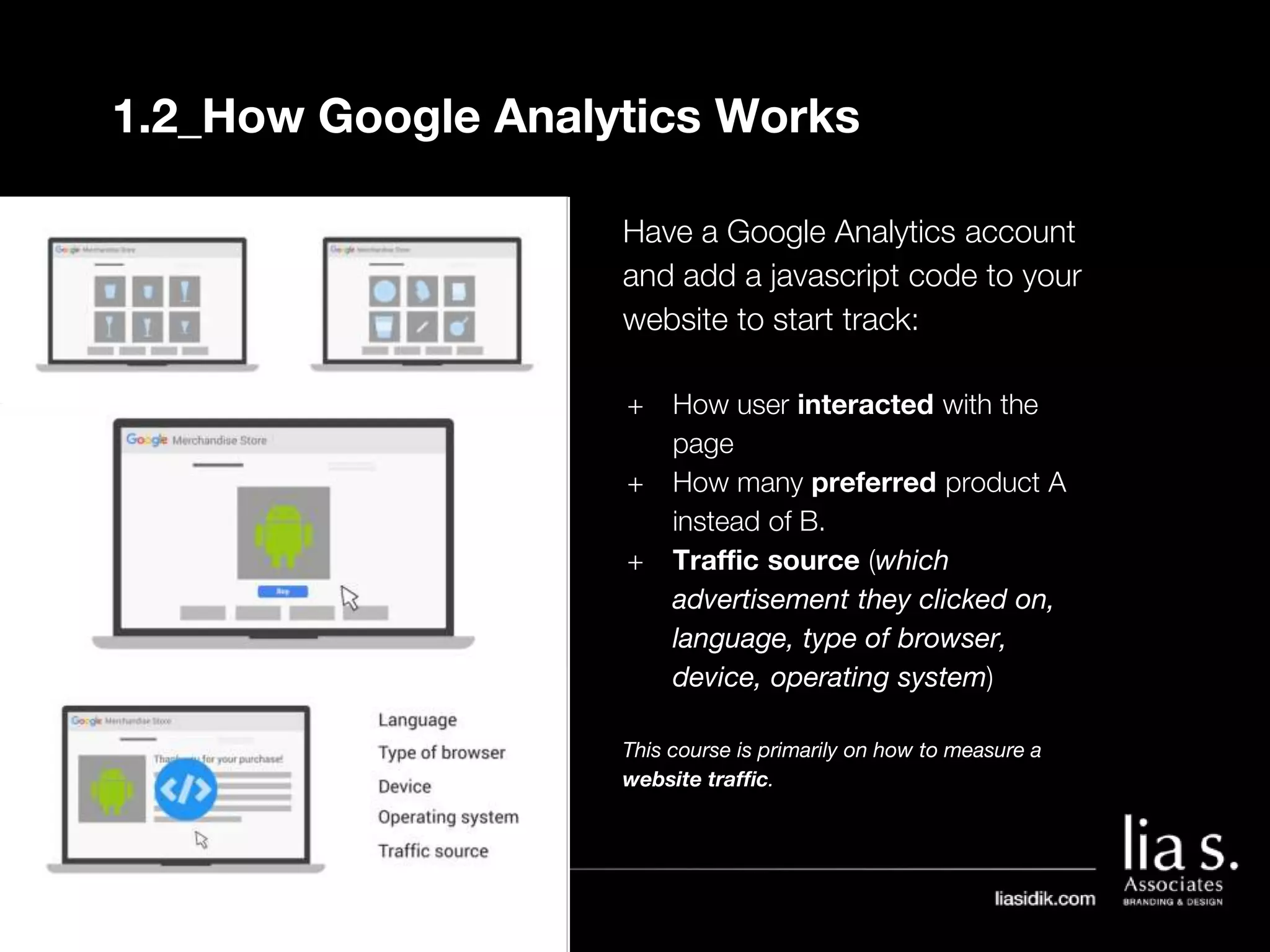
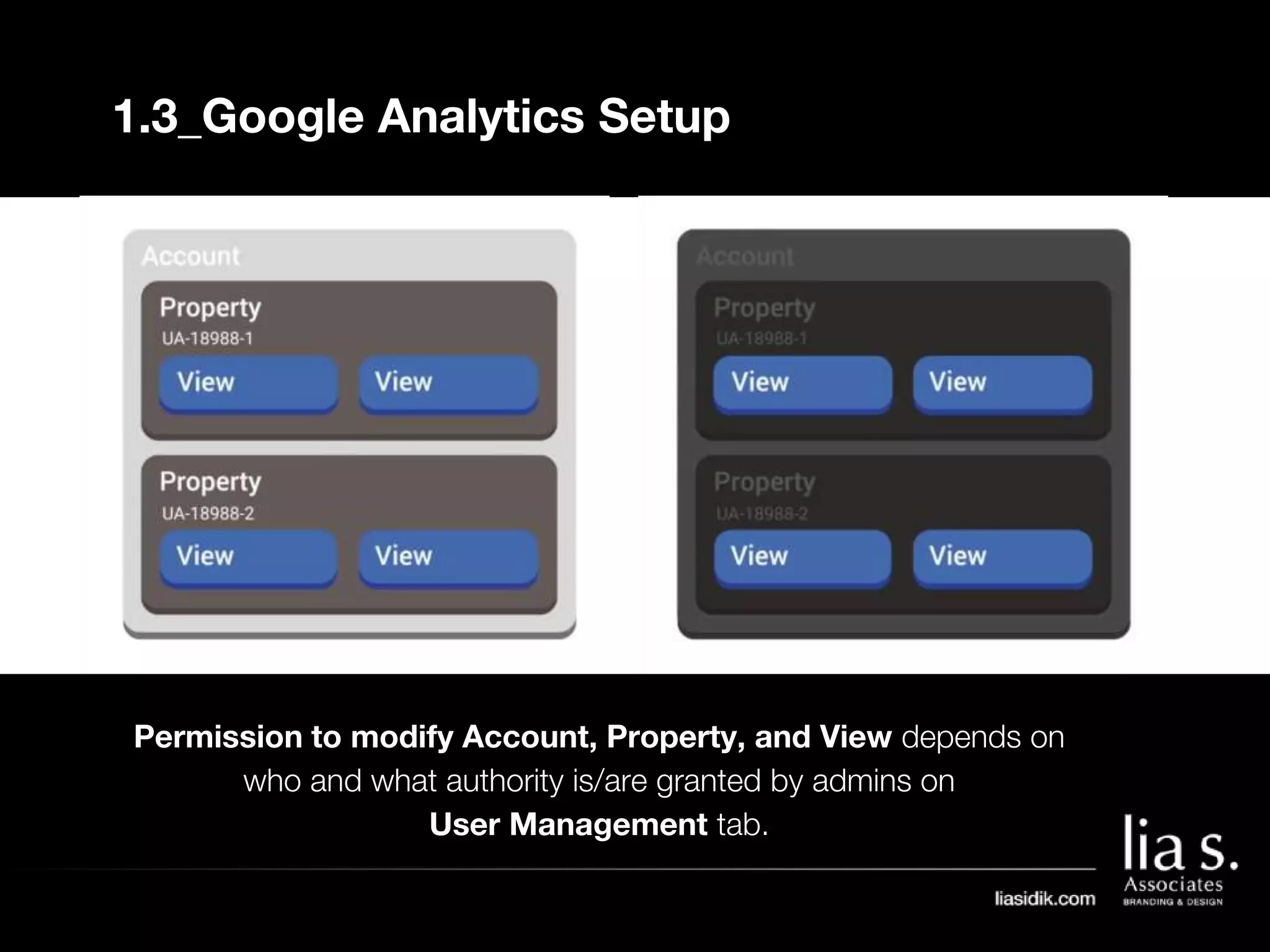
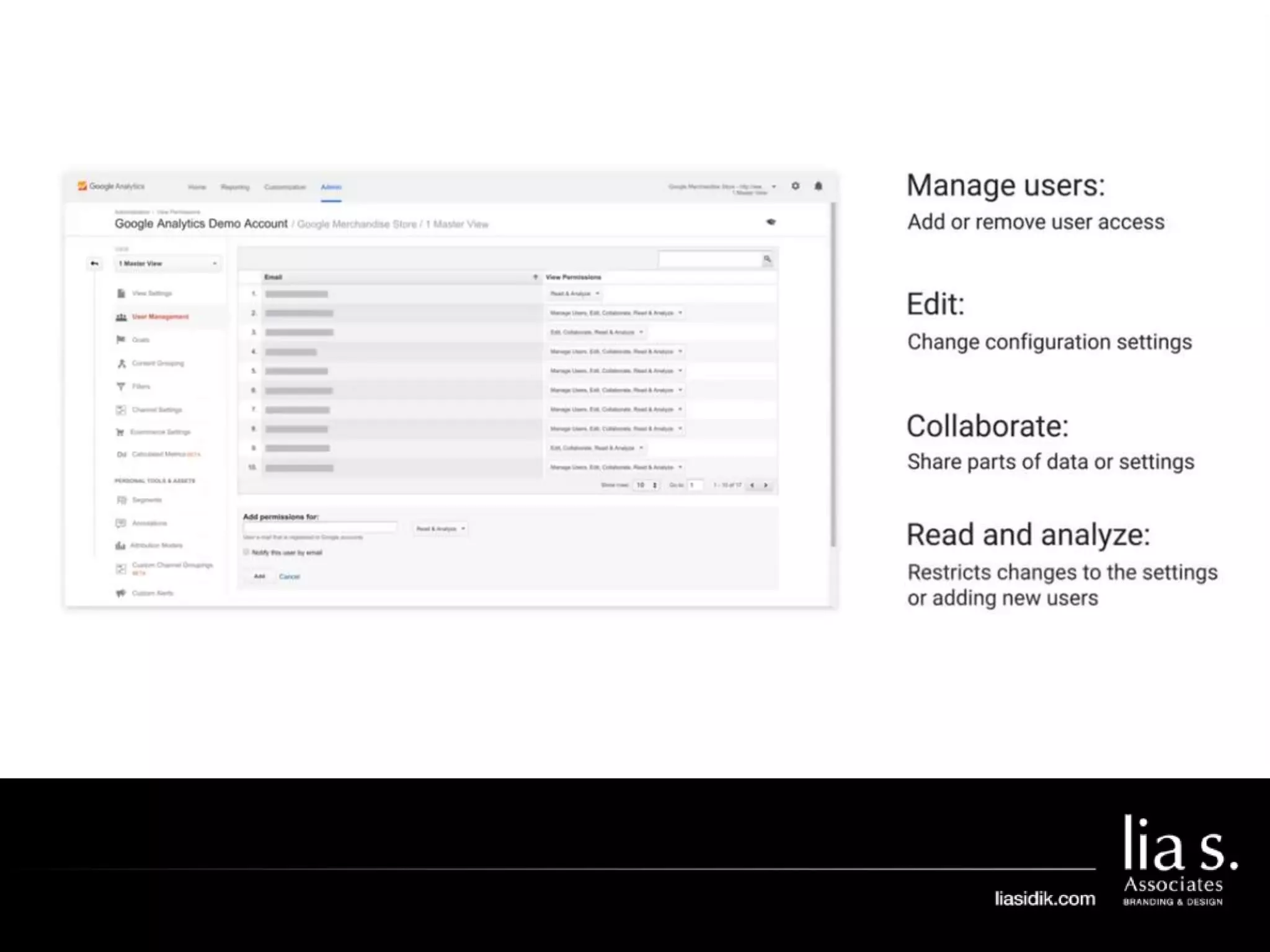
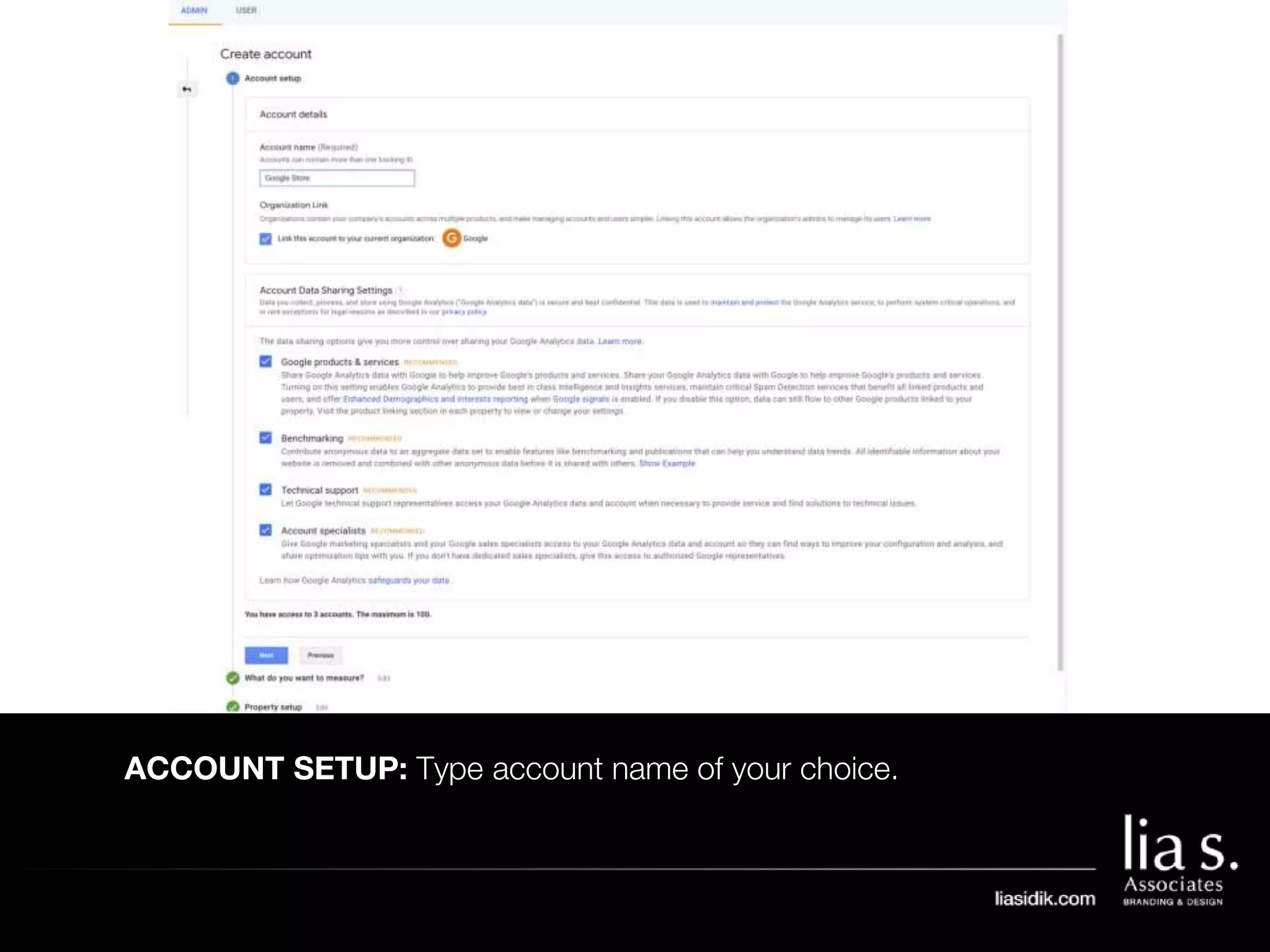
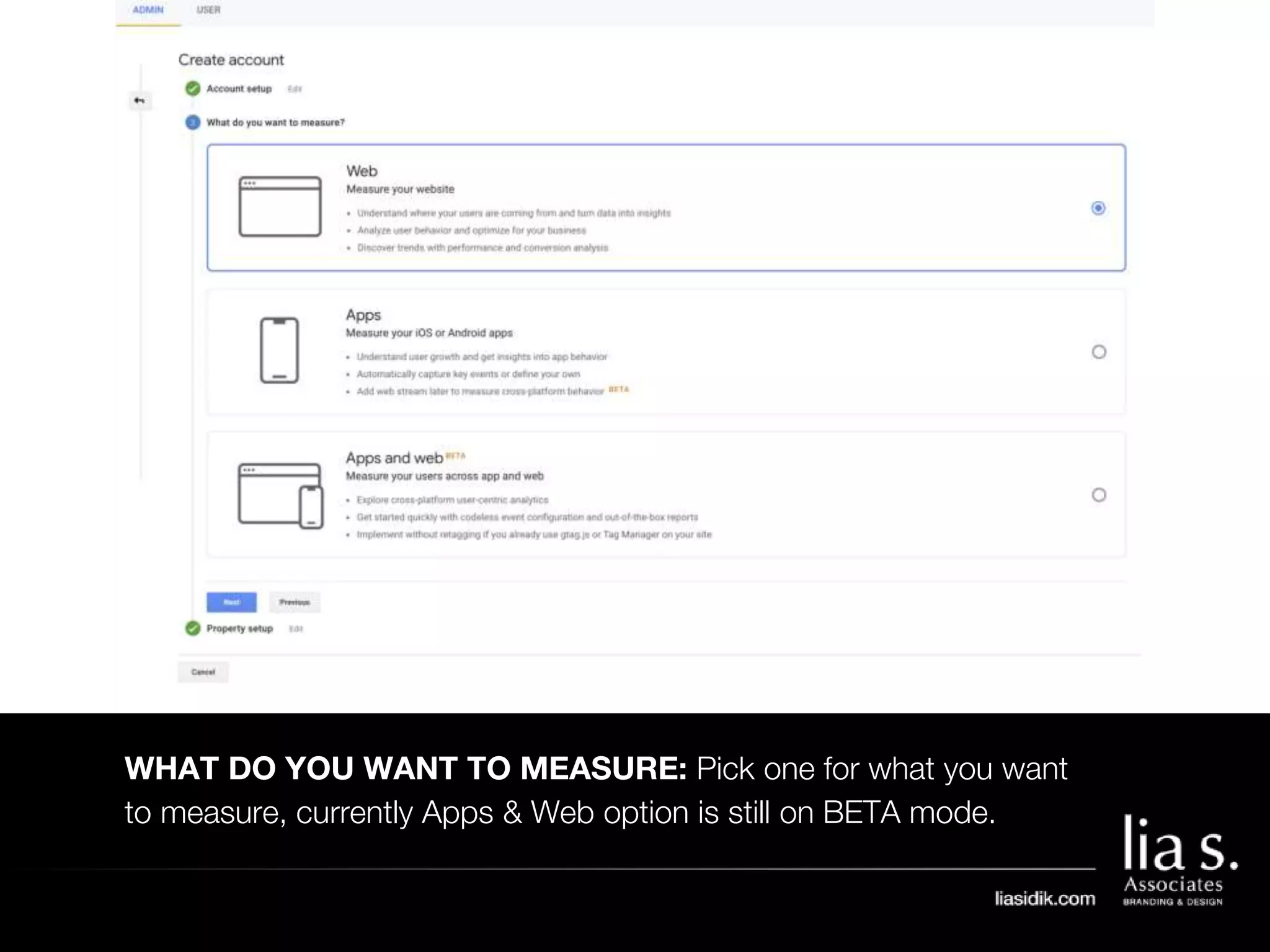
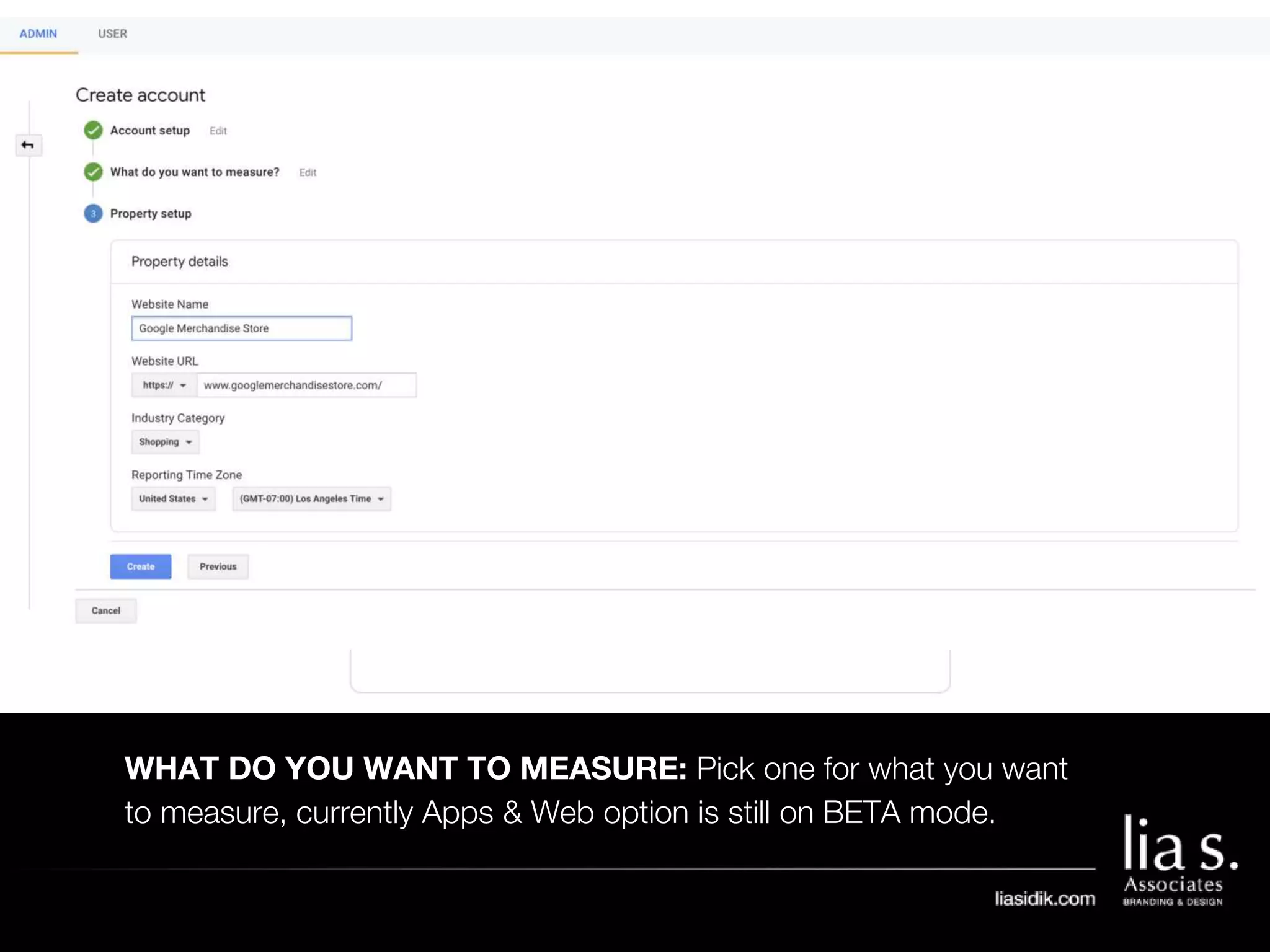
