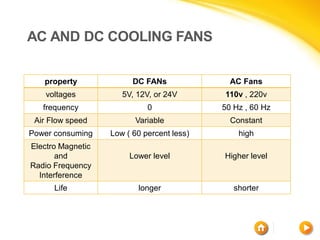
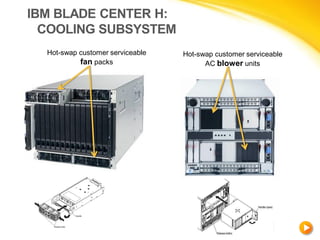
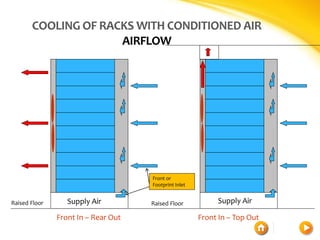
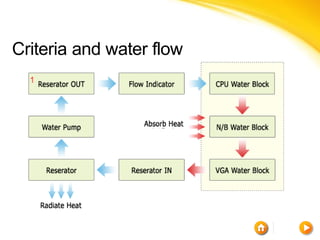
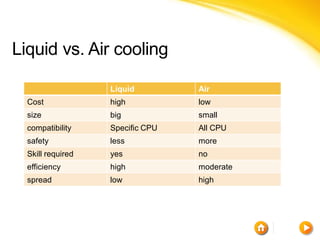
This document discusses different cooling techniques for electronic devices, including air cooling, liquid cooling, and their components. It provides details on heat sinks, thermal interface materials, fans, blowers, and their differences. Liquid cooling uses water to transmit heat more efficiently than air cooling due to water's higher heat capacity and conductivity. While more effective, liquid cooling systems are more expensive, larger, require technical skills, and carry safety risks if leaked.