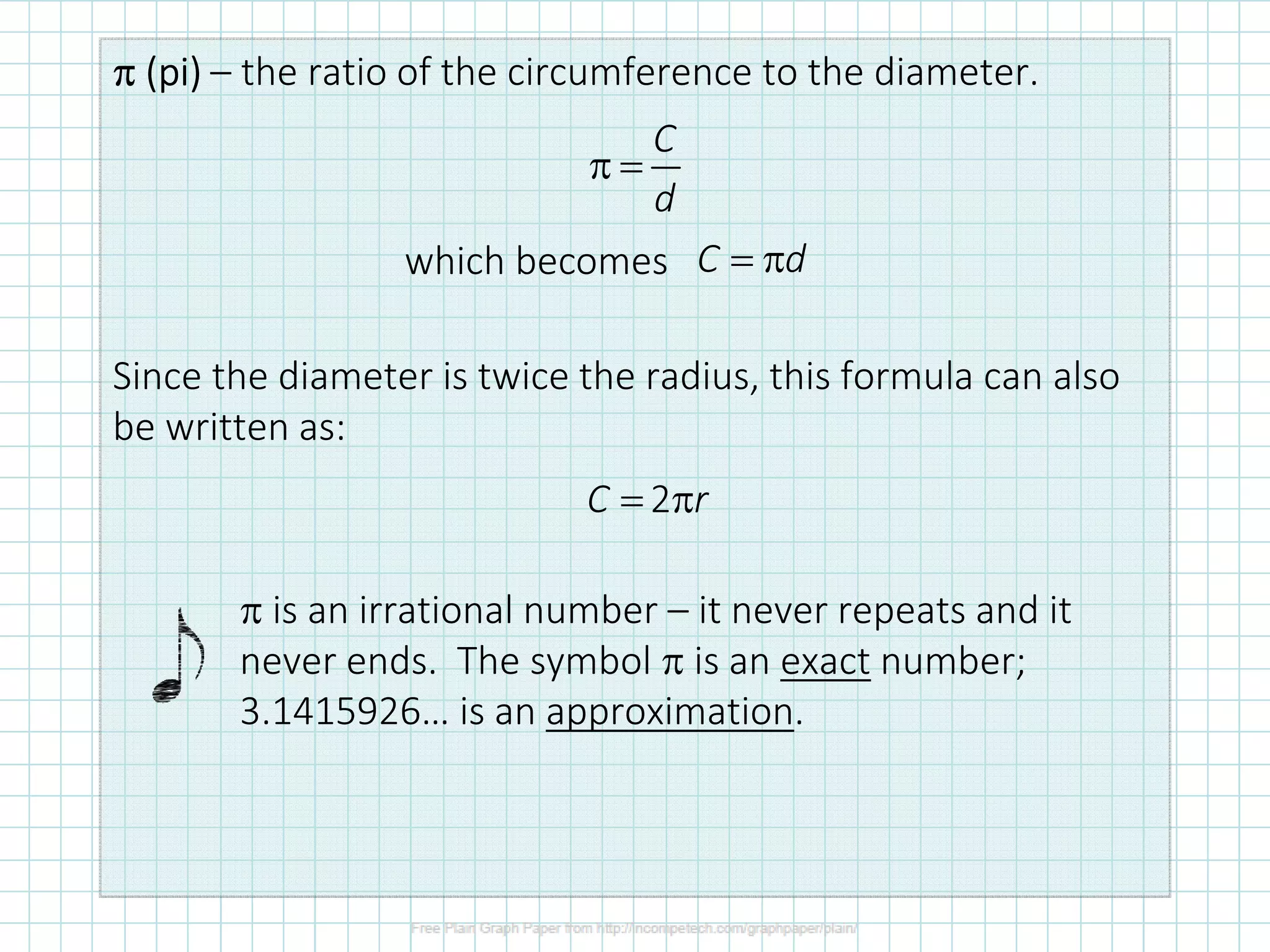