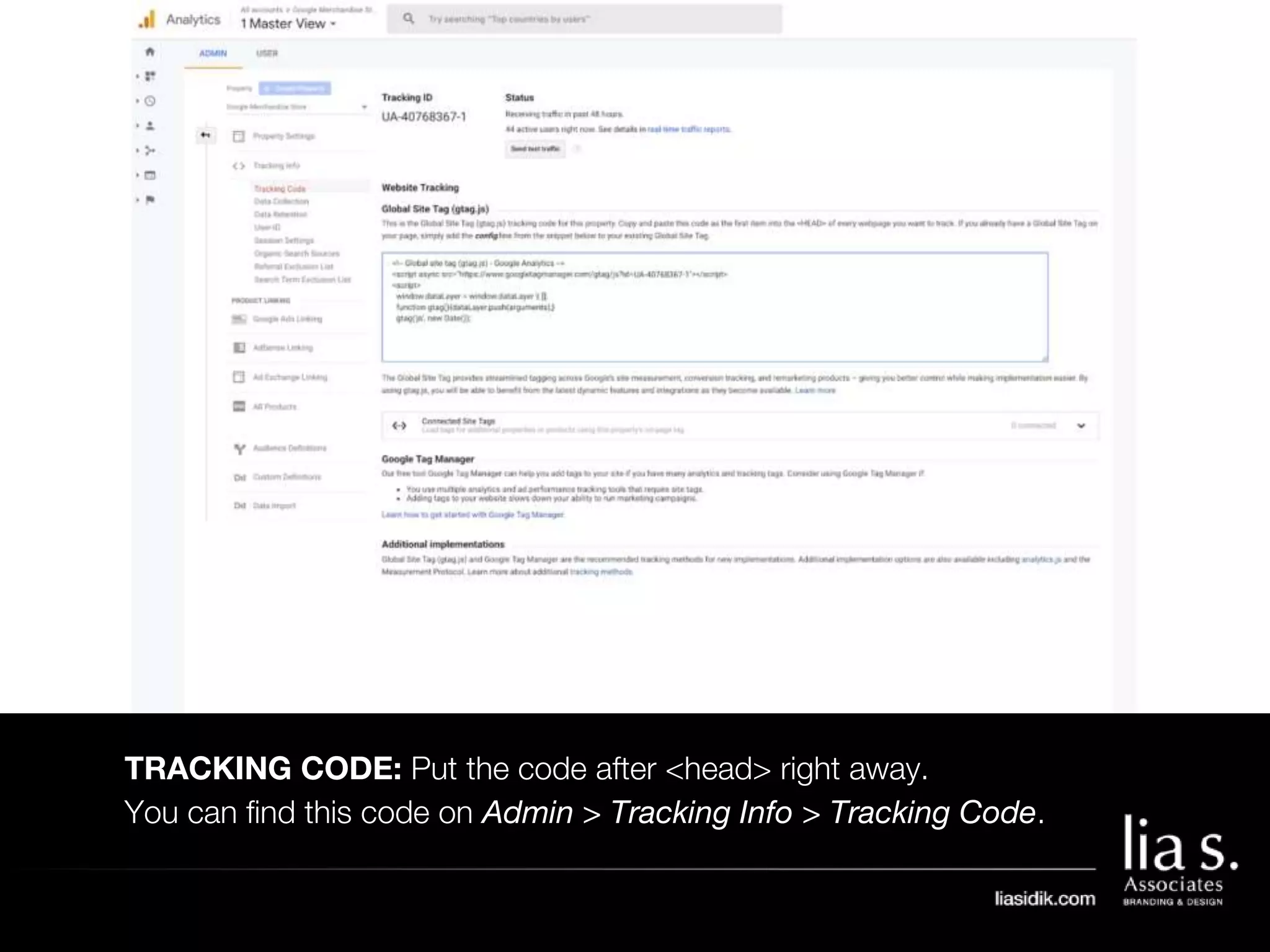
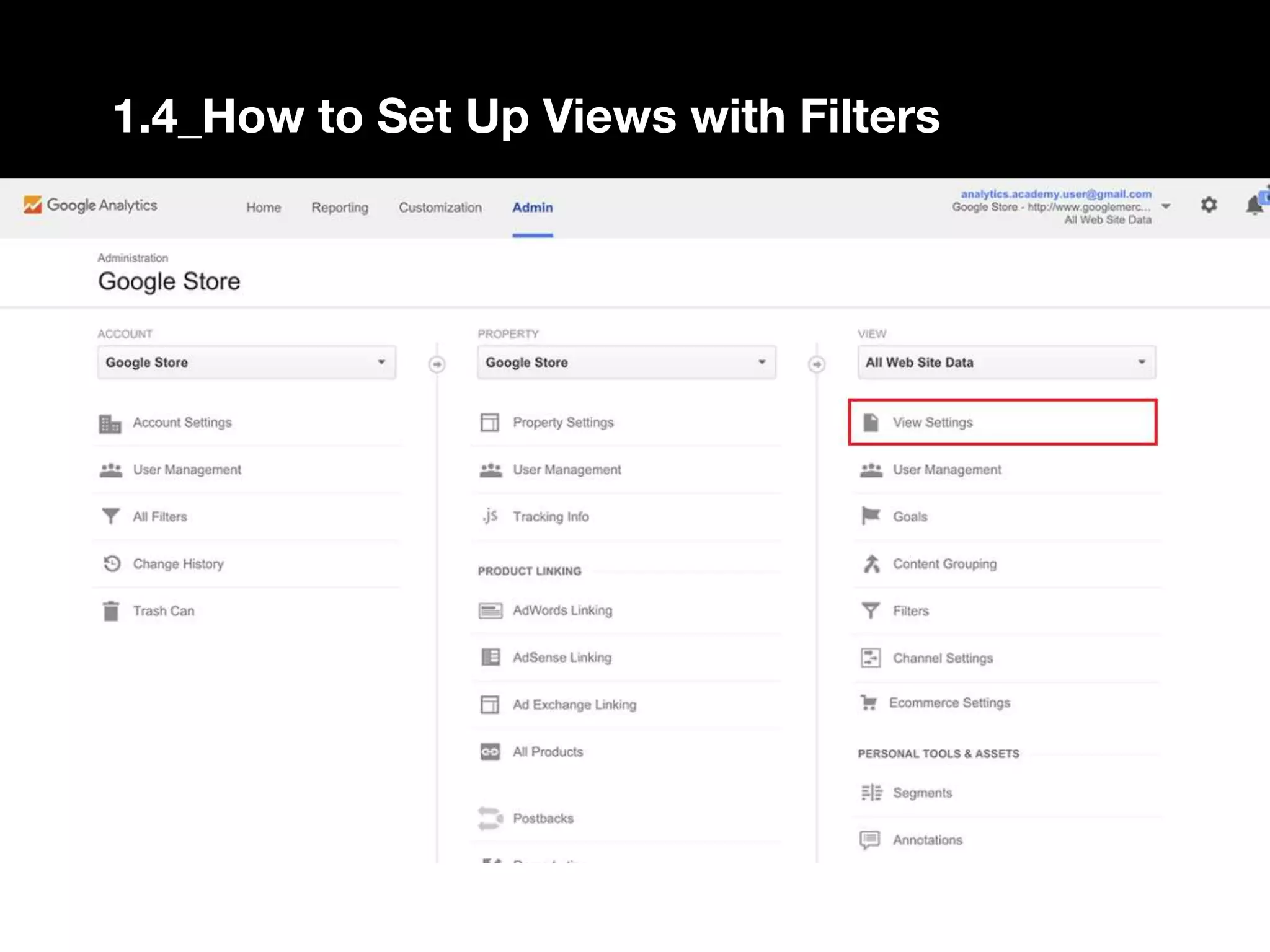
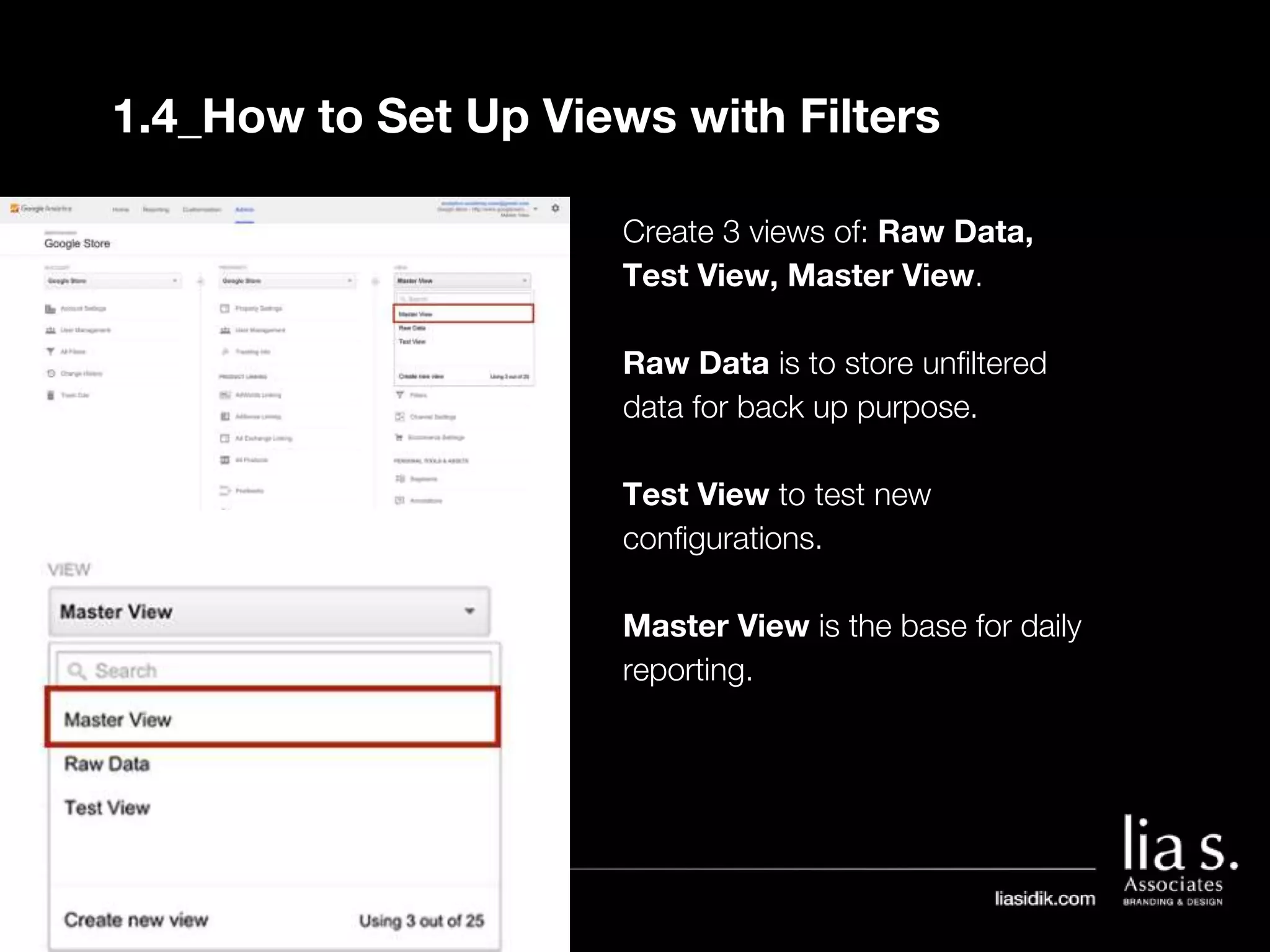
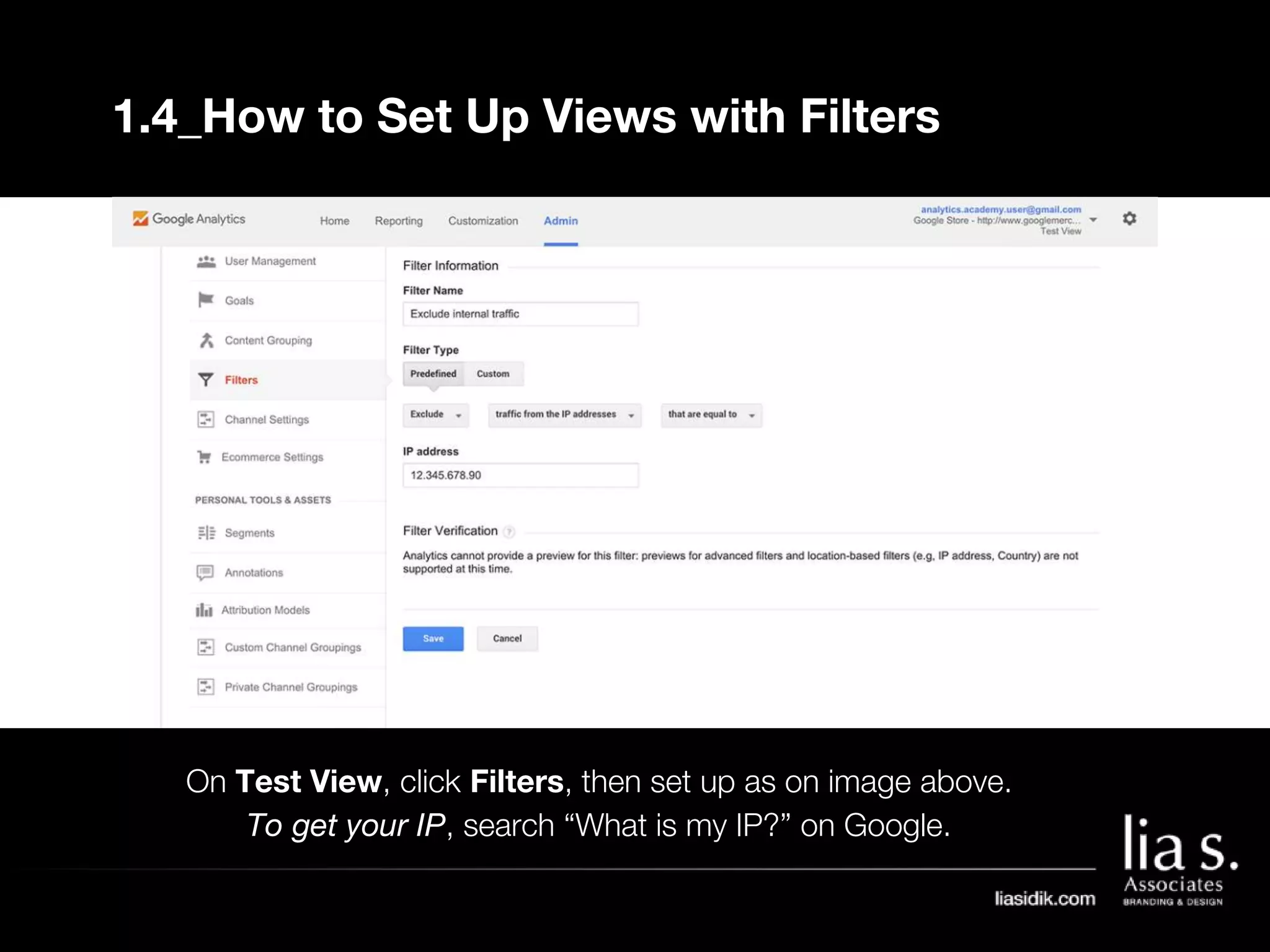
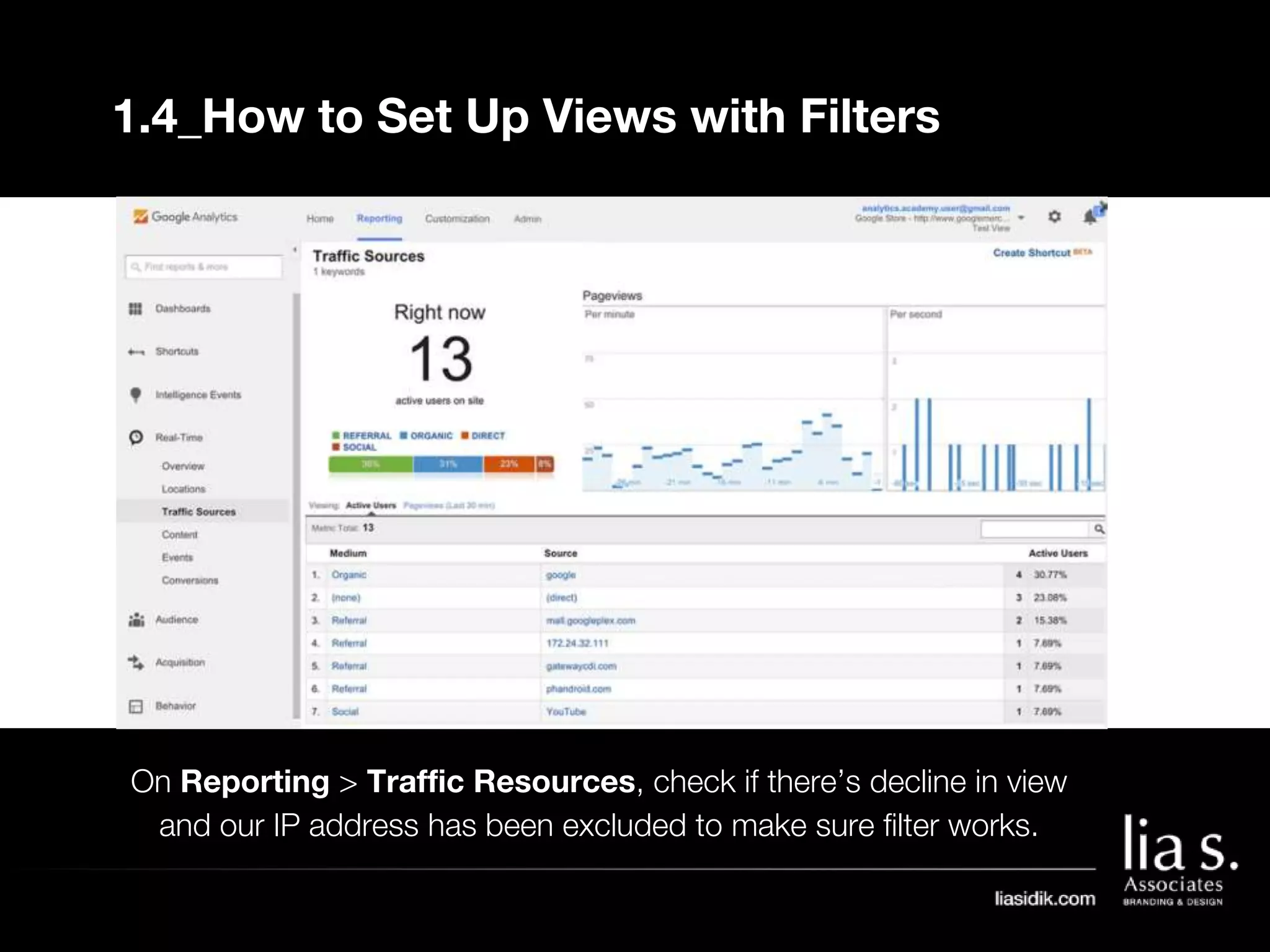
