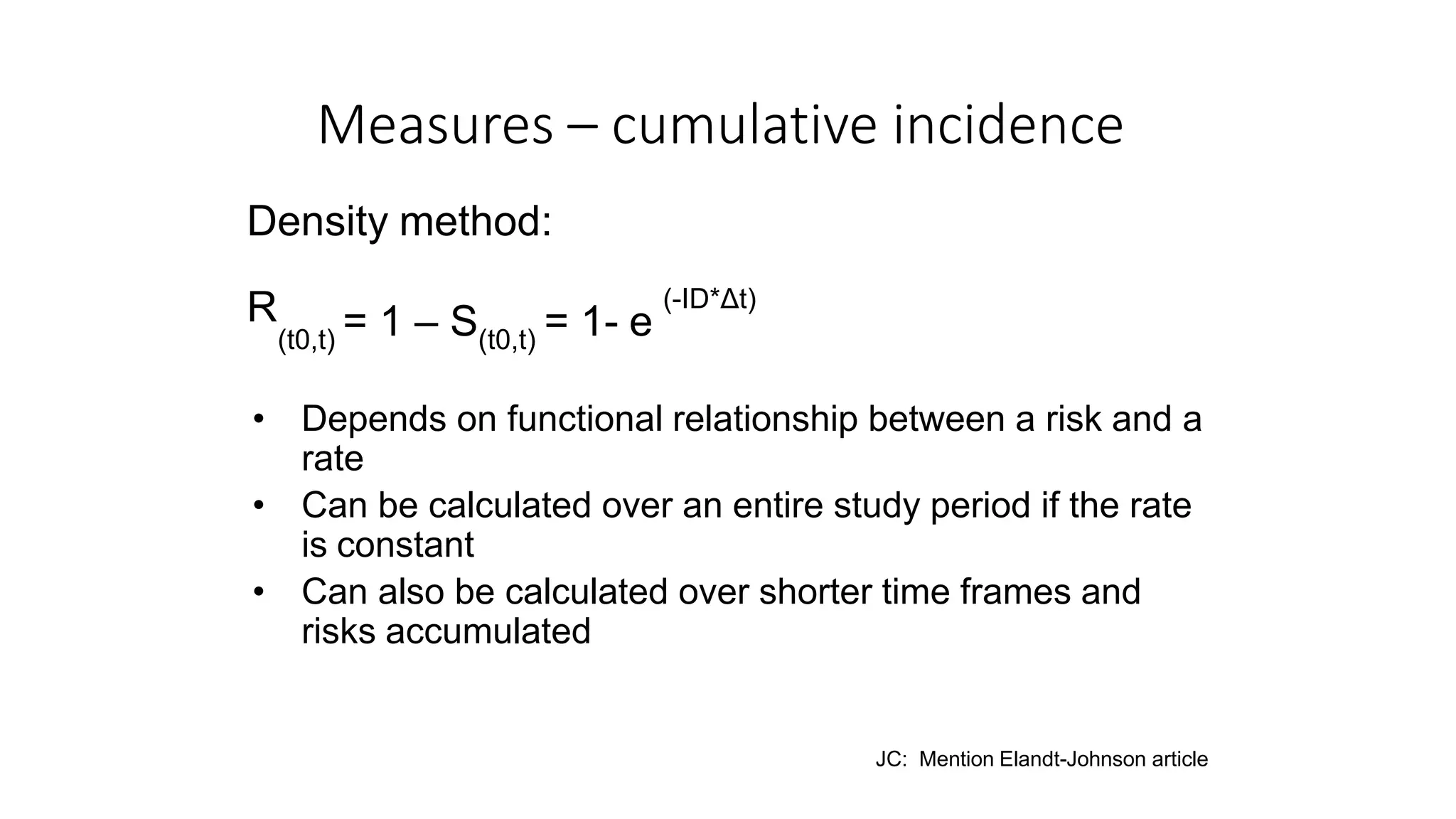
This document discusses different methods for calculating cumulative incidence (CI) when studying disease occurrence over time, including simple CI, actuarial CI, Kaplan-Meier CI, and density CI. It provides details on the notation, formulas, and steps used for each method. The key differences between the methods relate to whether and how they account for withdrawals/censoring over time. The appropriate method depends on the type of data available and study time frame.