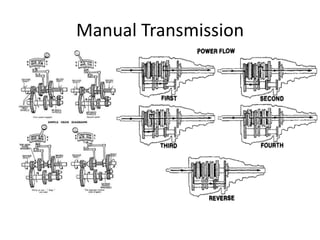
The document discusses troubleshooting issues with manual transmissions. It provides information on transmission locations, purposes, lubricants, common diagnosis issues, and service procedures. Some key points:
- Manual transmissions are located between the clutch and driveshaft in rear-wheel drive vehicles, and between the clutch and differential in front-wheel drive transaxles.
- Transmissions provide speed and torque conversion and facilitate reversing. Gearbox lubricants must lubricate, prevent wear, protect from rust/corrosion, and cool.
- Common diagnosis issues include hard shifting, sticking gears, slipping out of gear, noise, and gear clash. Troubleshooting involves road tests and examining components like linkages, synchron