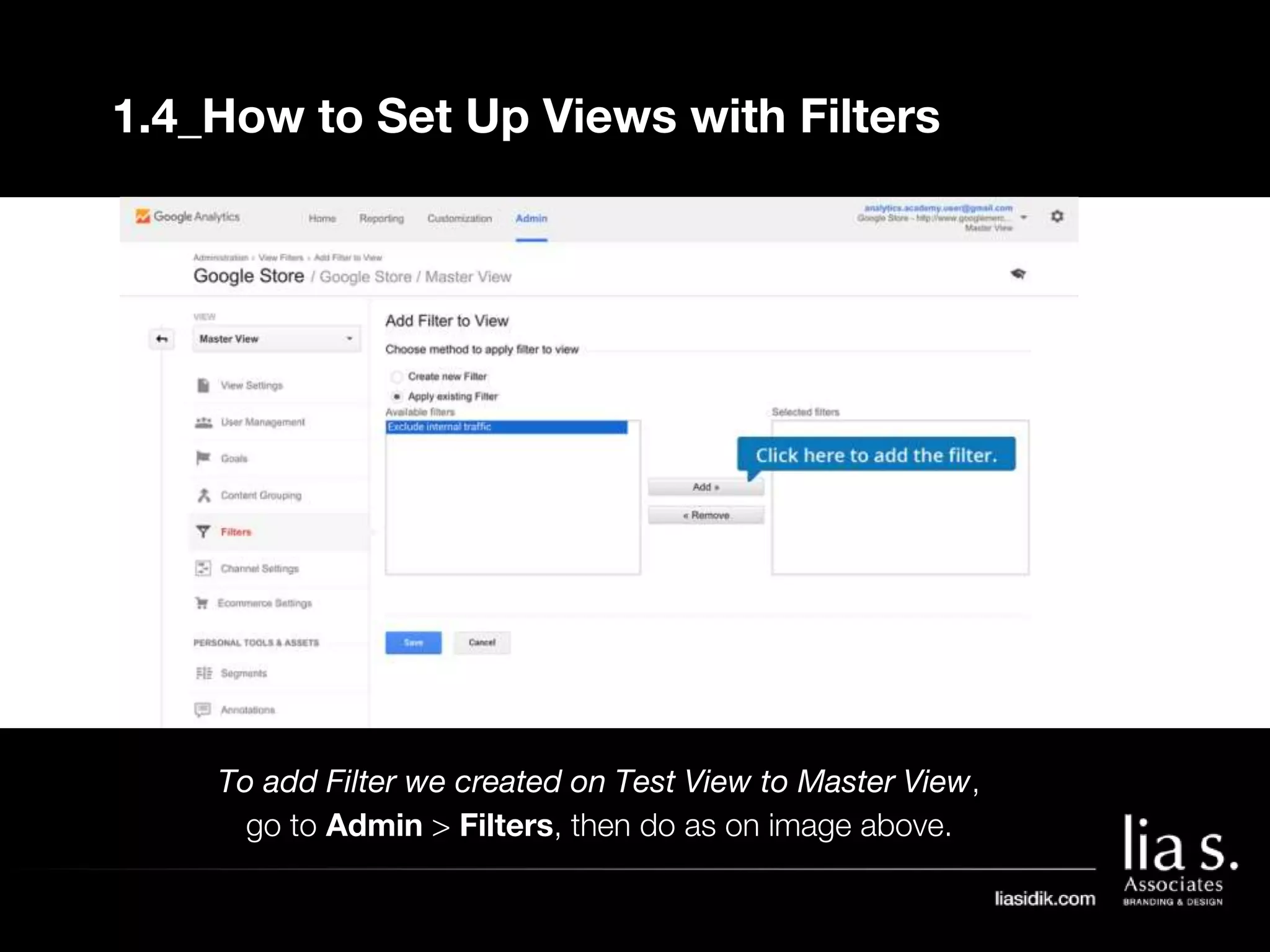
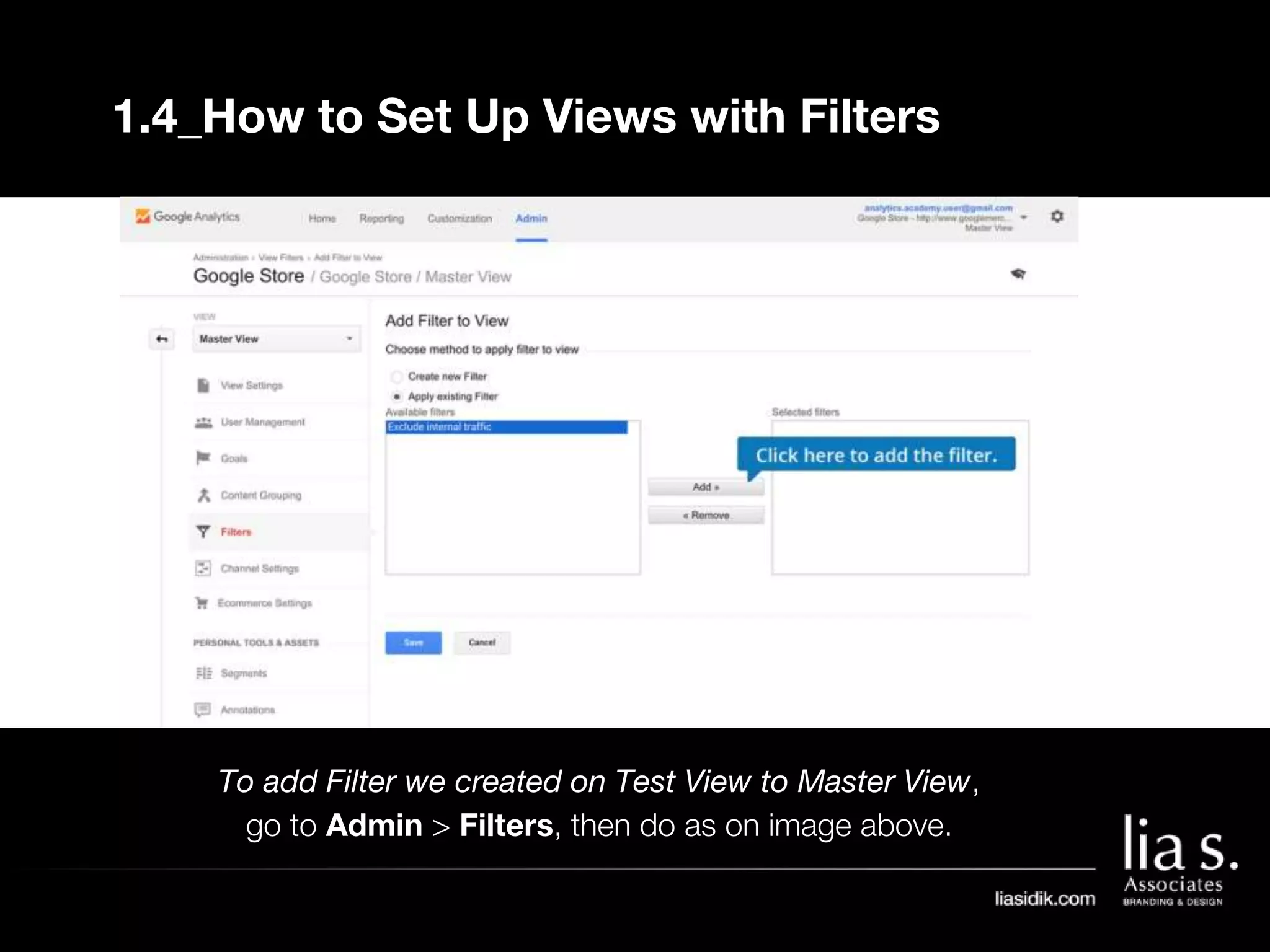
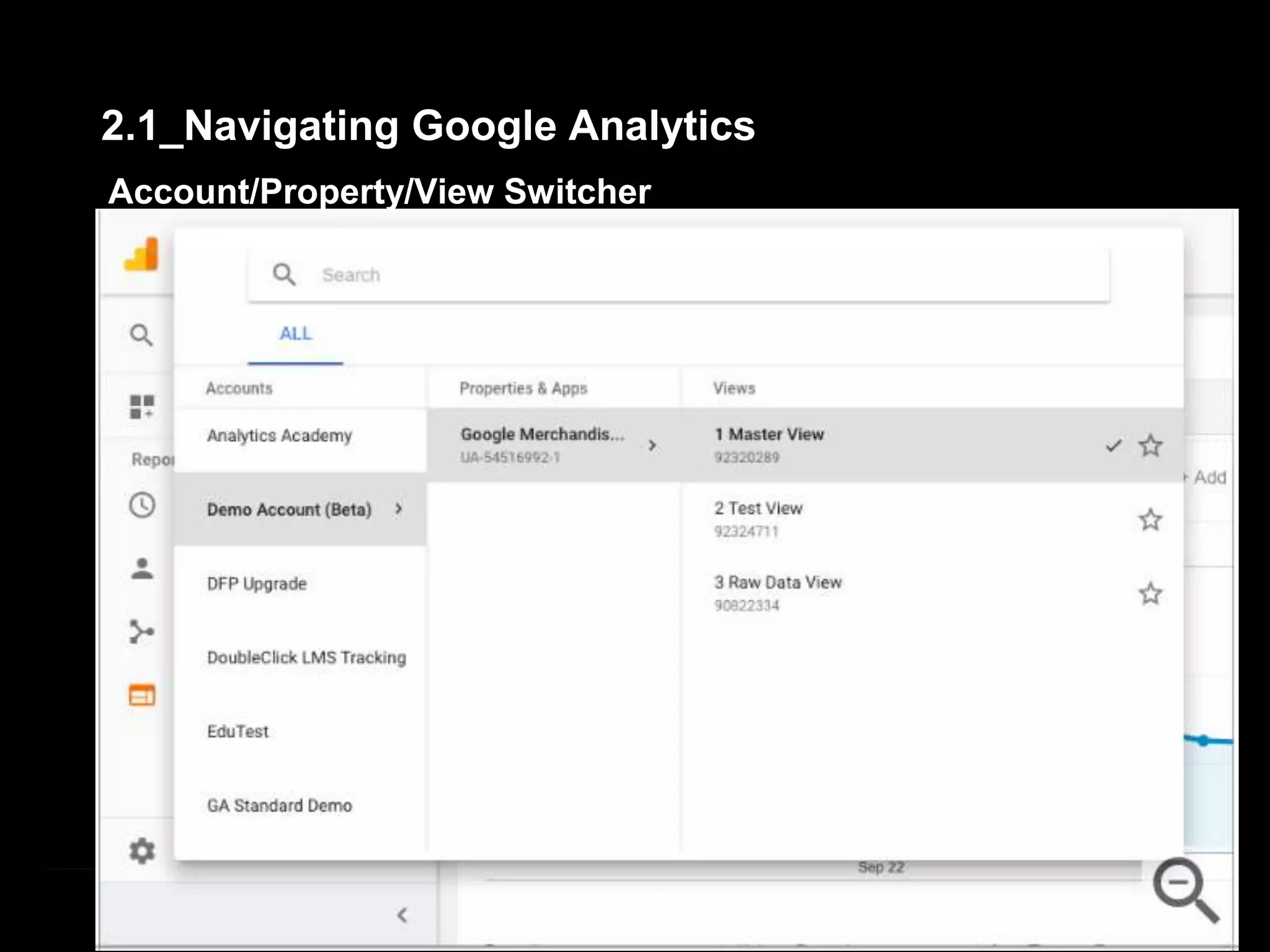
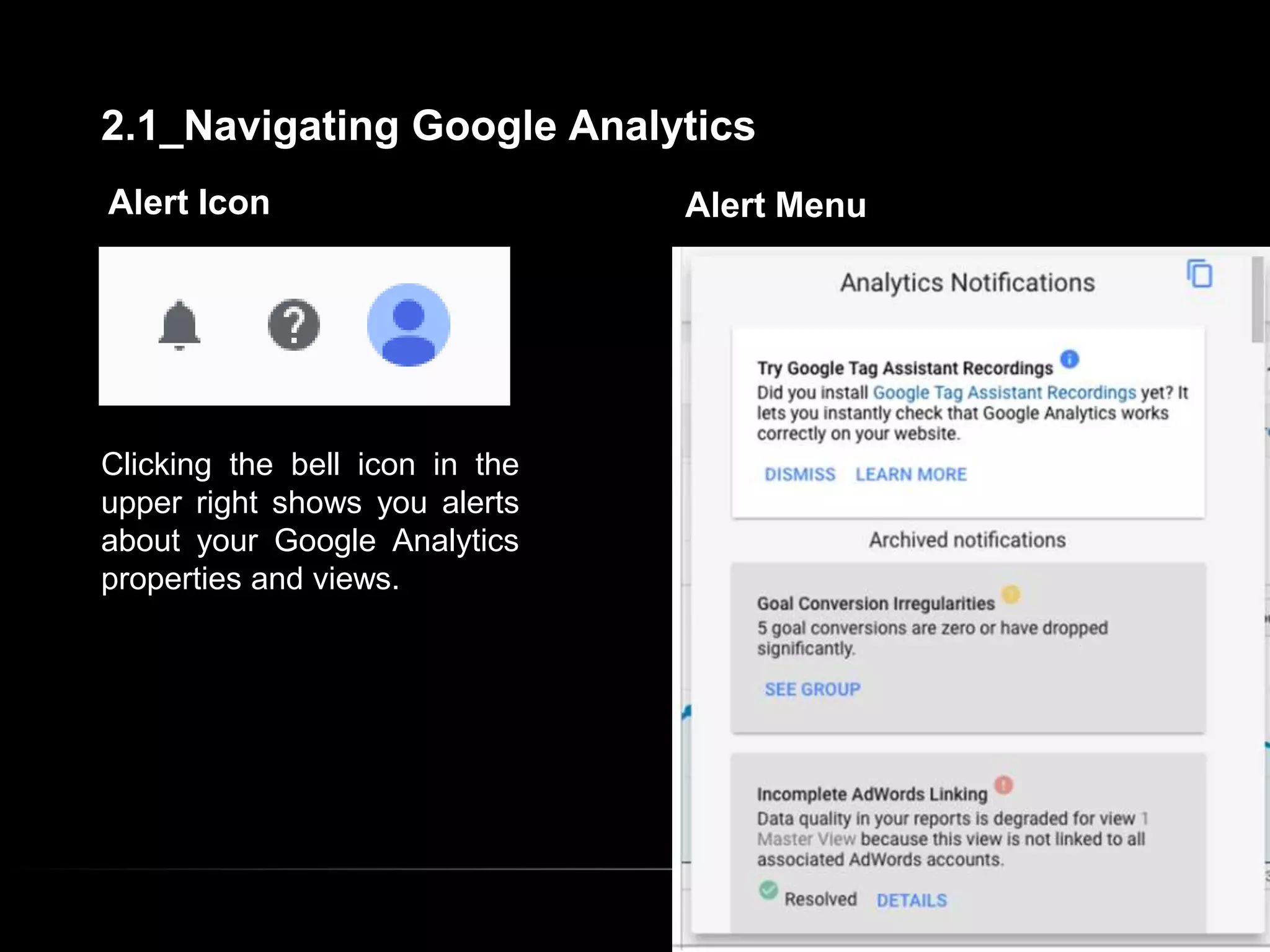
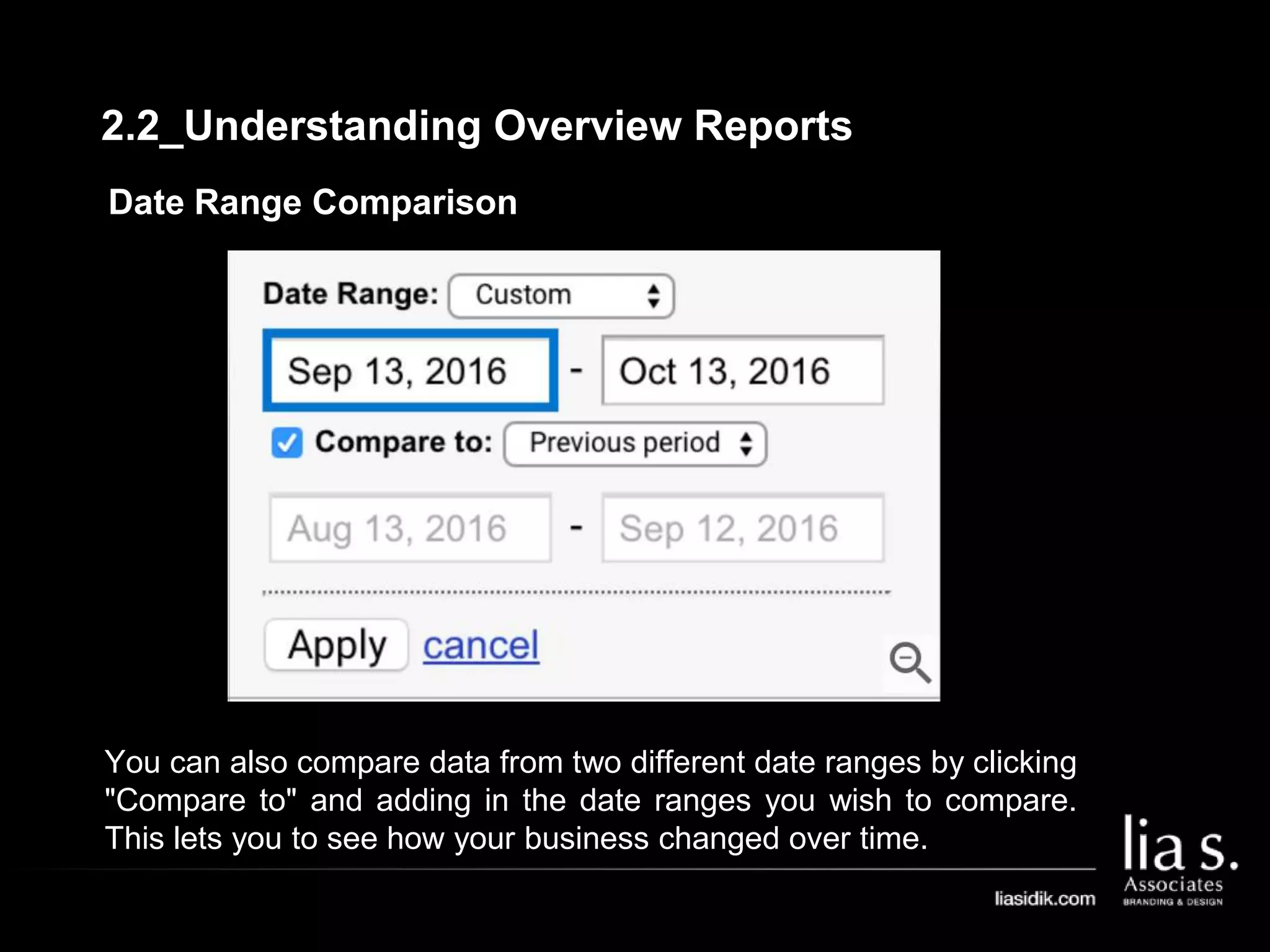
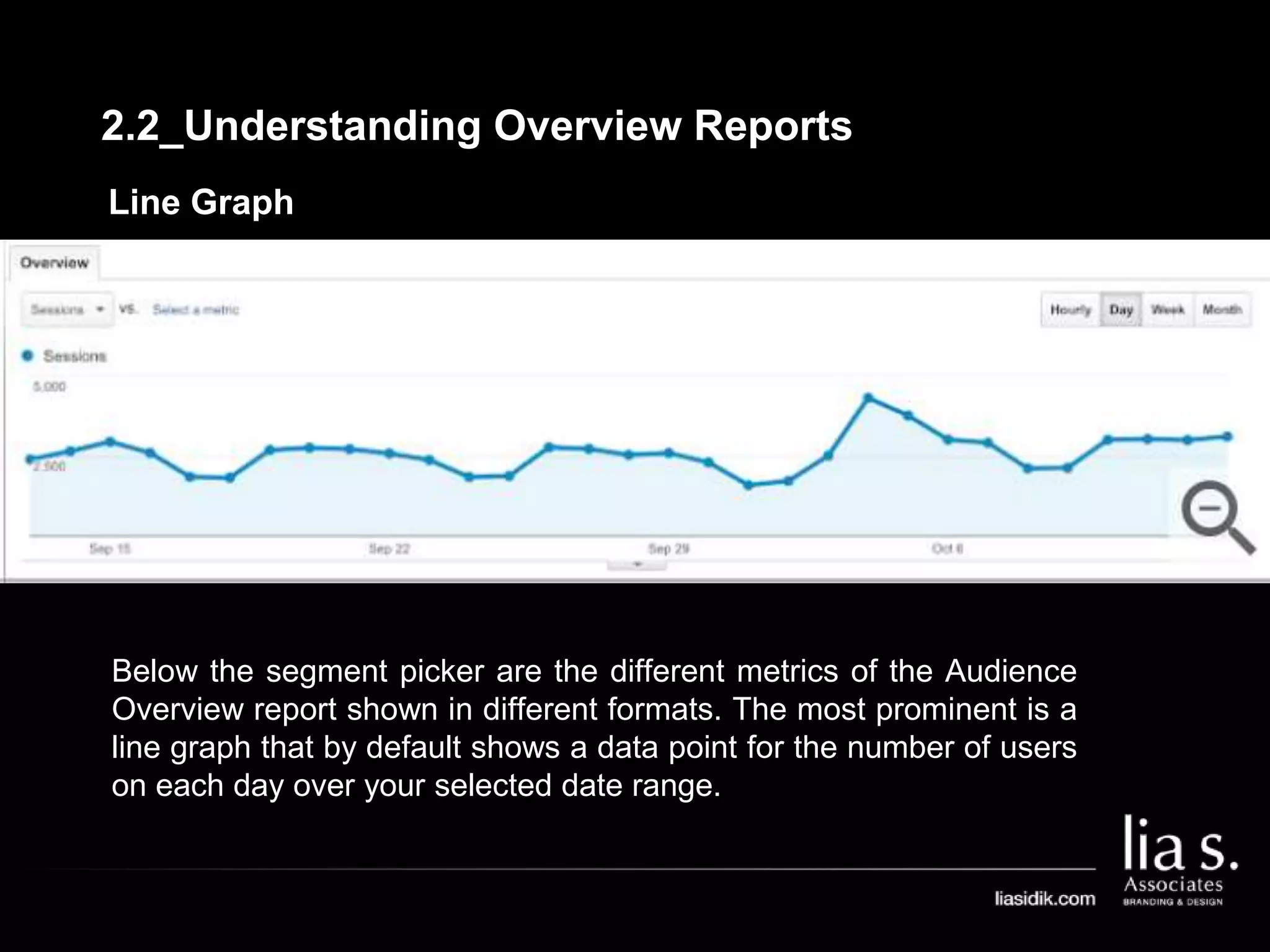