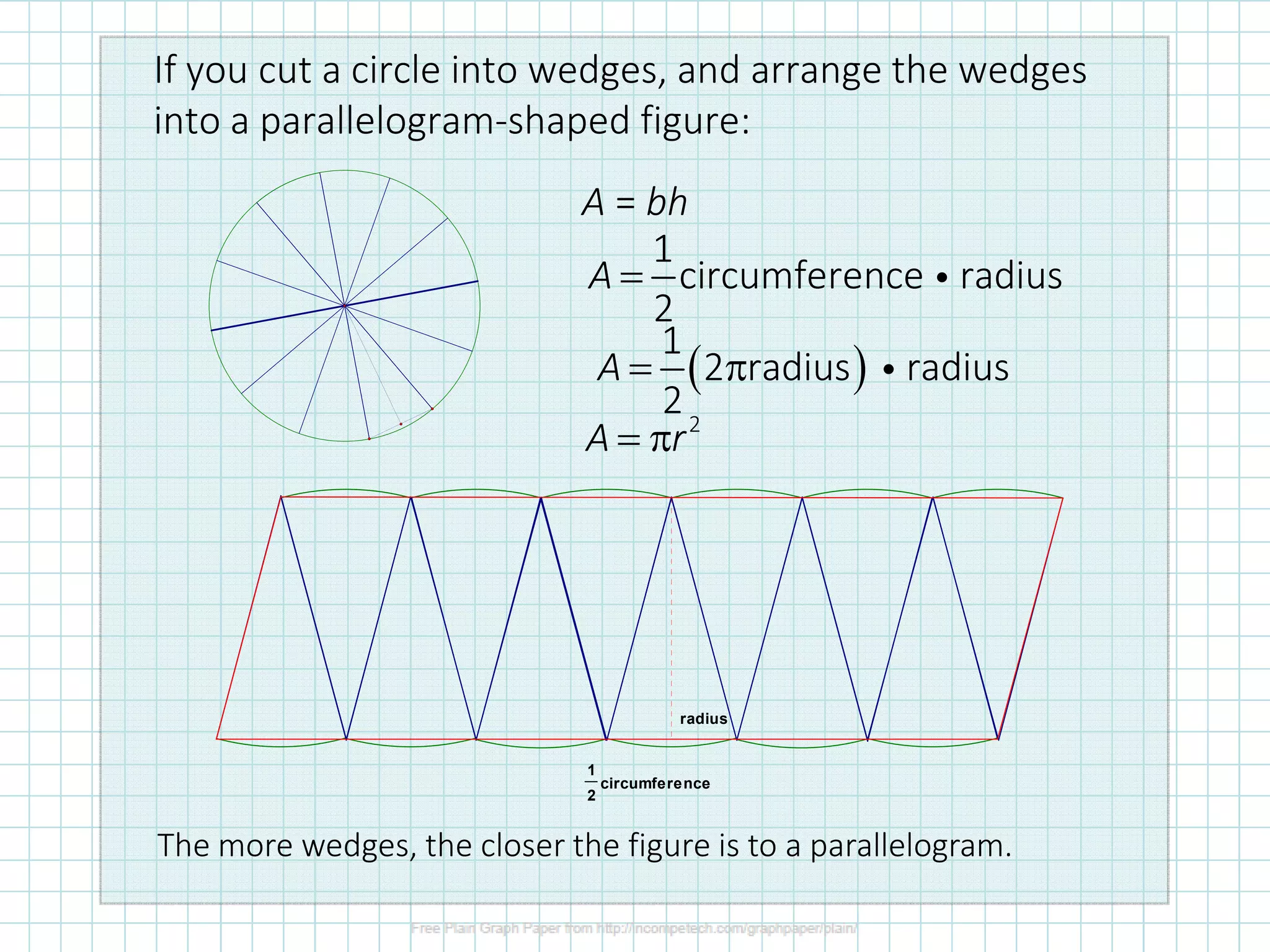
