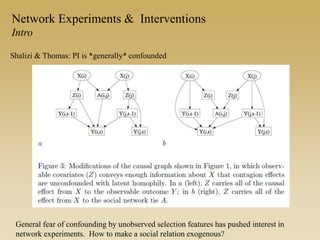
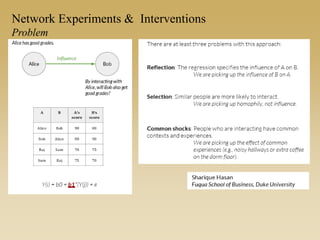
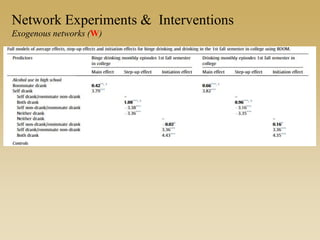
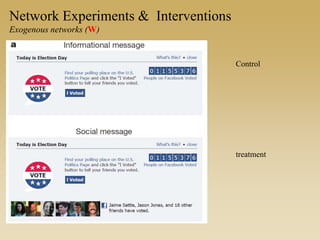
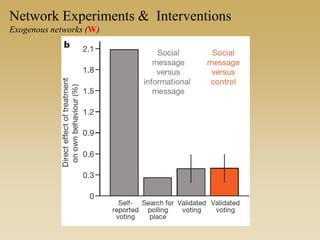
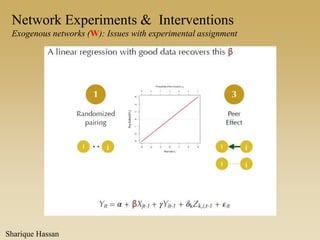
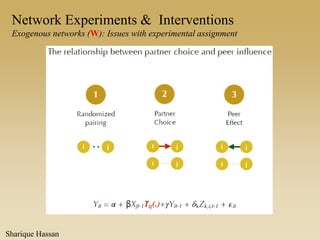
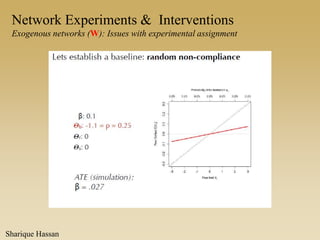
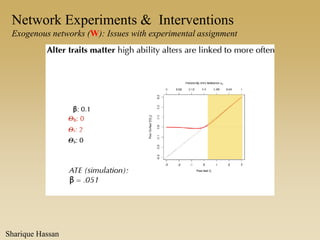
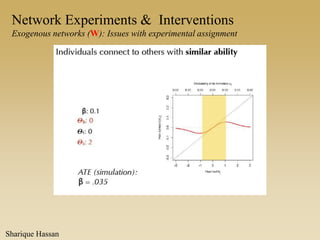
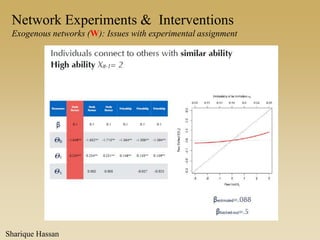
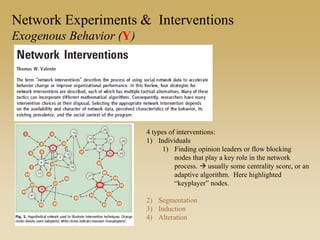
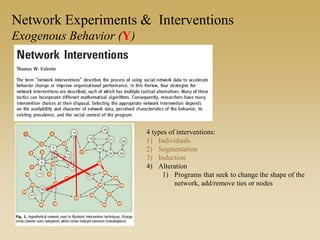
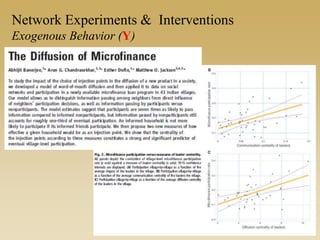
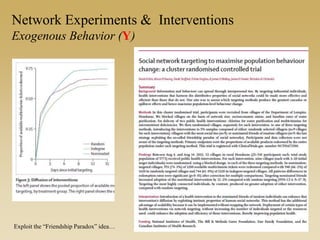
This document discusses different types of network experiments and interventions. It describes (1) using roommate assignments to make social connections exogenous, assessing peer effects on outcomes like GPA. It also discusses (2) natural experiments that manipulate exposure over existing networks, like popularity or voter turnout. Finally, it outlines (3) different types of network interventions, including targeting influential individuals, segmenting groups, inducing new connections, and altering network structure. The conclusion is that evidence from these experiments shows peer influence is real and we can now focus on how to leverage networks most effectively.