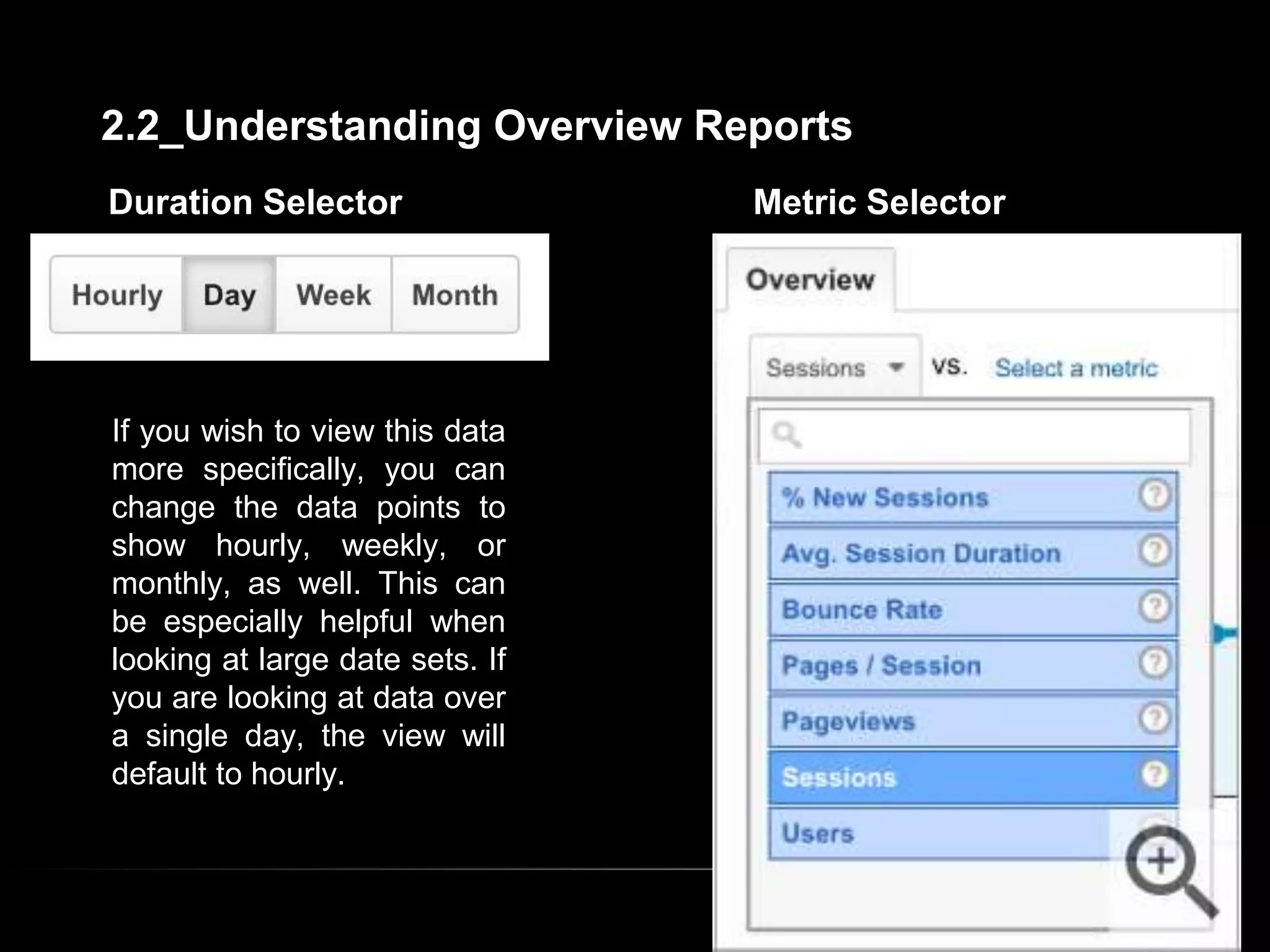
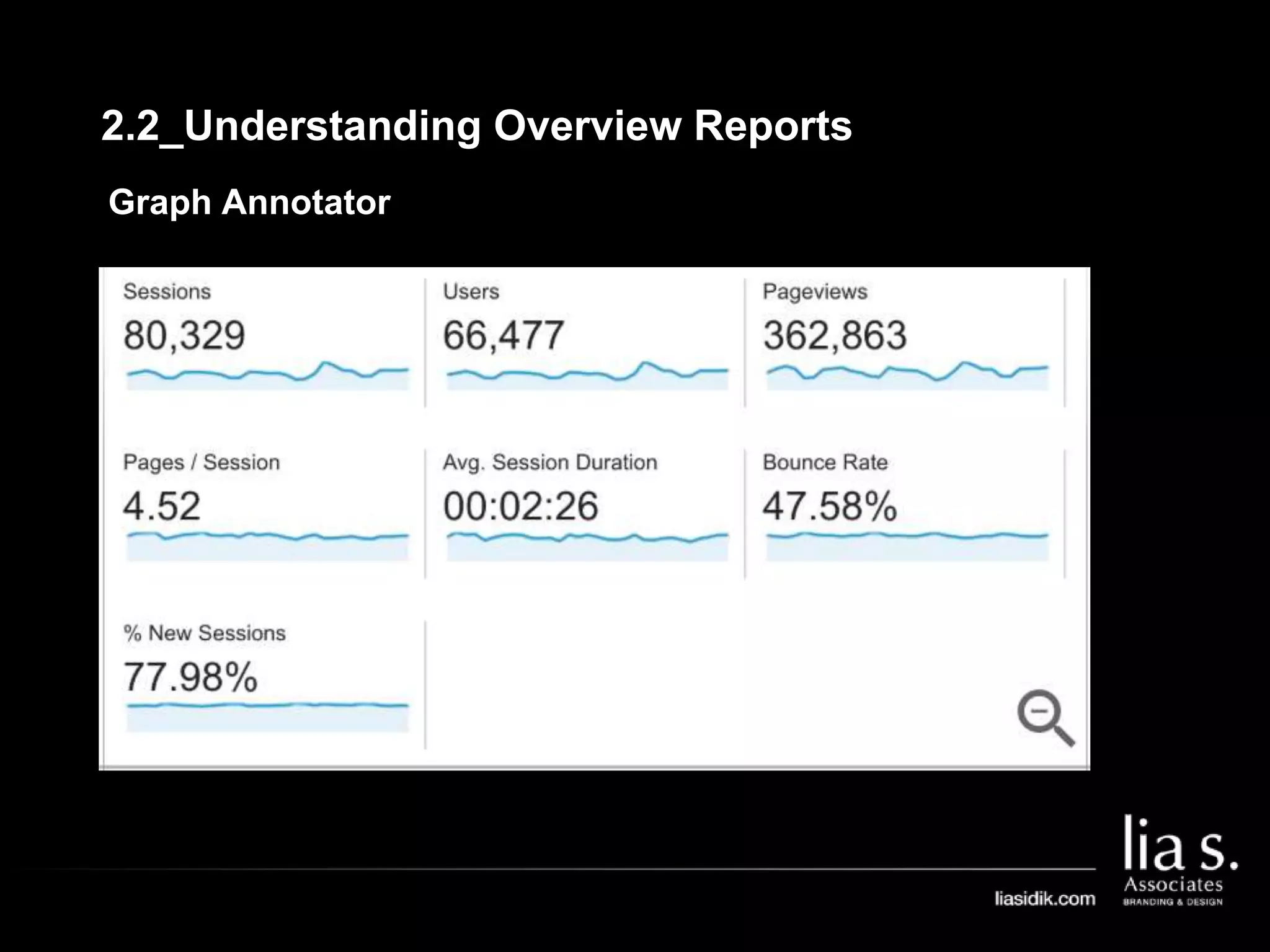
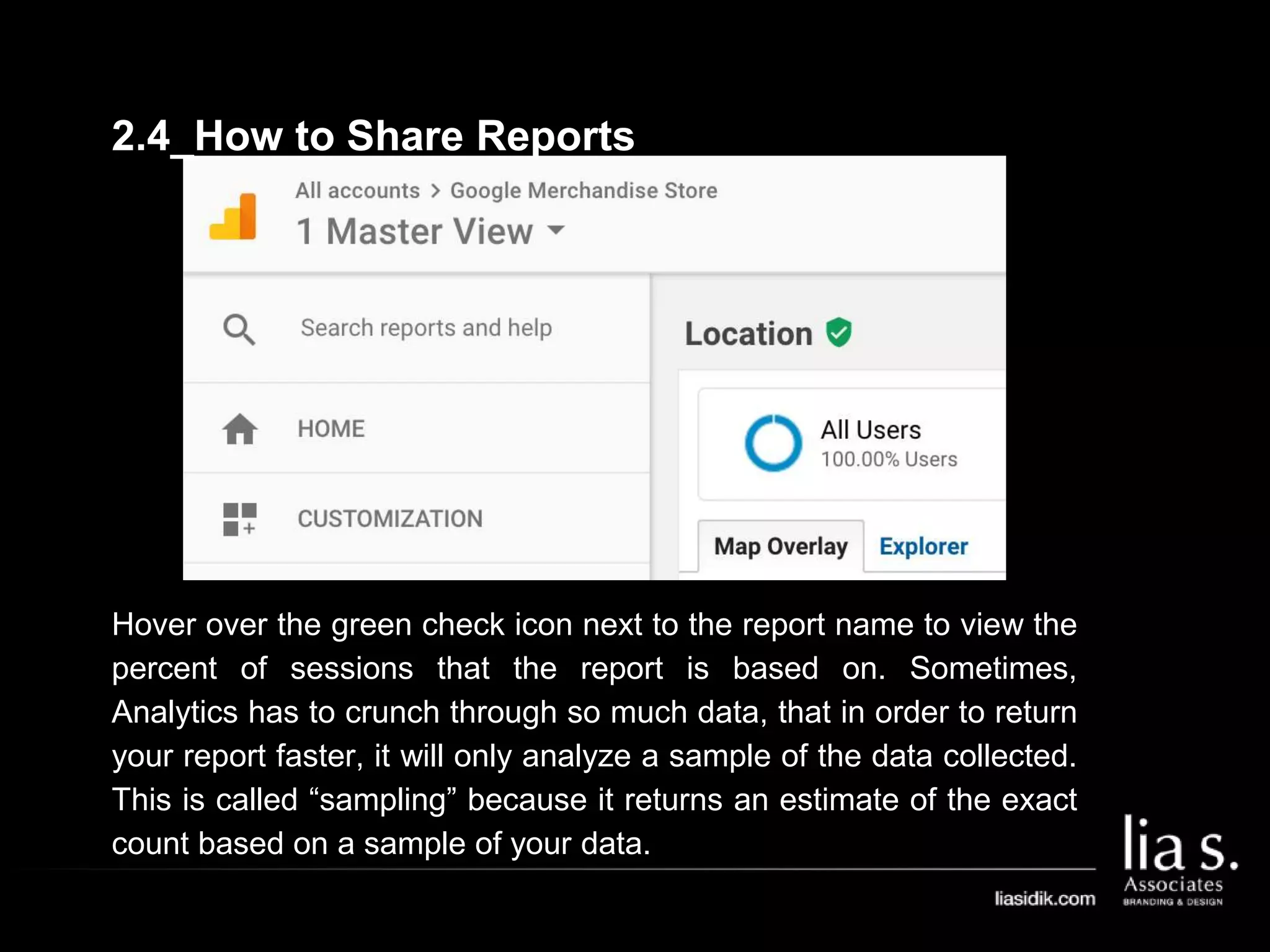
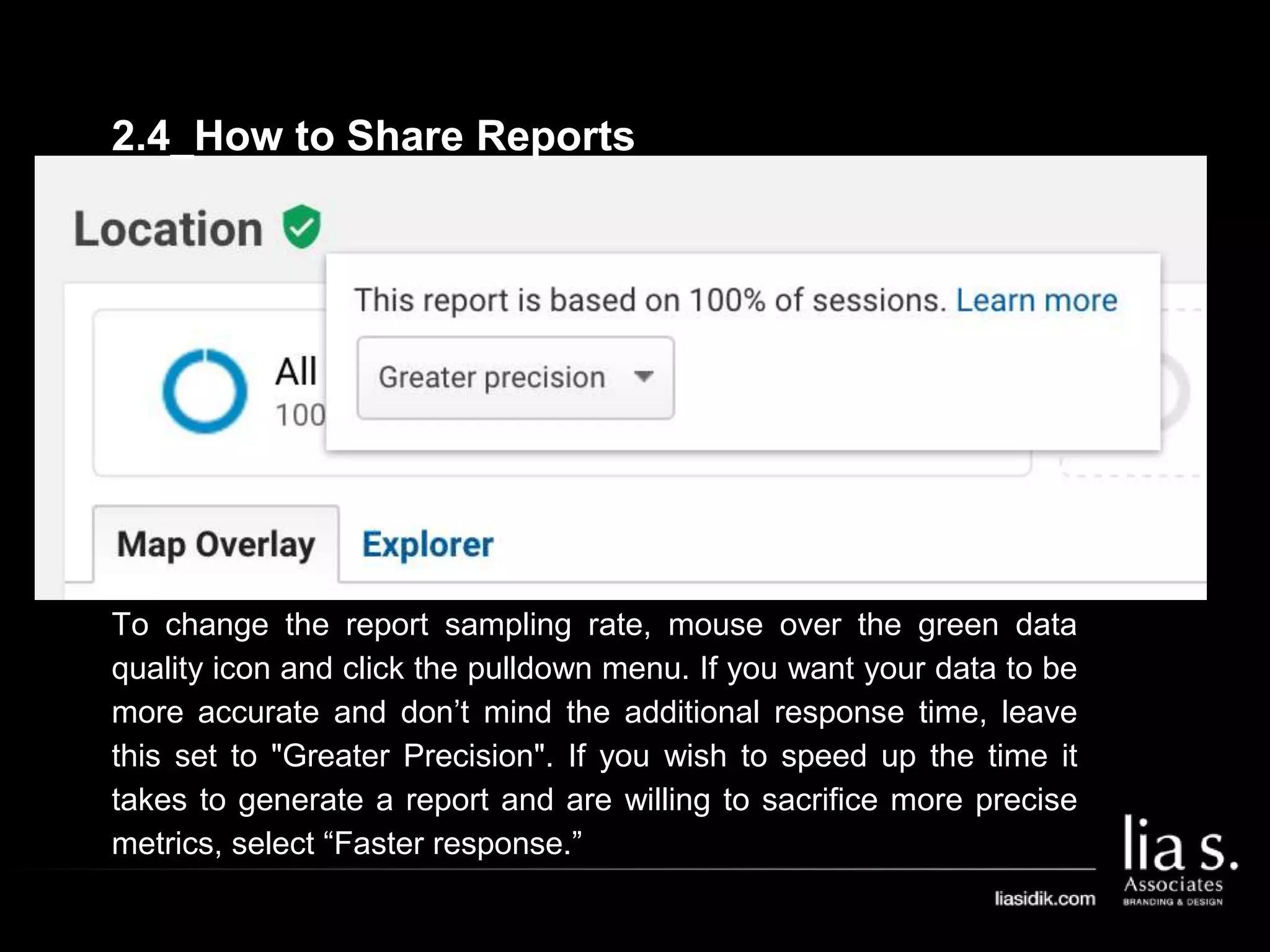
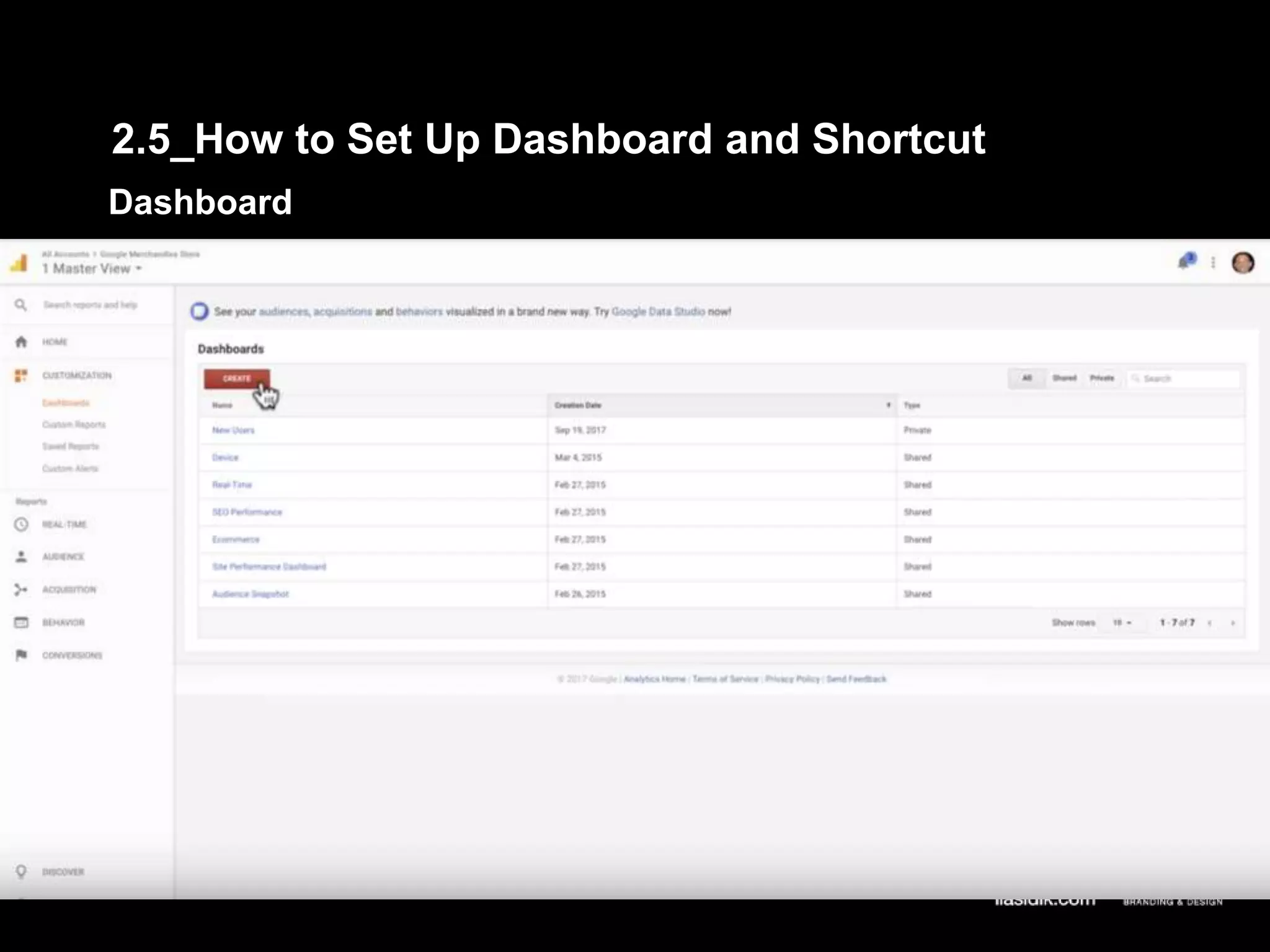
