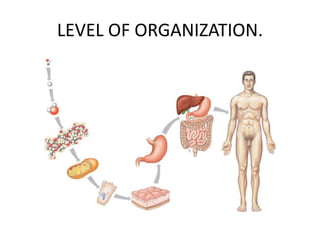
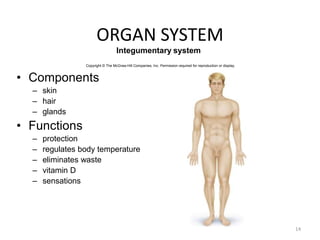
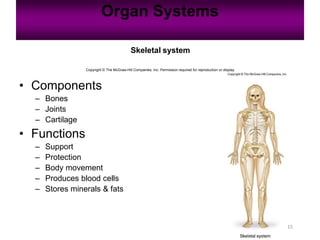
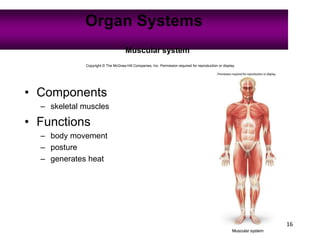
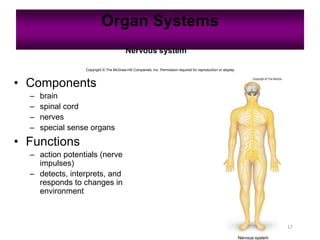
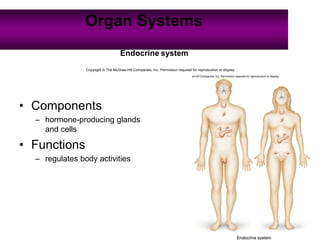
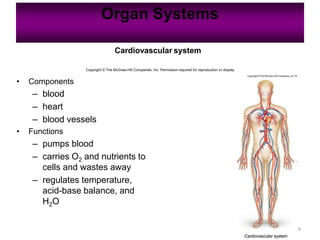
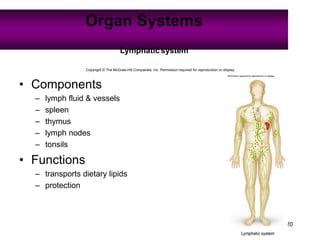
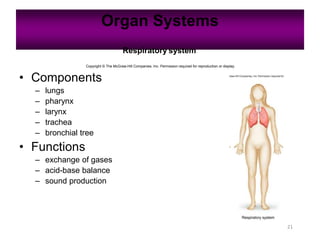
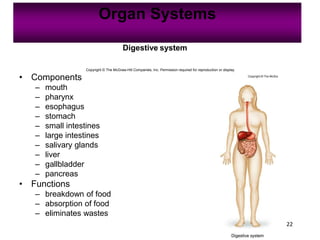
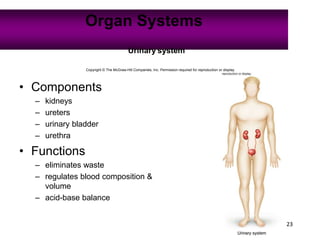
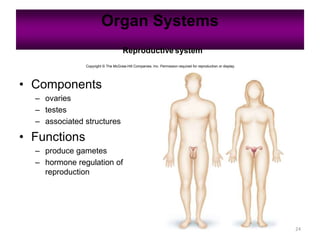
Anatomy is the study of structure, while physiology is the study of function. Anatomy can be studied at both the macroscopic and microscopic levels. Microscopic anatomy includes histology, the study of tissues, and cytology, the study of cells. The human body is composed of organ systems that work together, including the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems. Each system contains different components that allow it to carry out its specialized functions necessary for maintaining life.