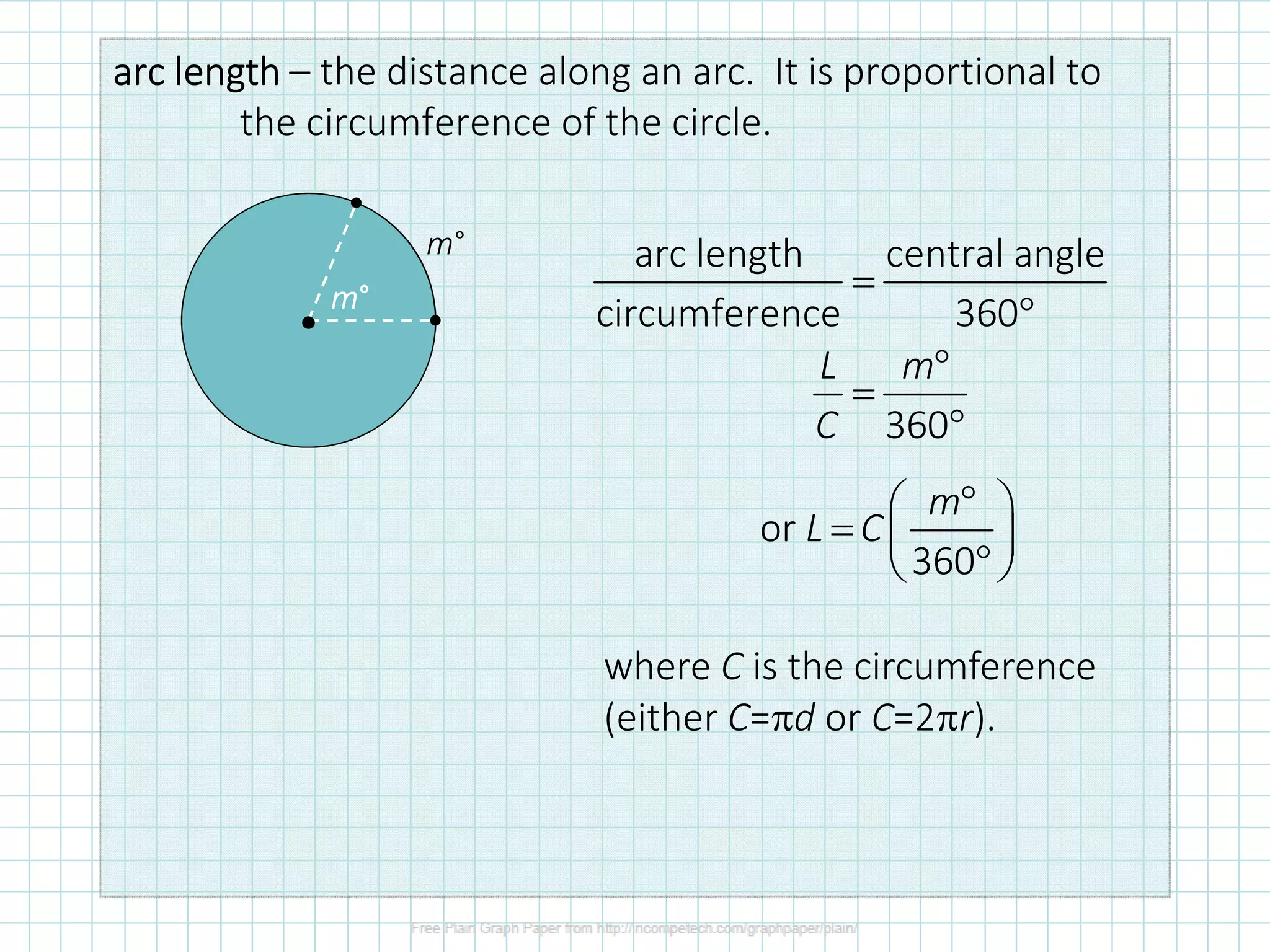