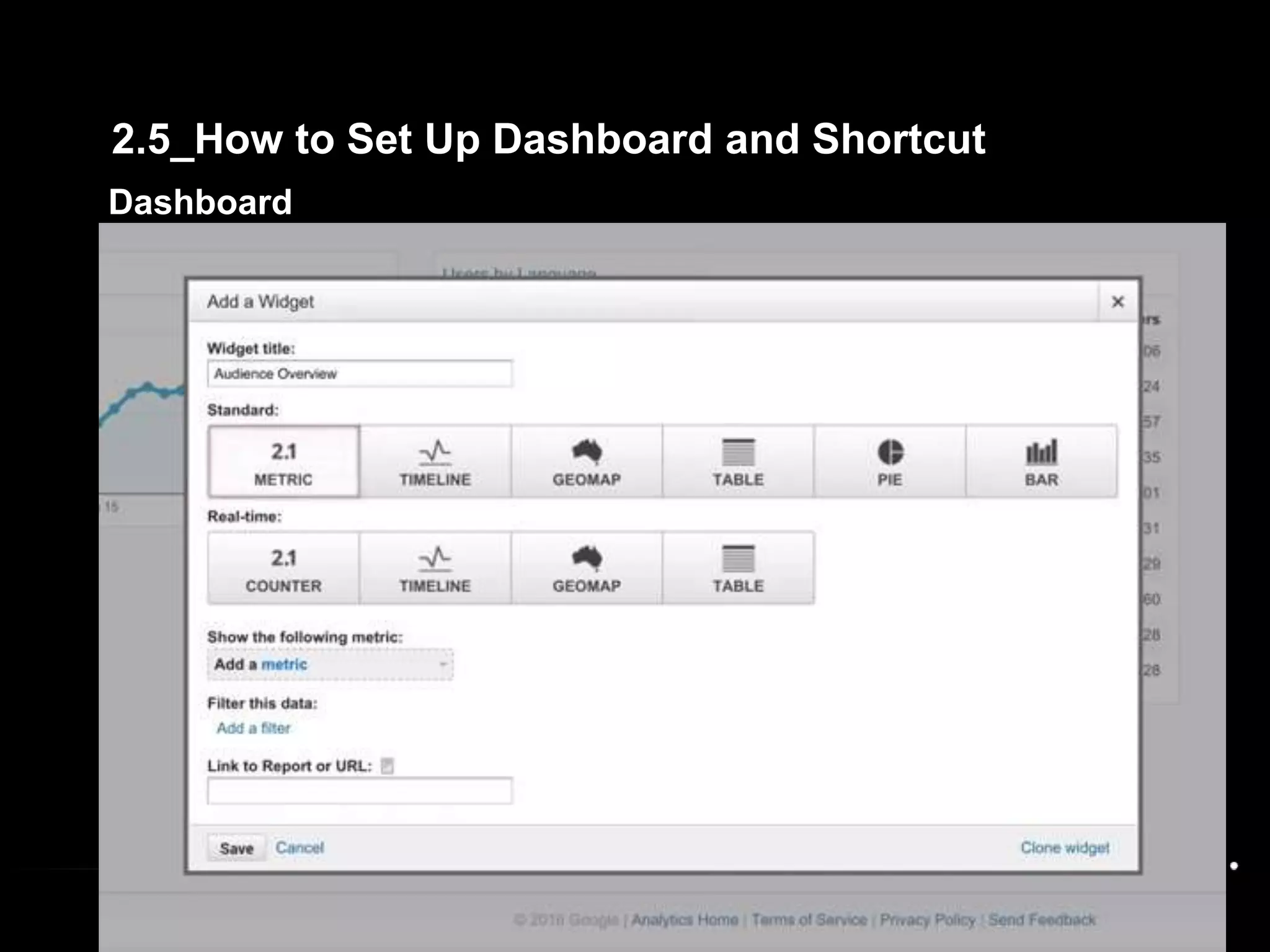
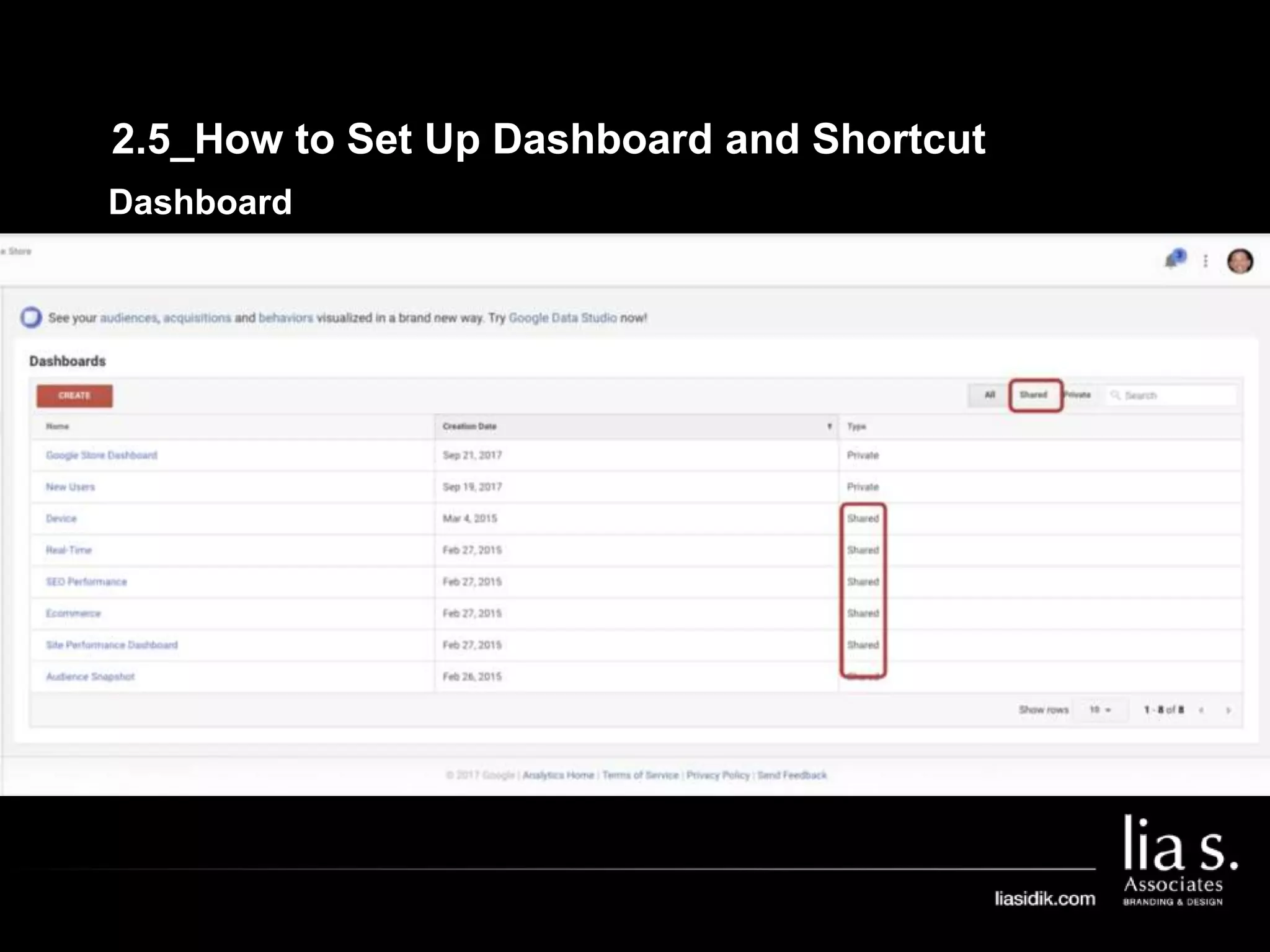
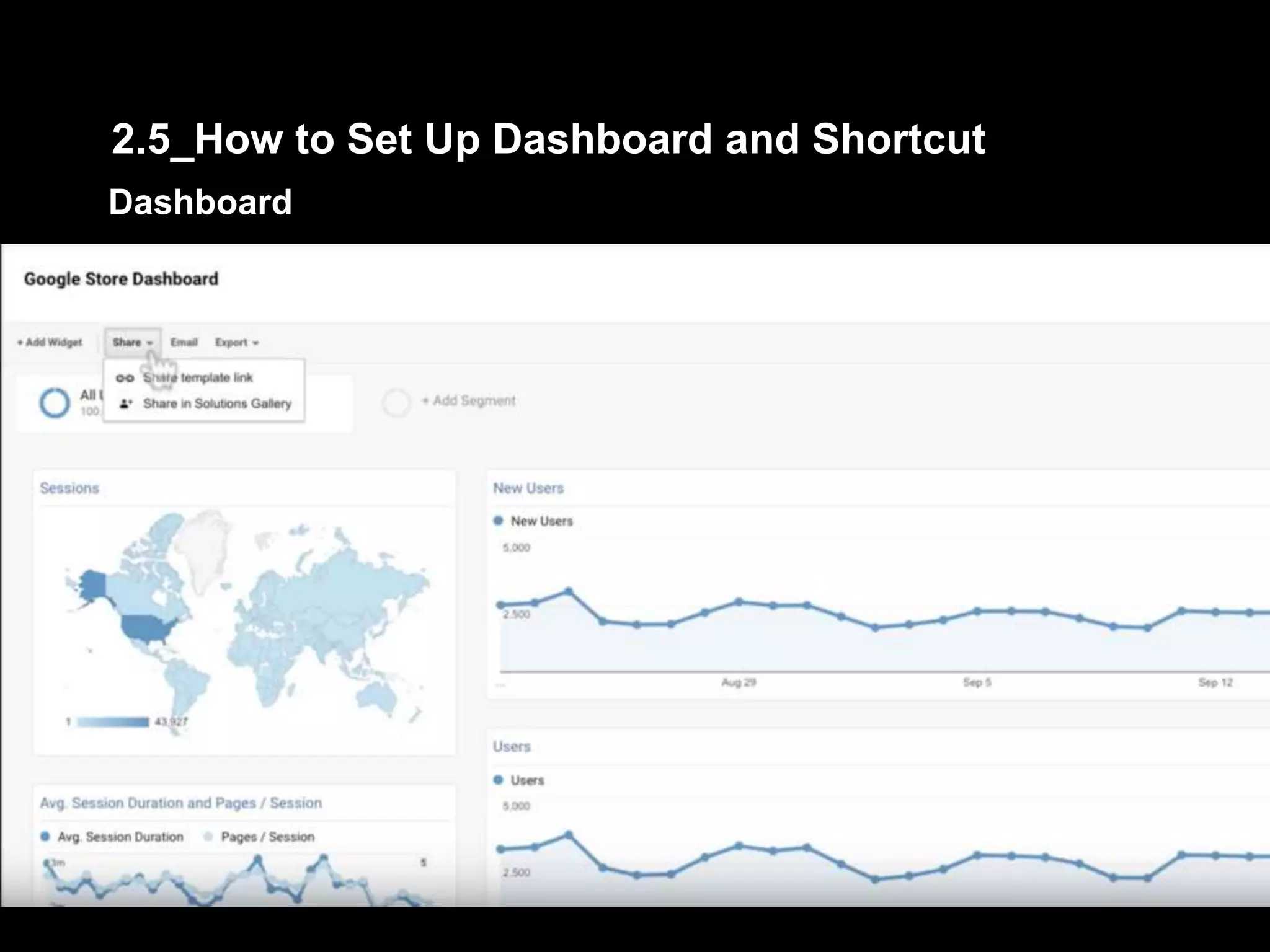
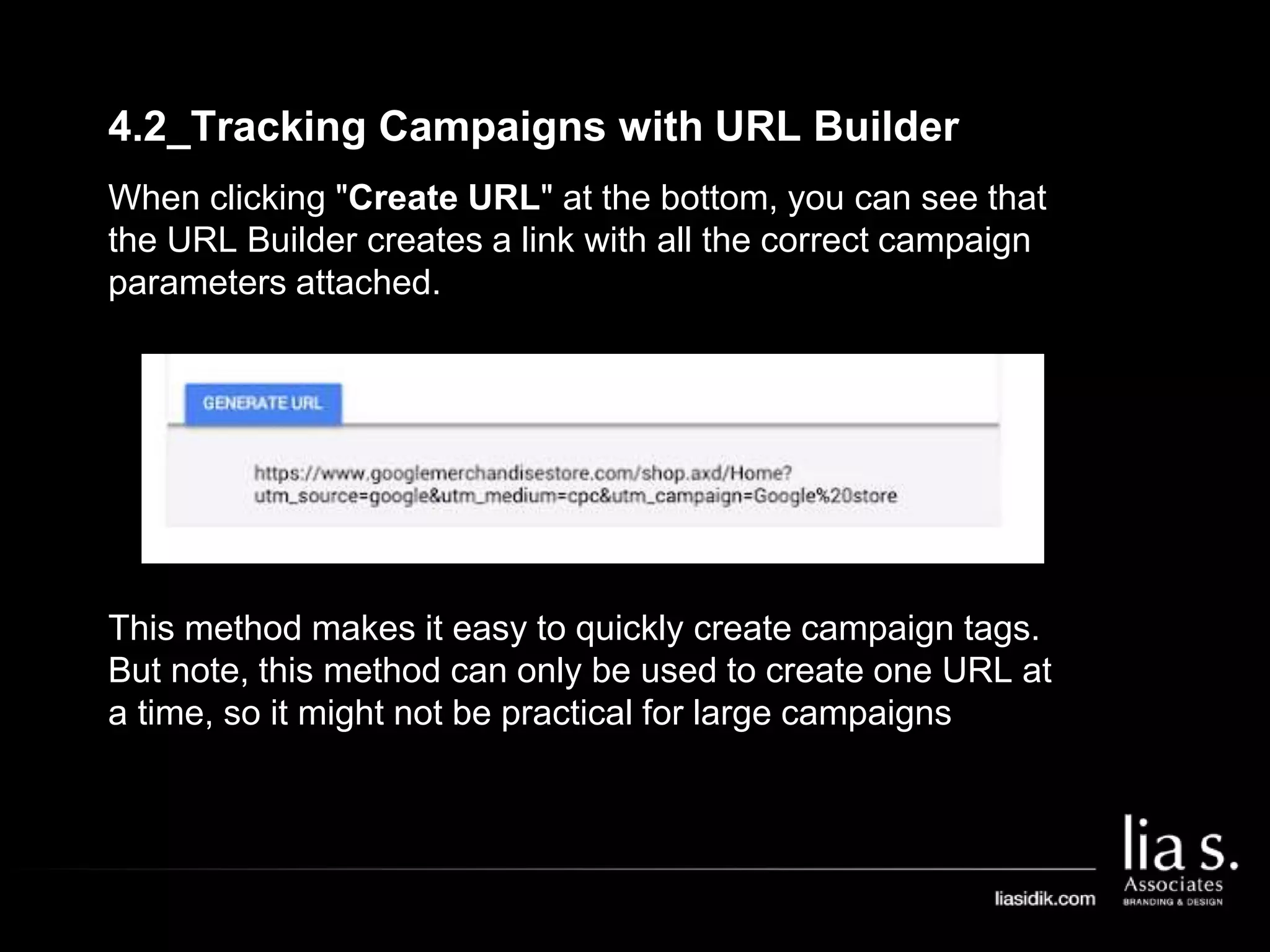
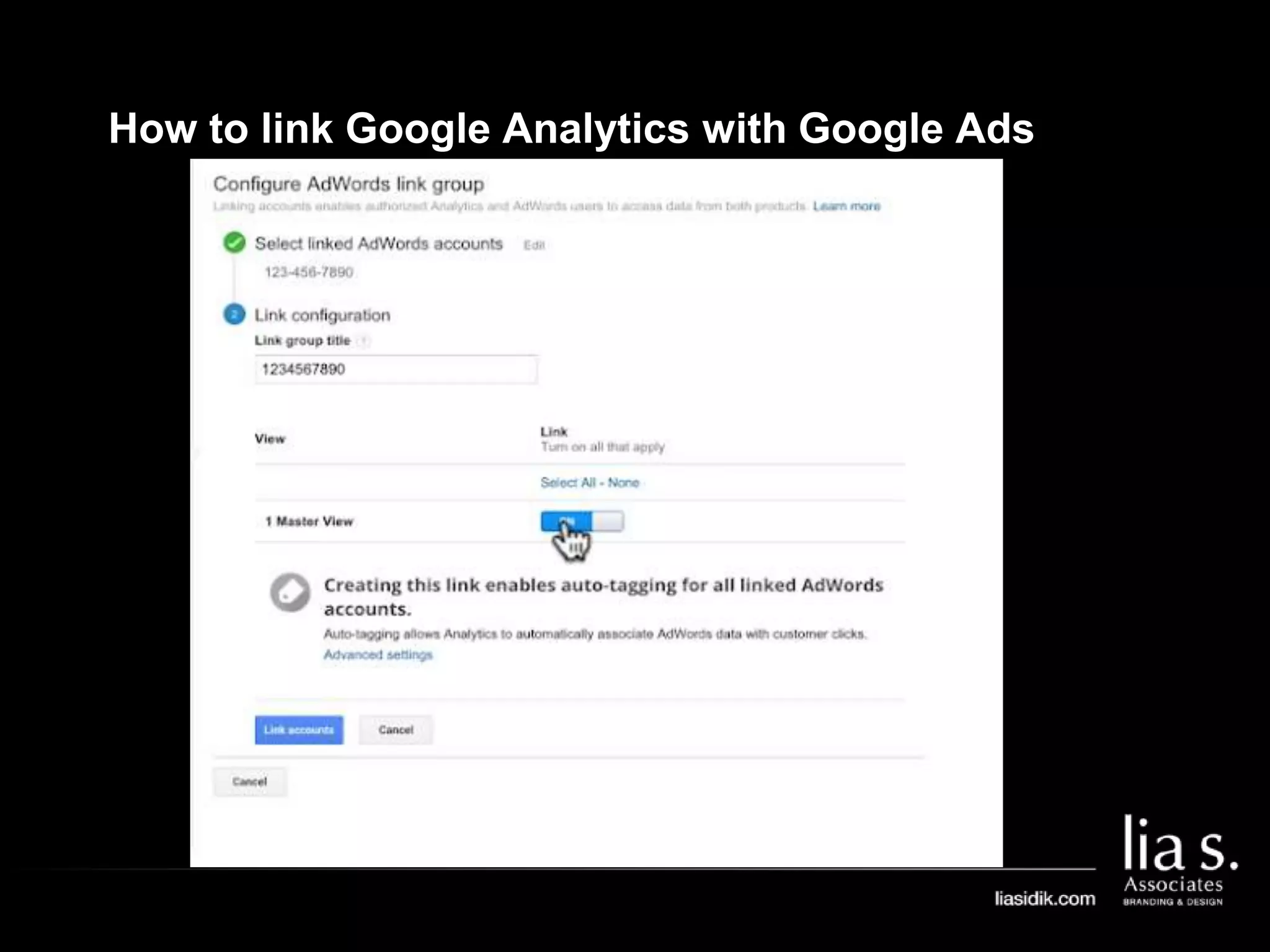
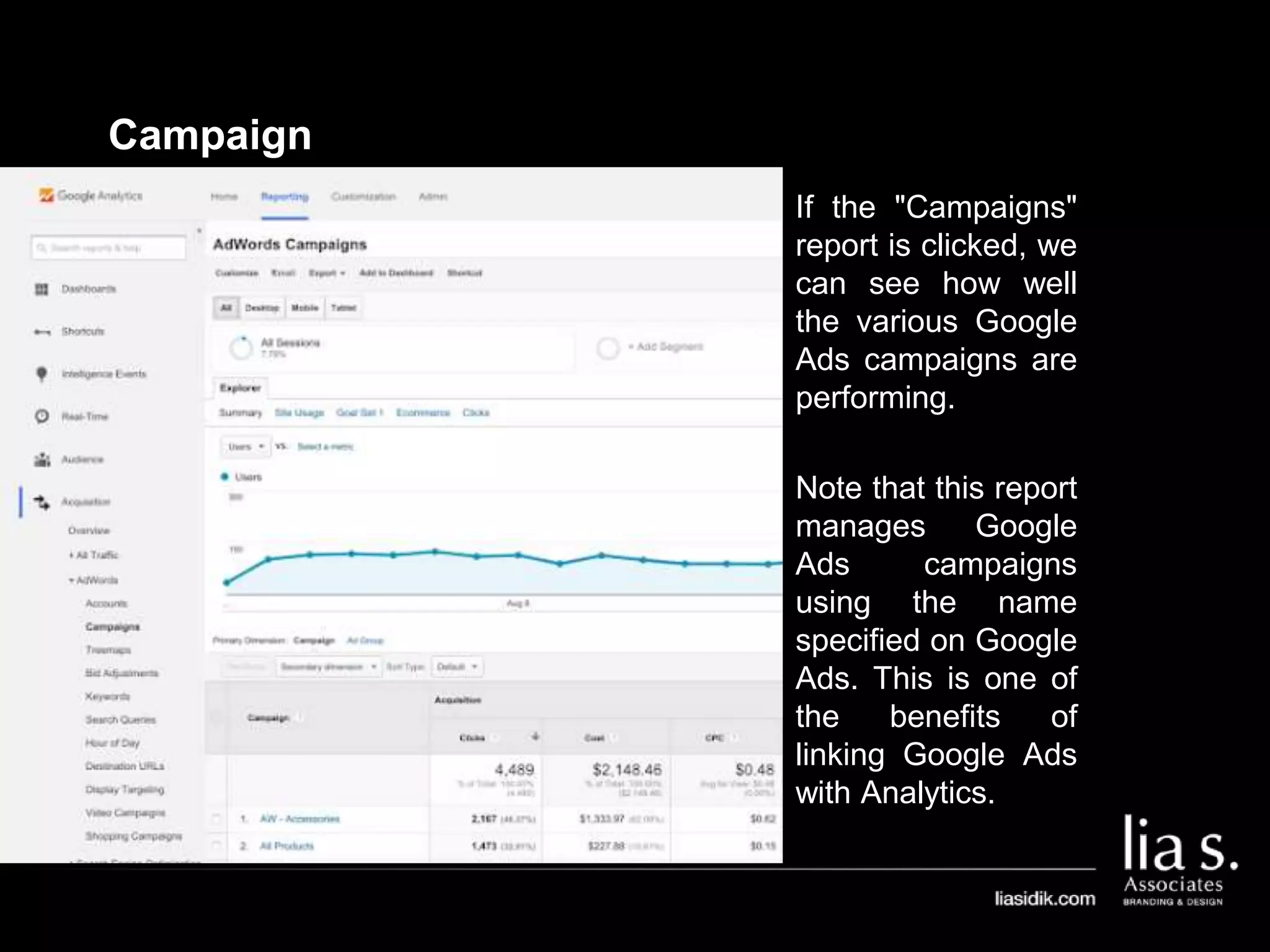
1. The document provides an overview of setting up and using Google Analytics. It discusses setting up views, filters, and accounts. It also covers how to track campaigns, set up goals, and link Google Analytics to Google Ads.
