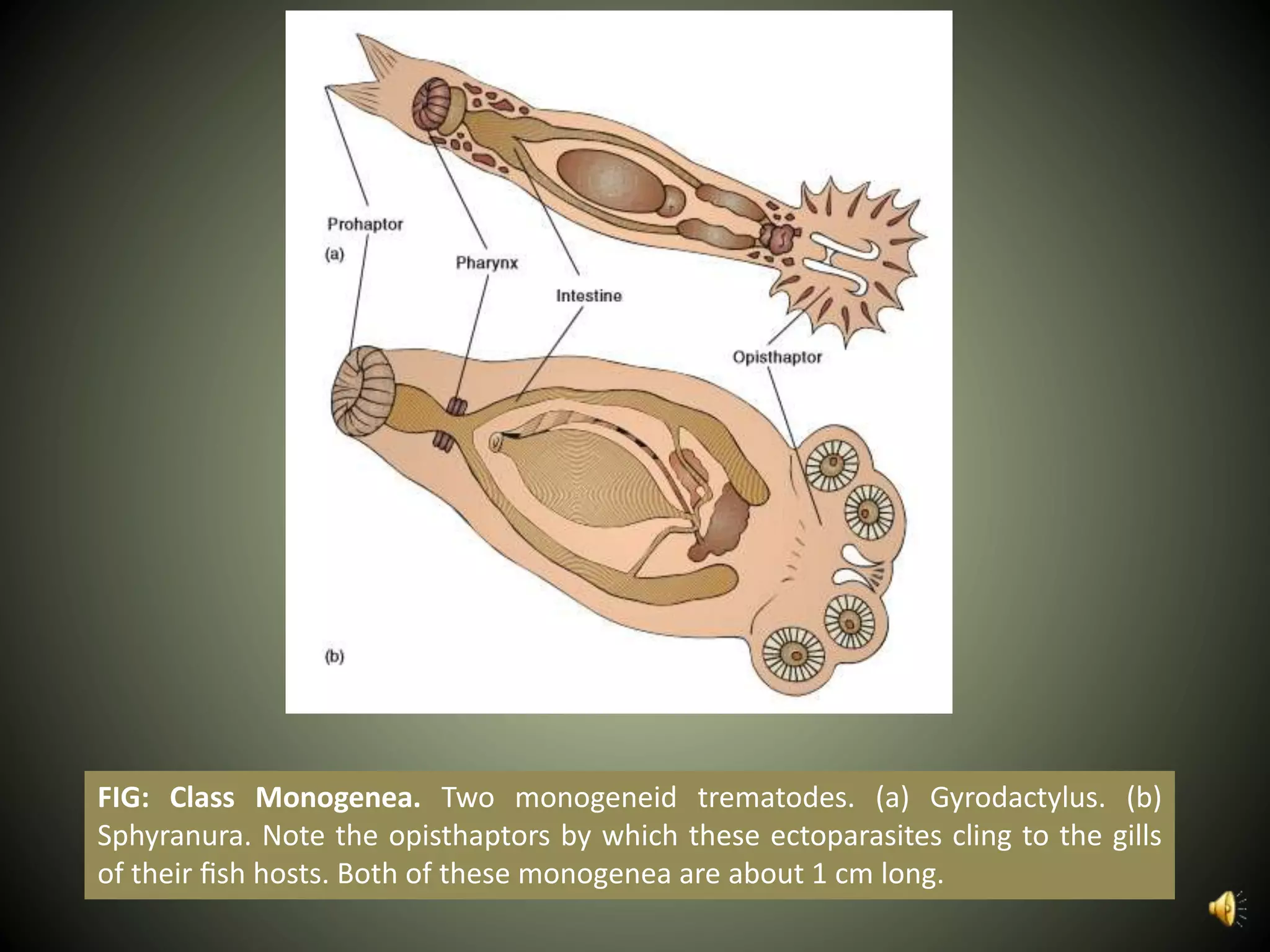
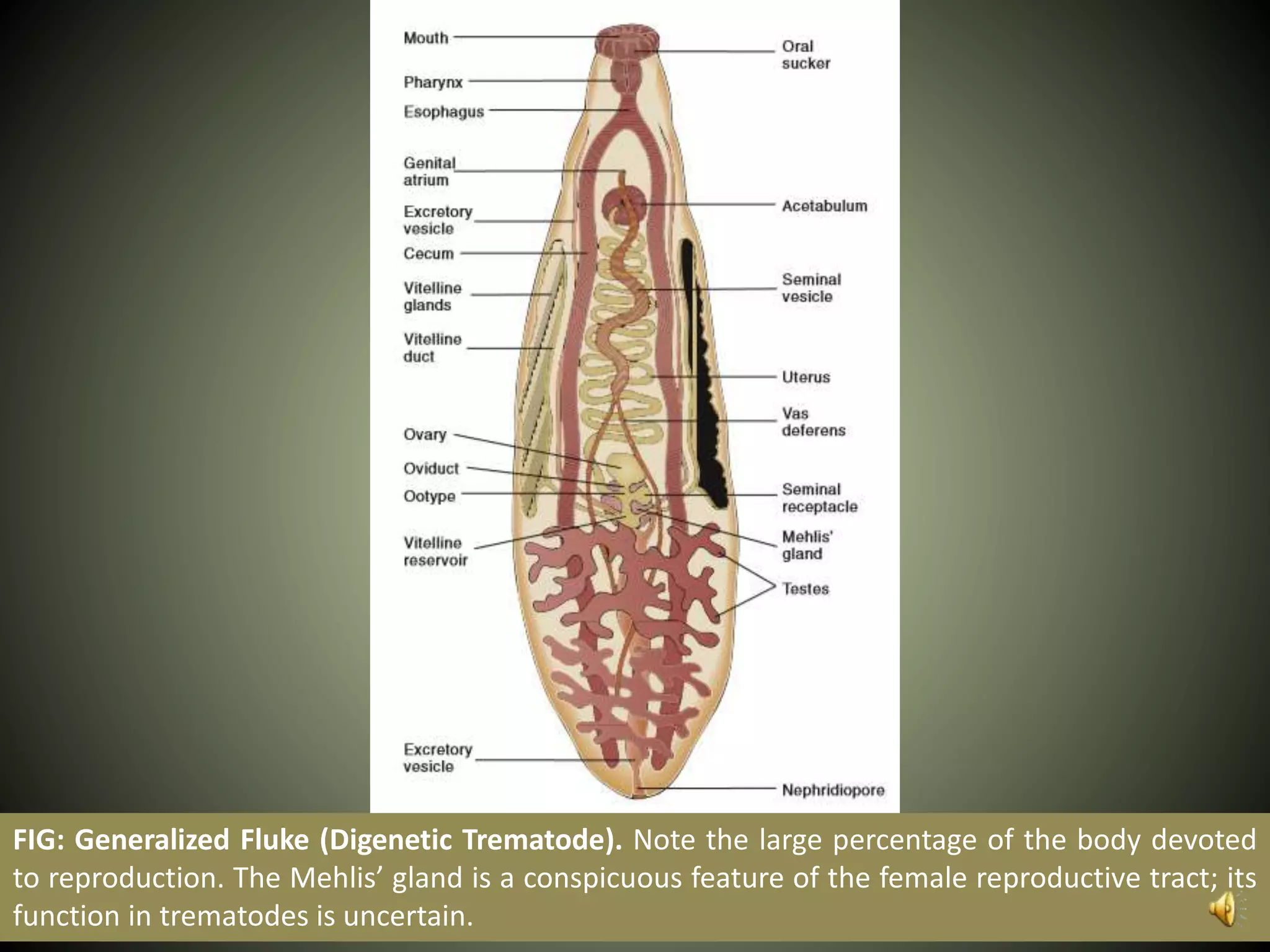
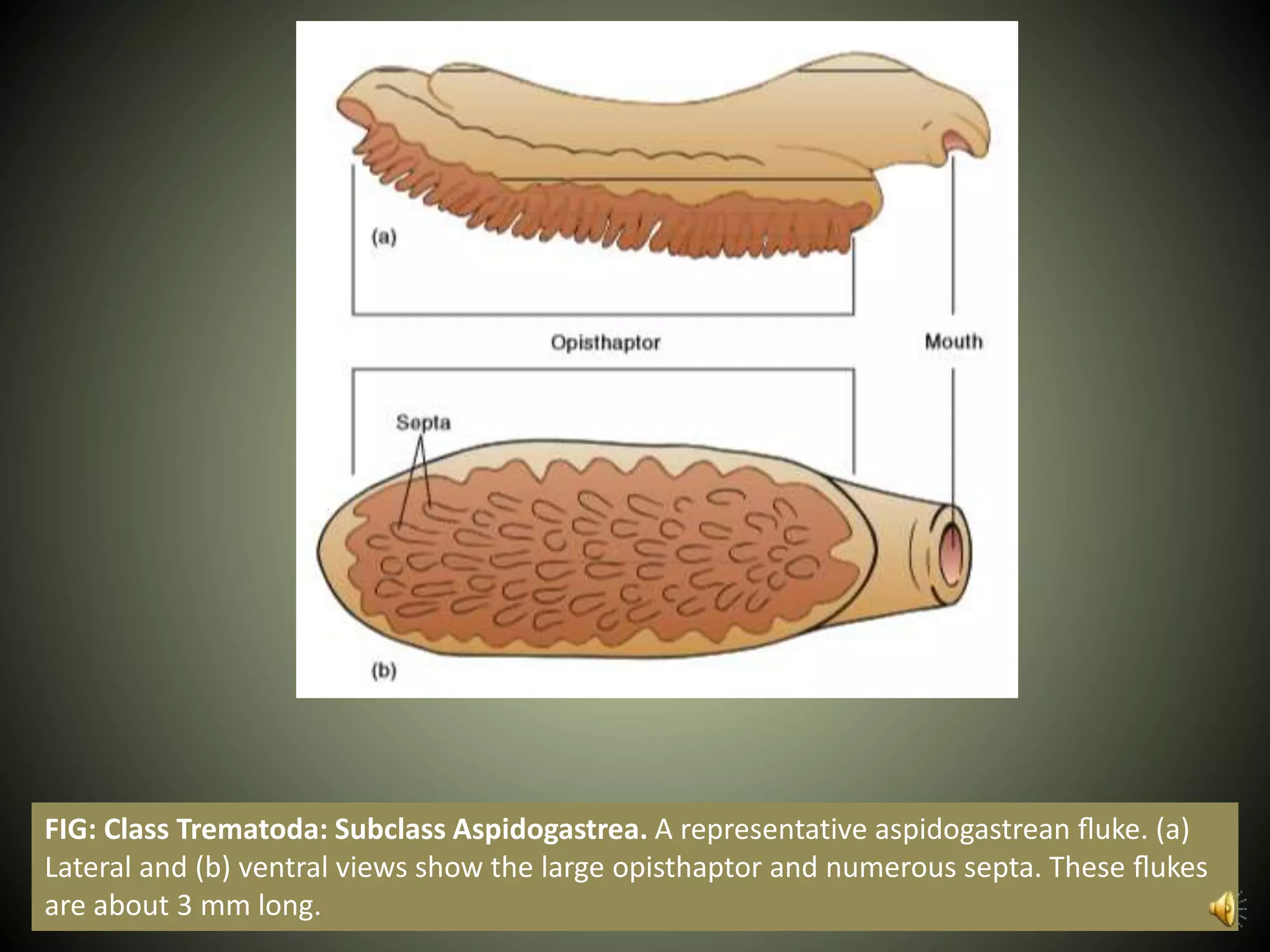