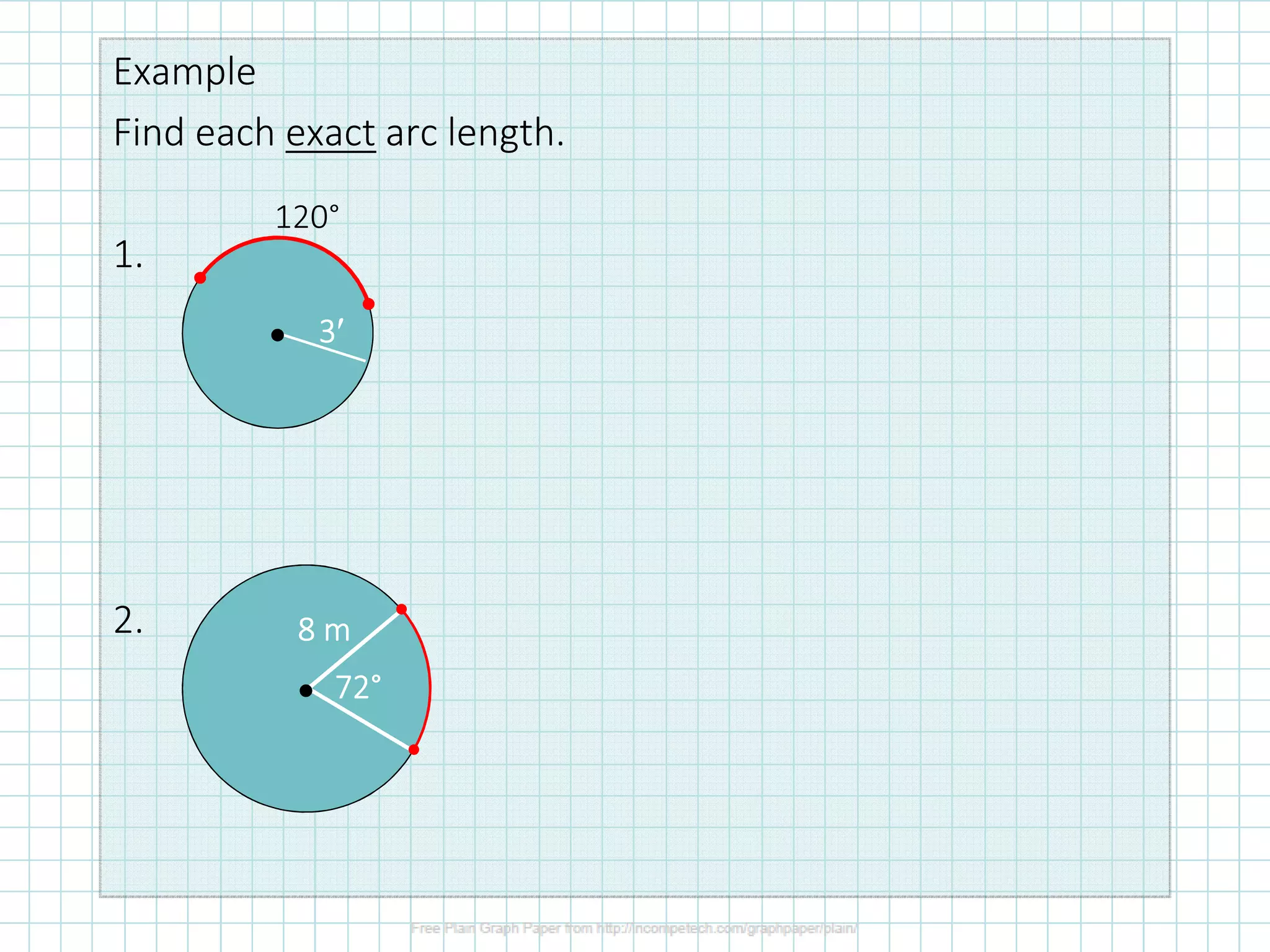