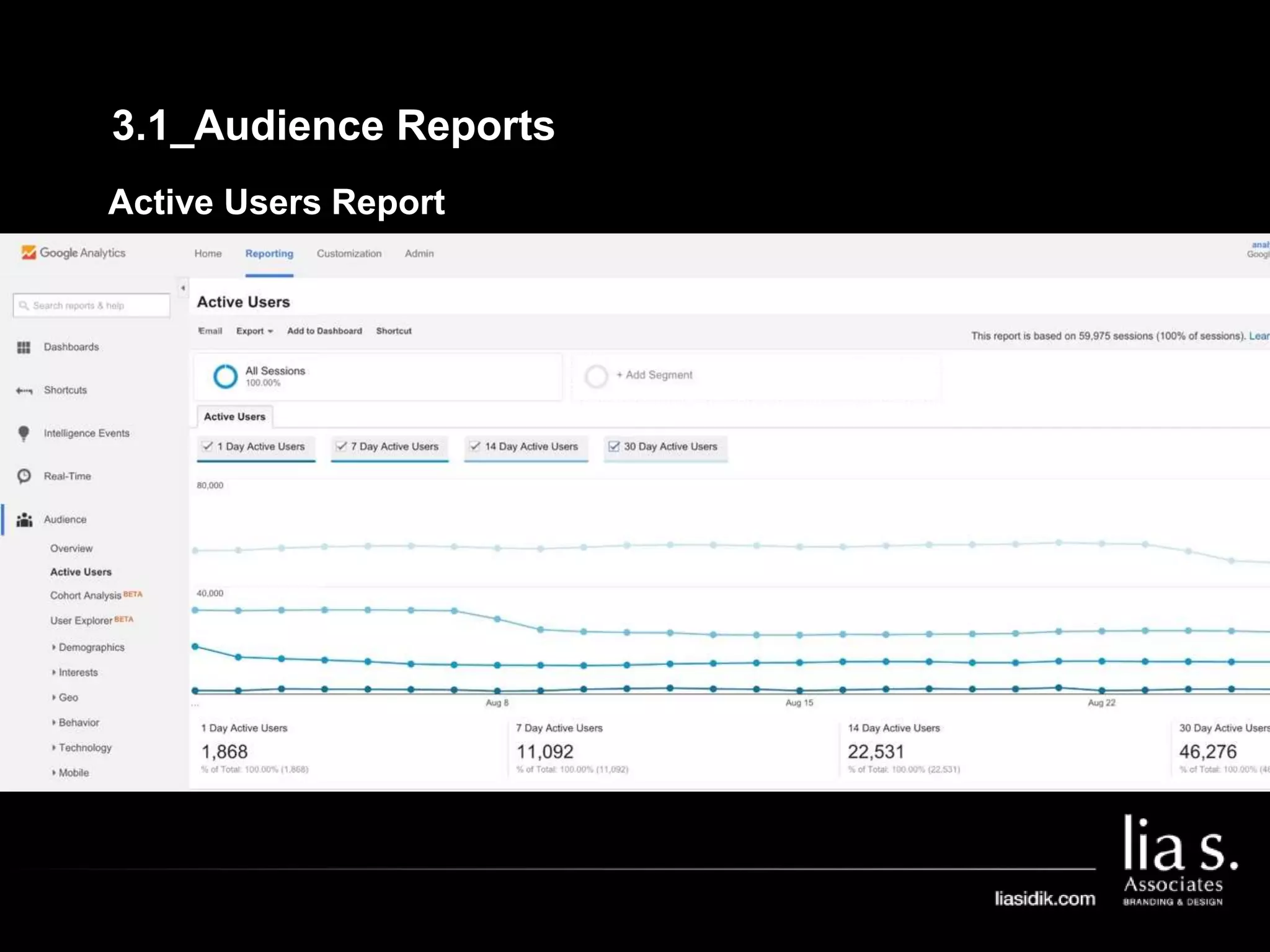
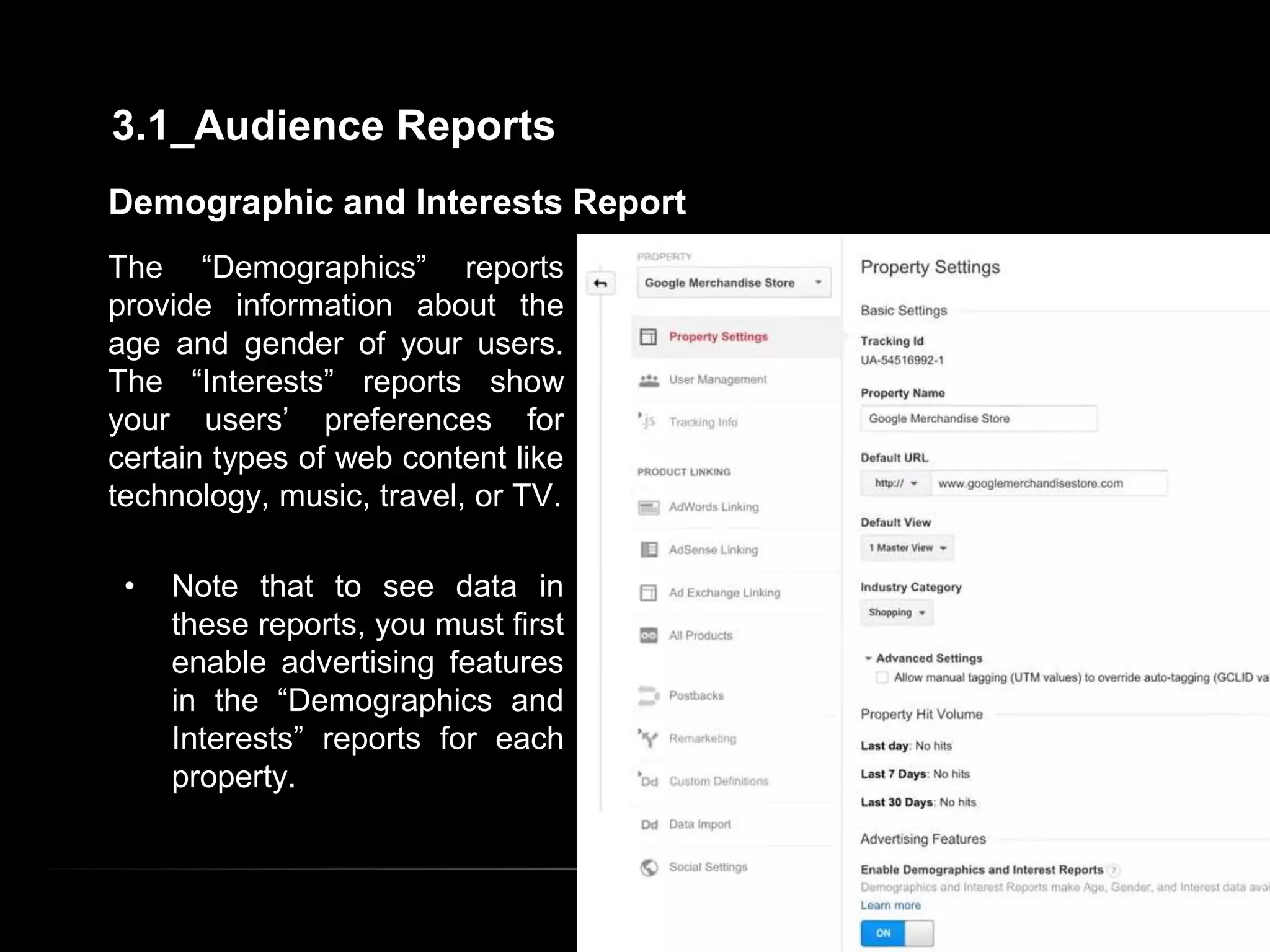
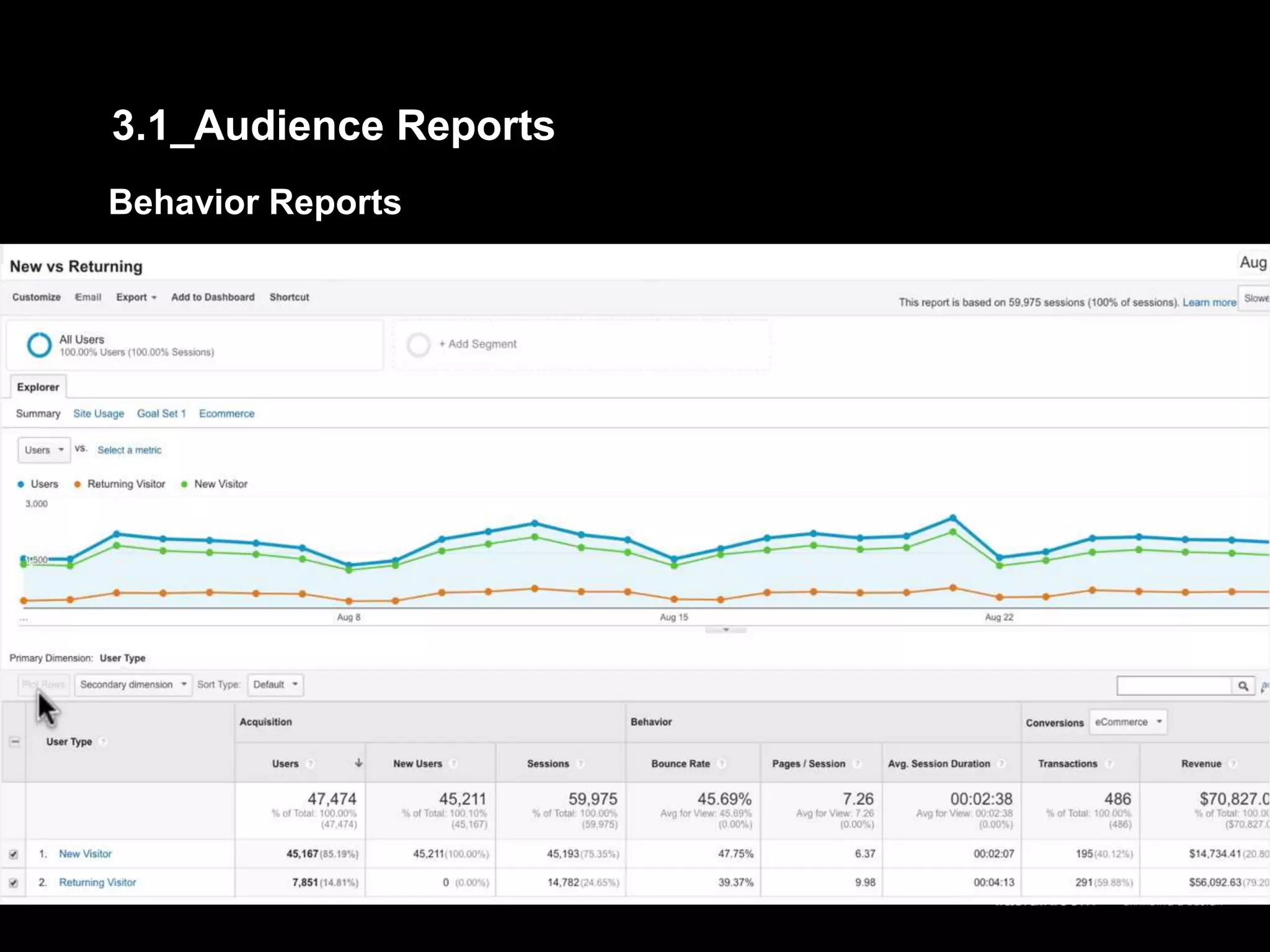
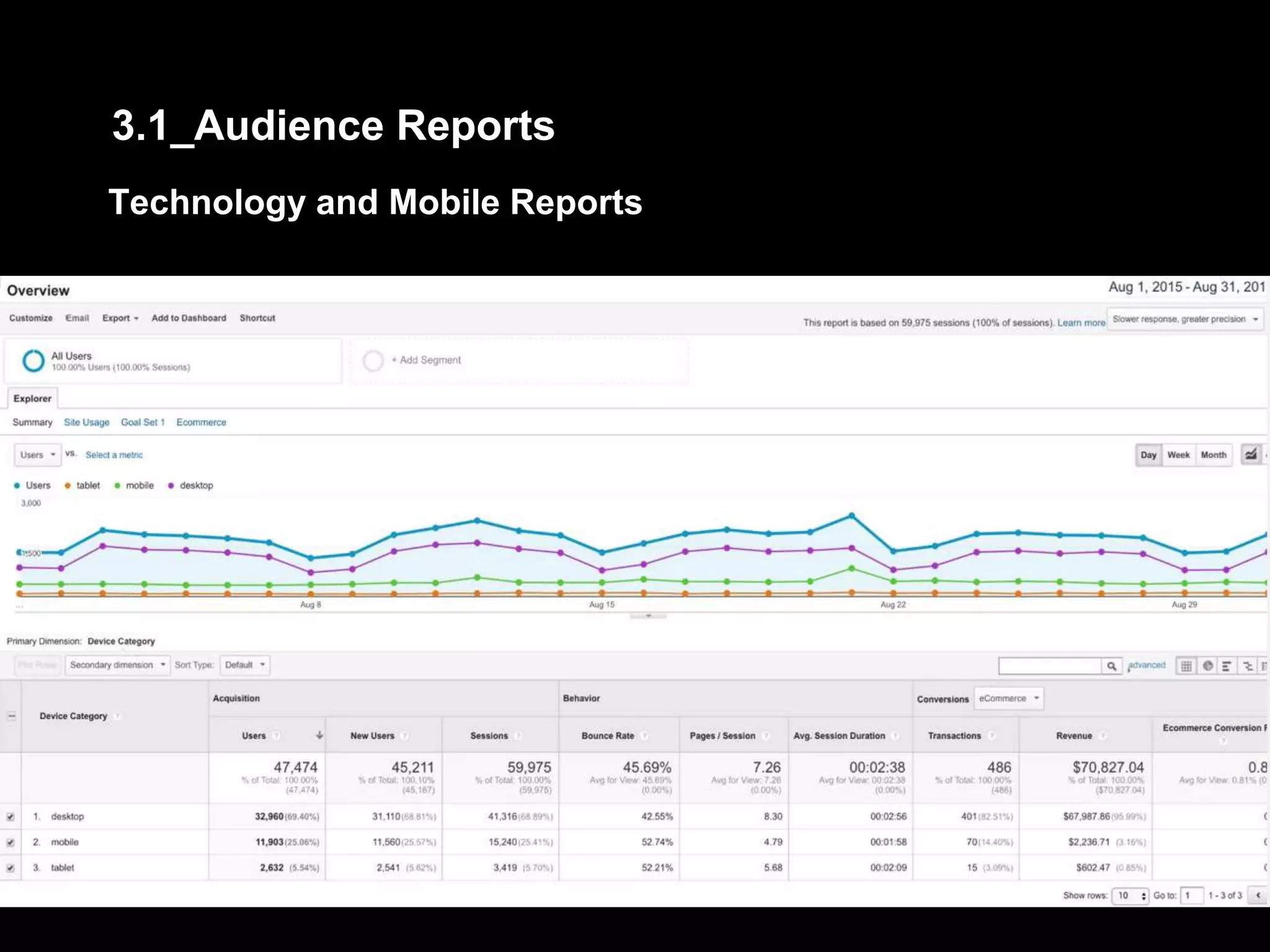
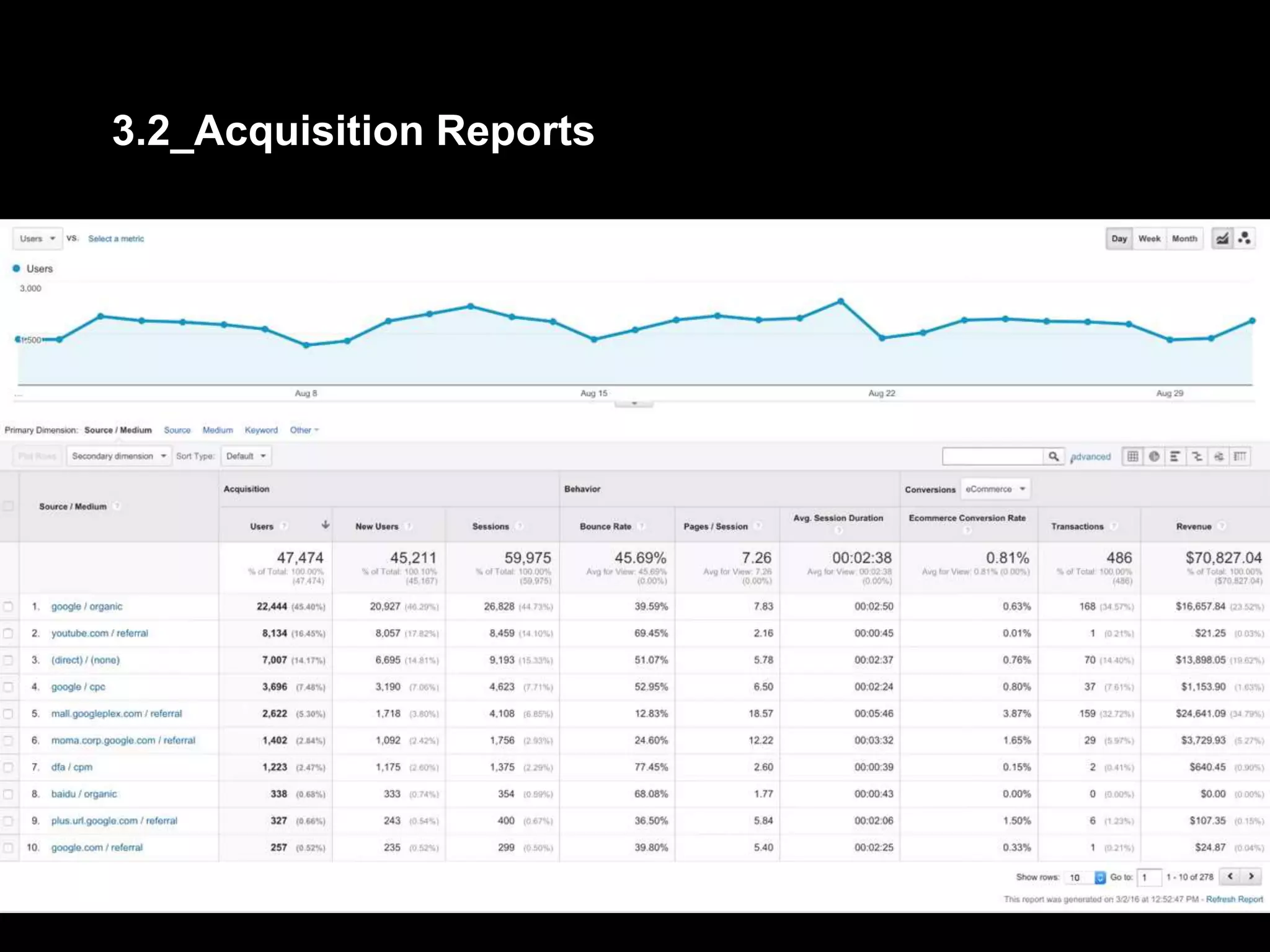
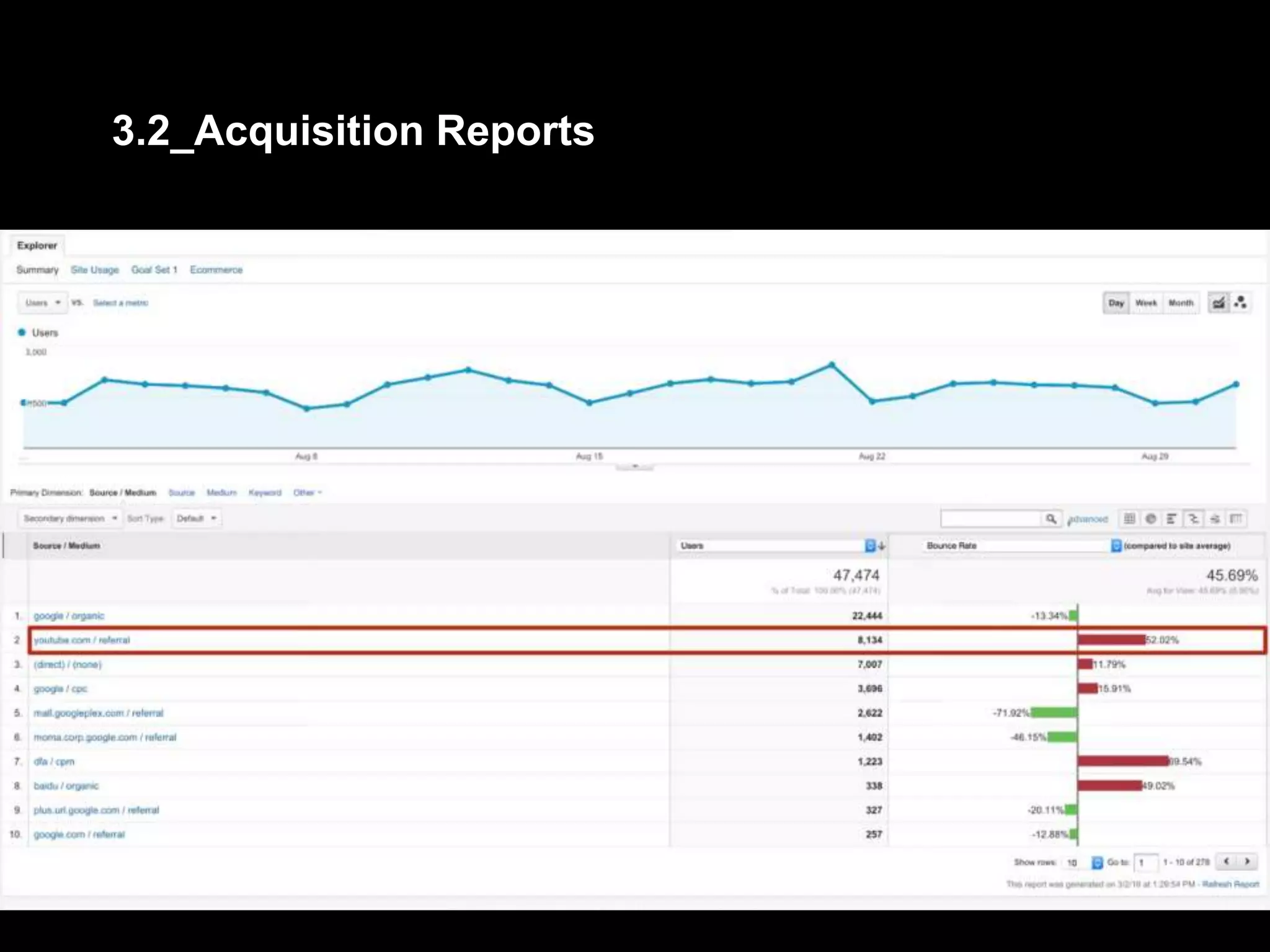
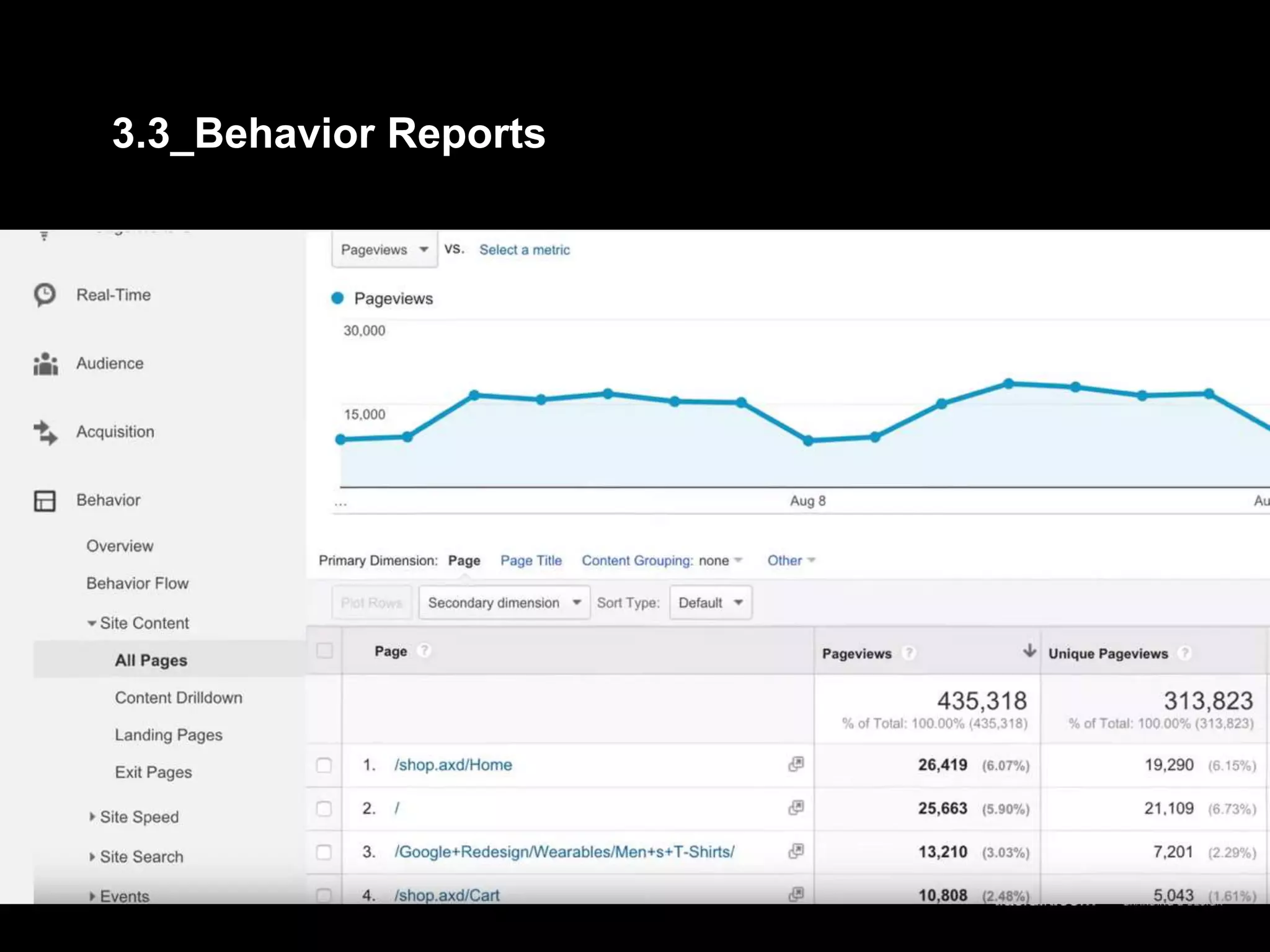
2. Basic reports in Google Analytics like audience, acquisition, and behavior reports are explained. The acquisition reports