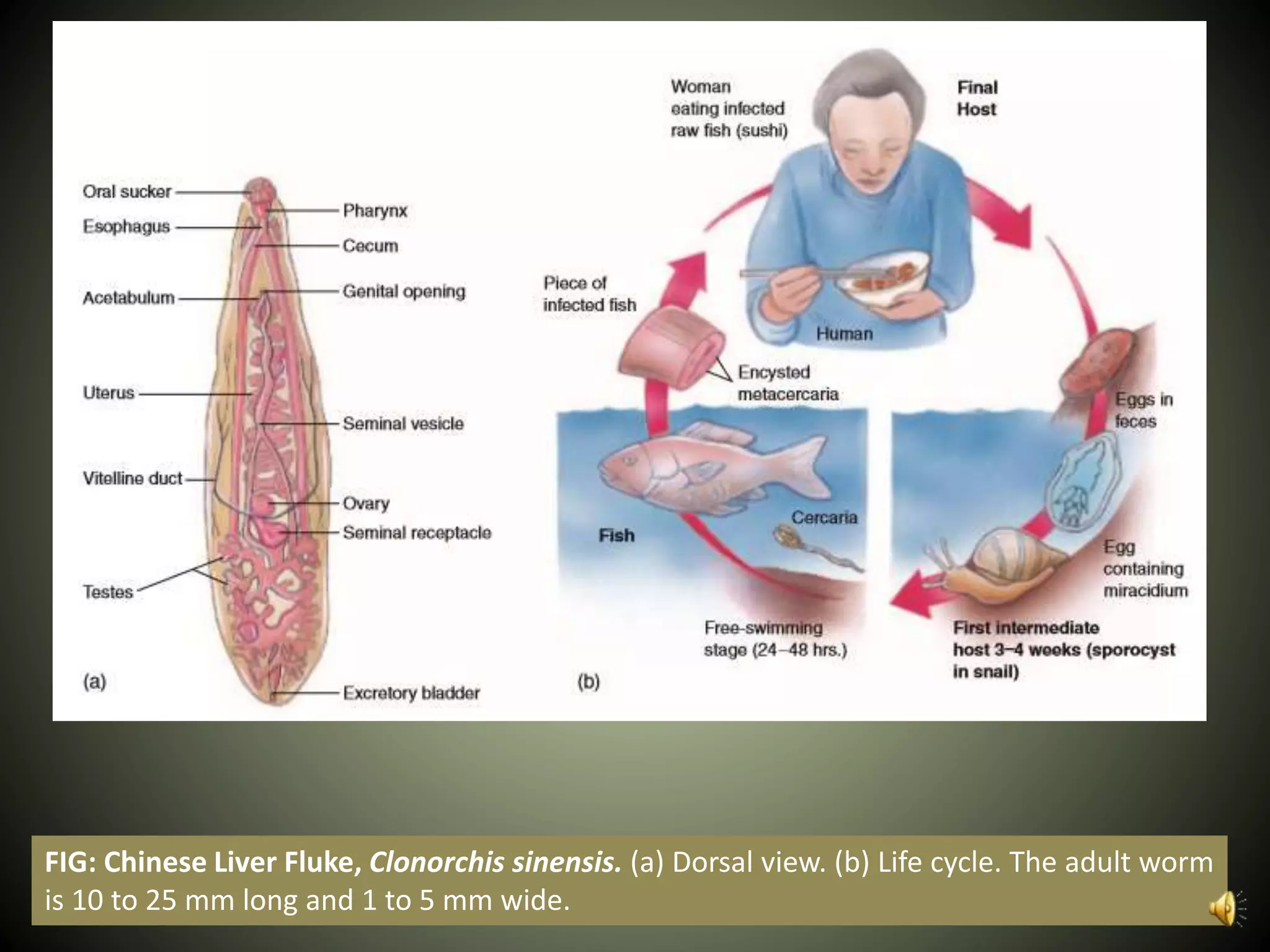
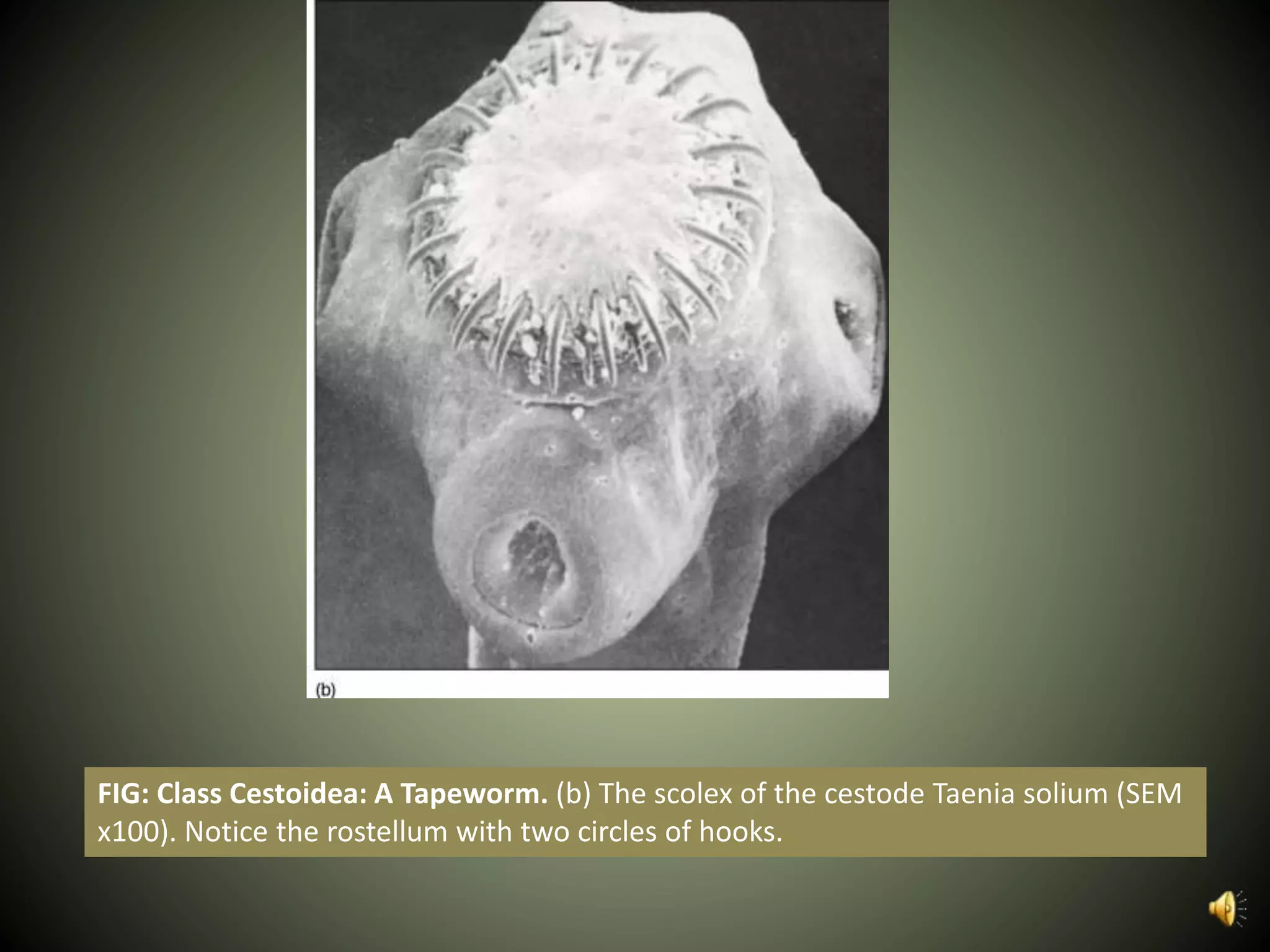
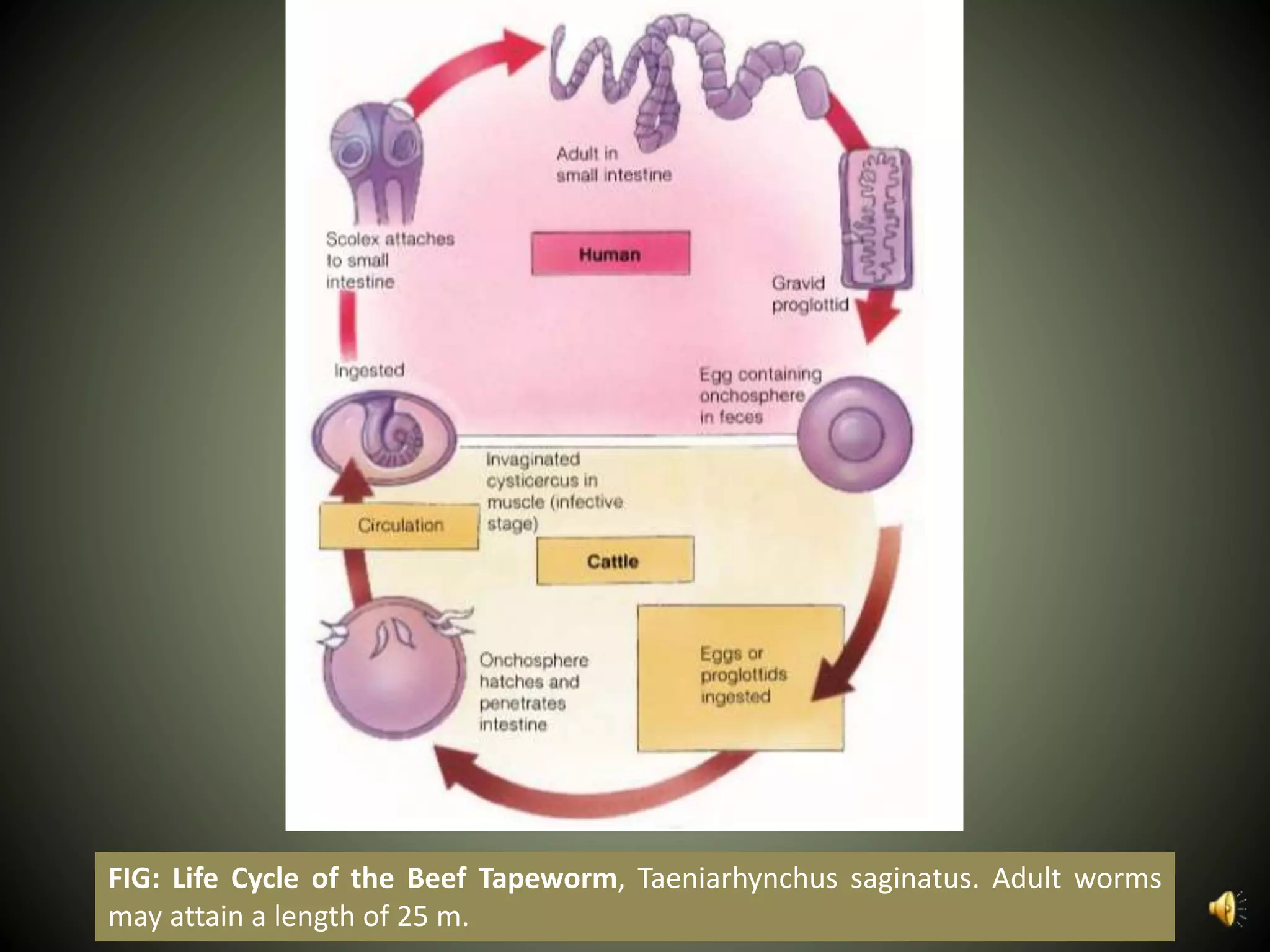
The document summarizes key aspects of three phyla of parasitic flatworms - Monogenea, Trematoda, and Cestoidea. It describes their life cycles, important anatomical features, examples of parasites of humans, and how they infect and reside within host organisms. Some key points are that Monogenea have a direct life cycle, Trematoda have indirect life cycles requiring multiple hosts, and Cestoidea (tapeworms) absorb nutrients directly through their skin and consist of repeating reproductive segments.