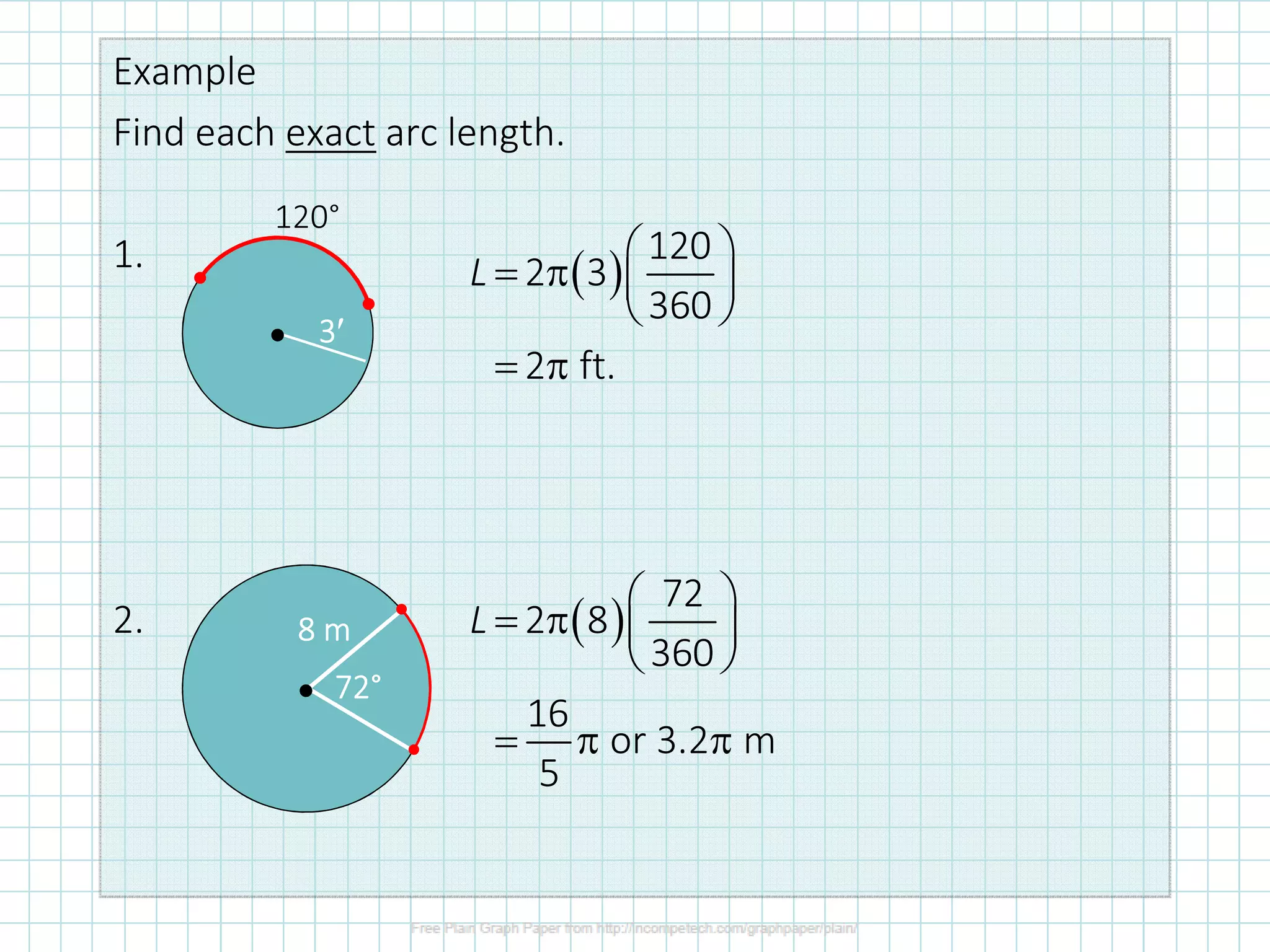
