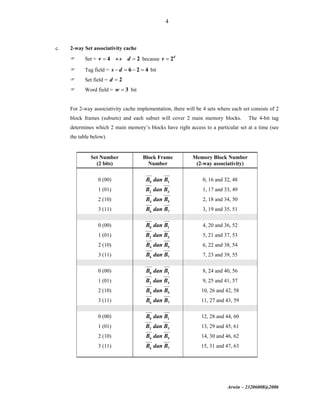
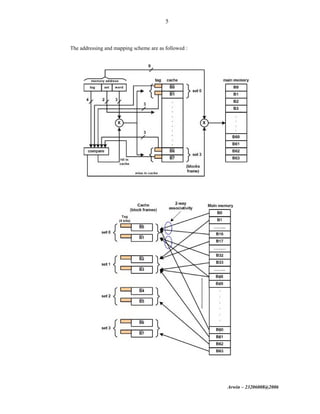
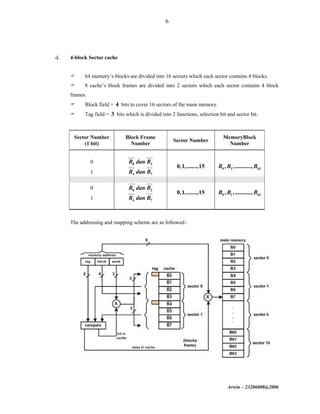
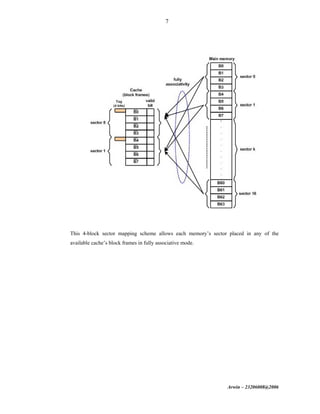
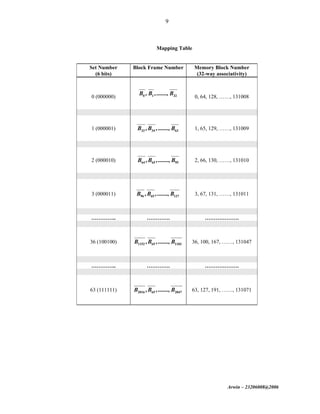
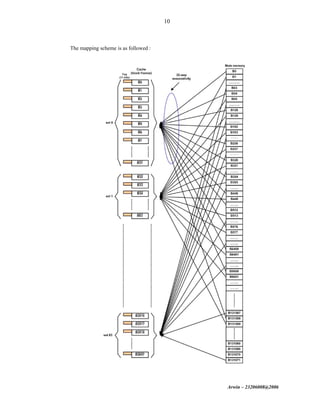
The document discusses cache memory organization and mapping schemes between main memory and cache memory. It provides examples of direct mapping, fully associative mapping, 2-way set associative mapping, and 4-block sector mapping. It also calculates the effective memory access time for a memory hierarchy with a 16KB cache and 1MB main memory, assuming an 8-word block size and 256-word set size with 32-way set associative mapping and a 95% cache hit ratio.