can show which marketing channels bring in users and the behavior reports show how users engage on the site.
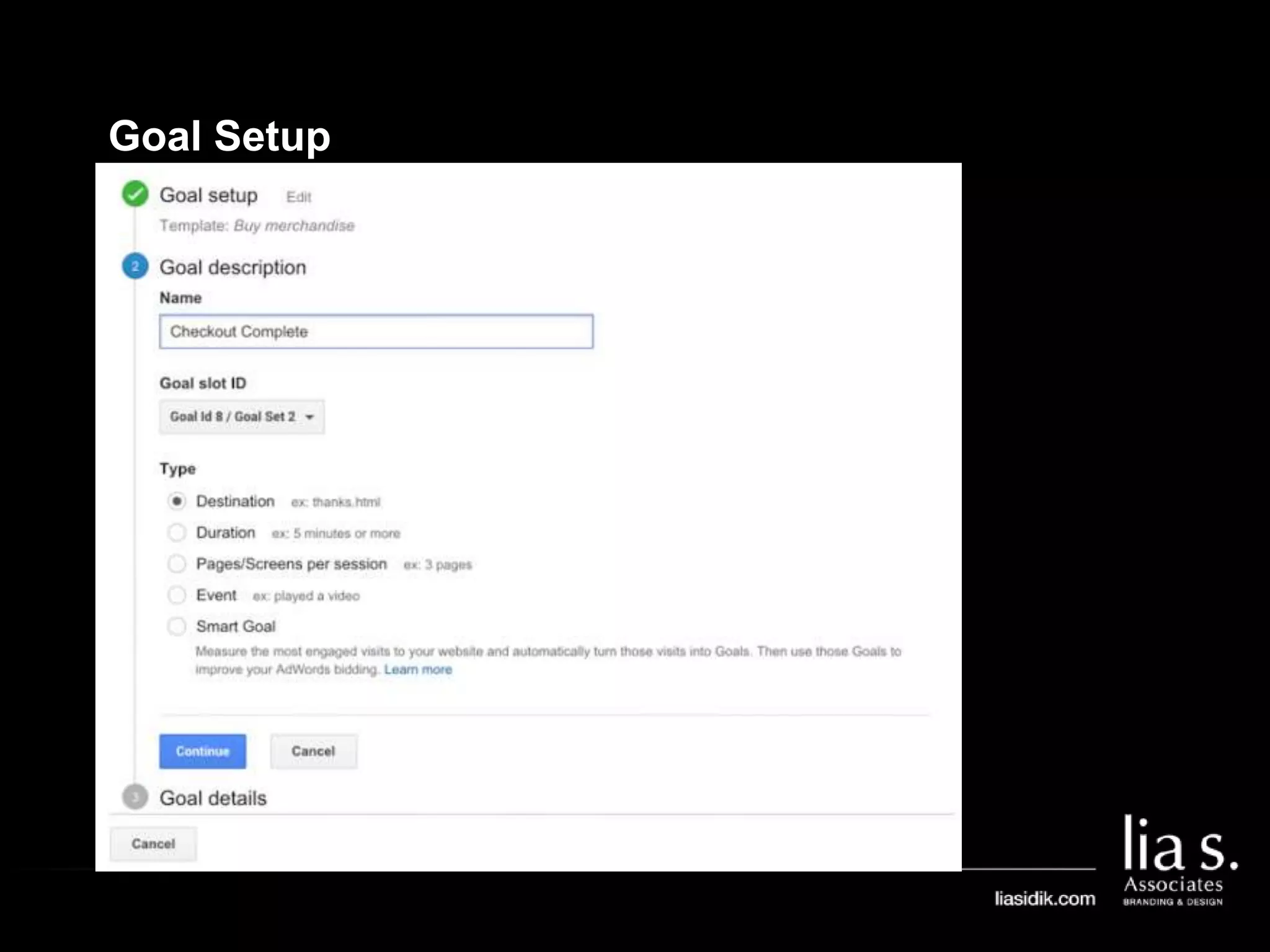
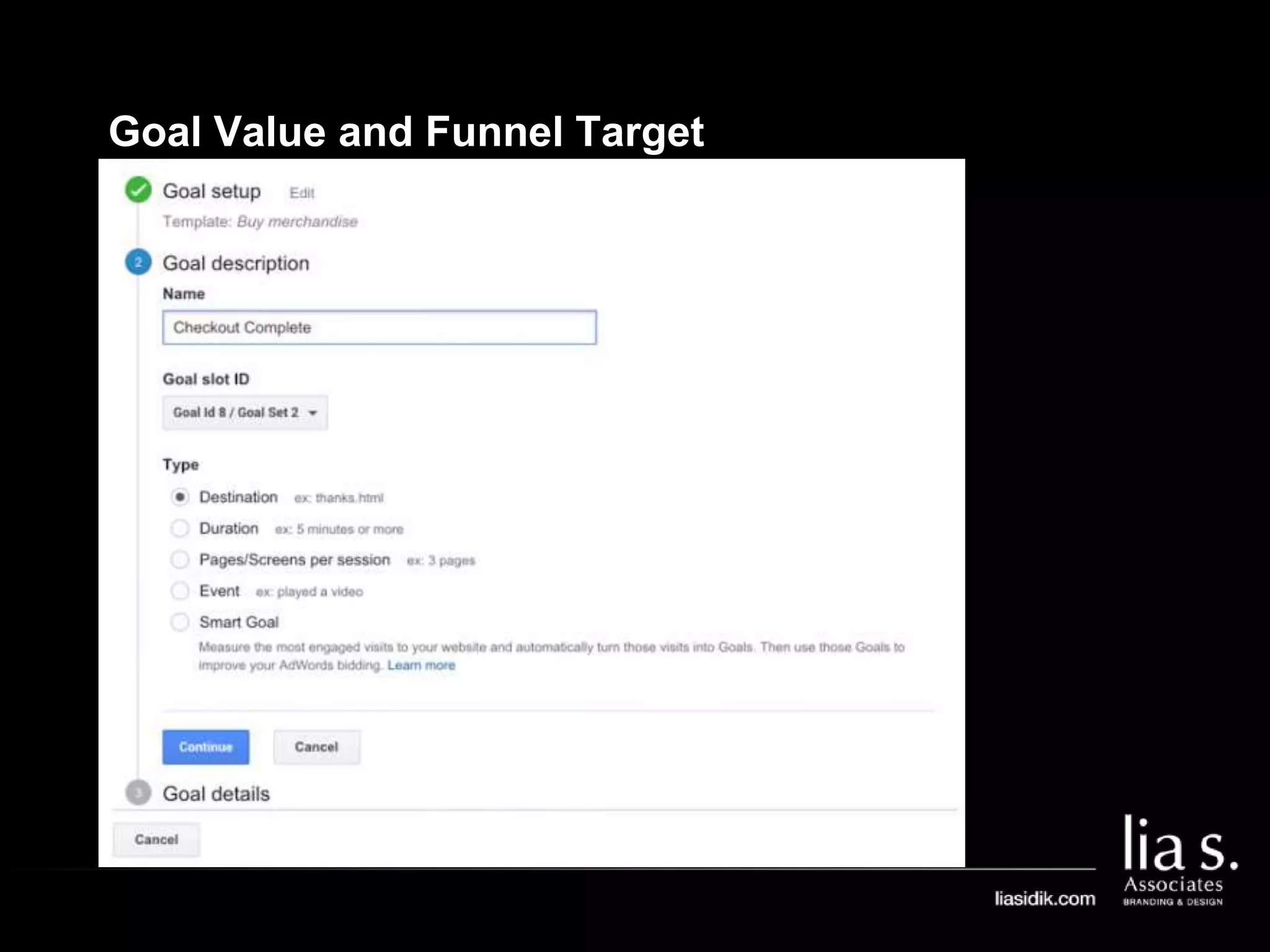
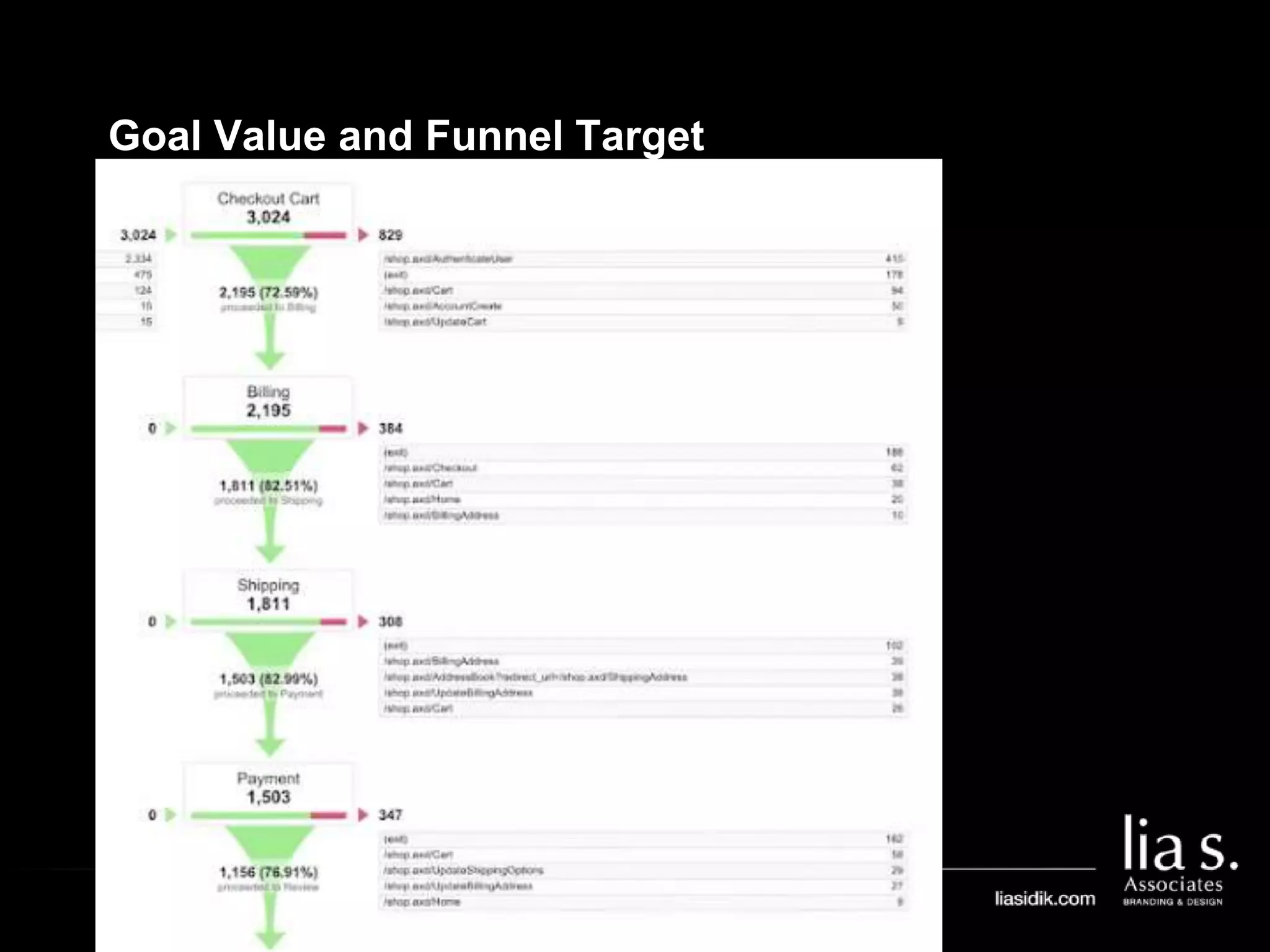
3. Goals in Google Analytics are used to track conversions. Configuring goals allows analytics to generate conversion metrics like the number of conversions and conversion rate.