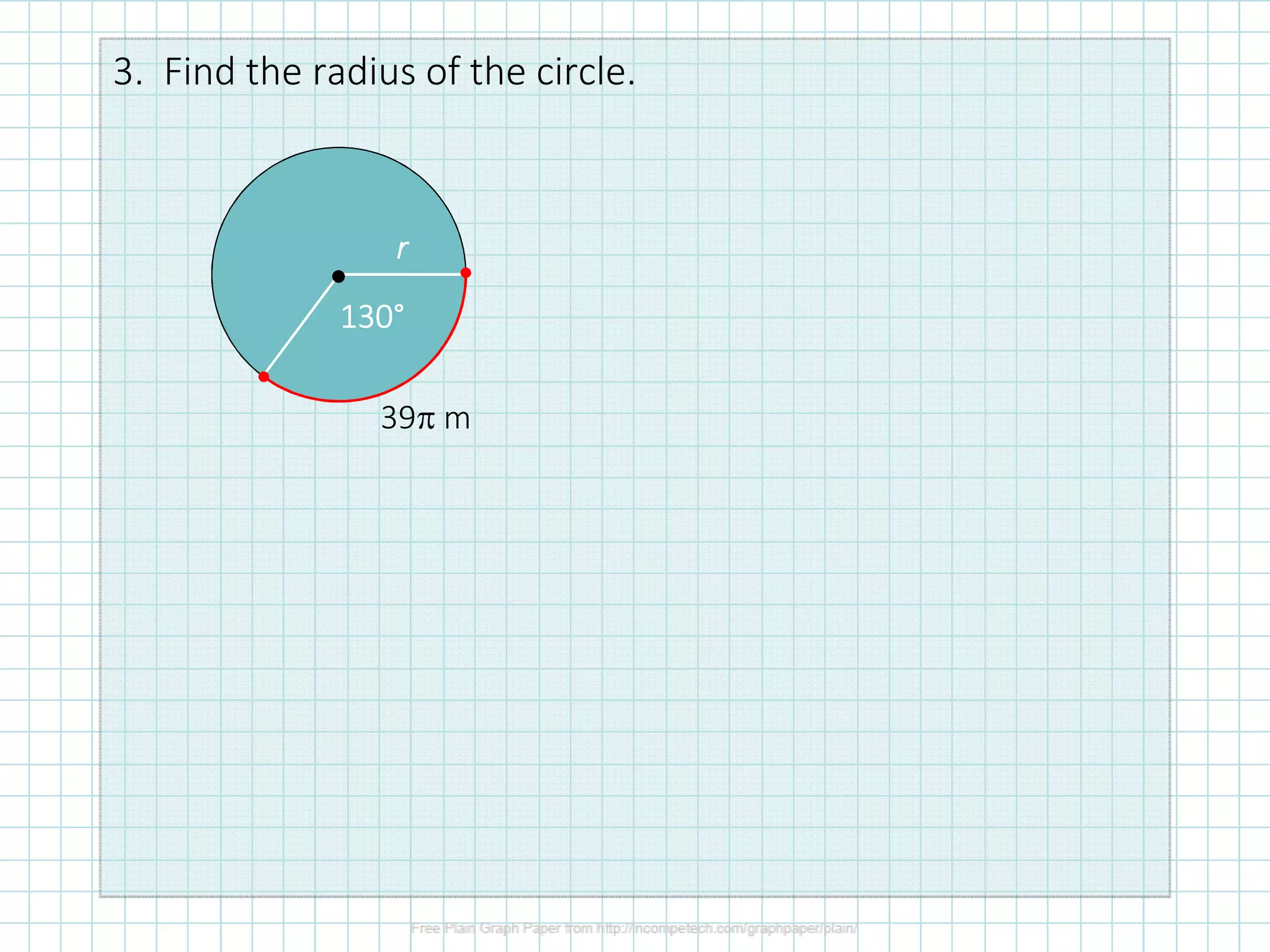
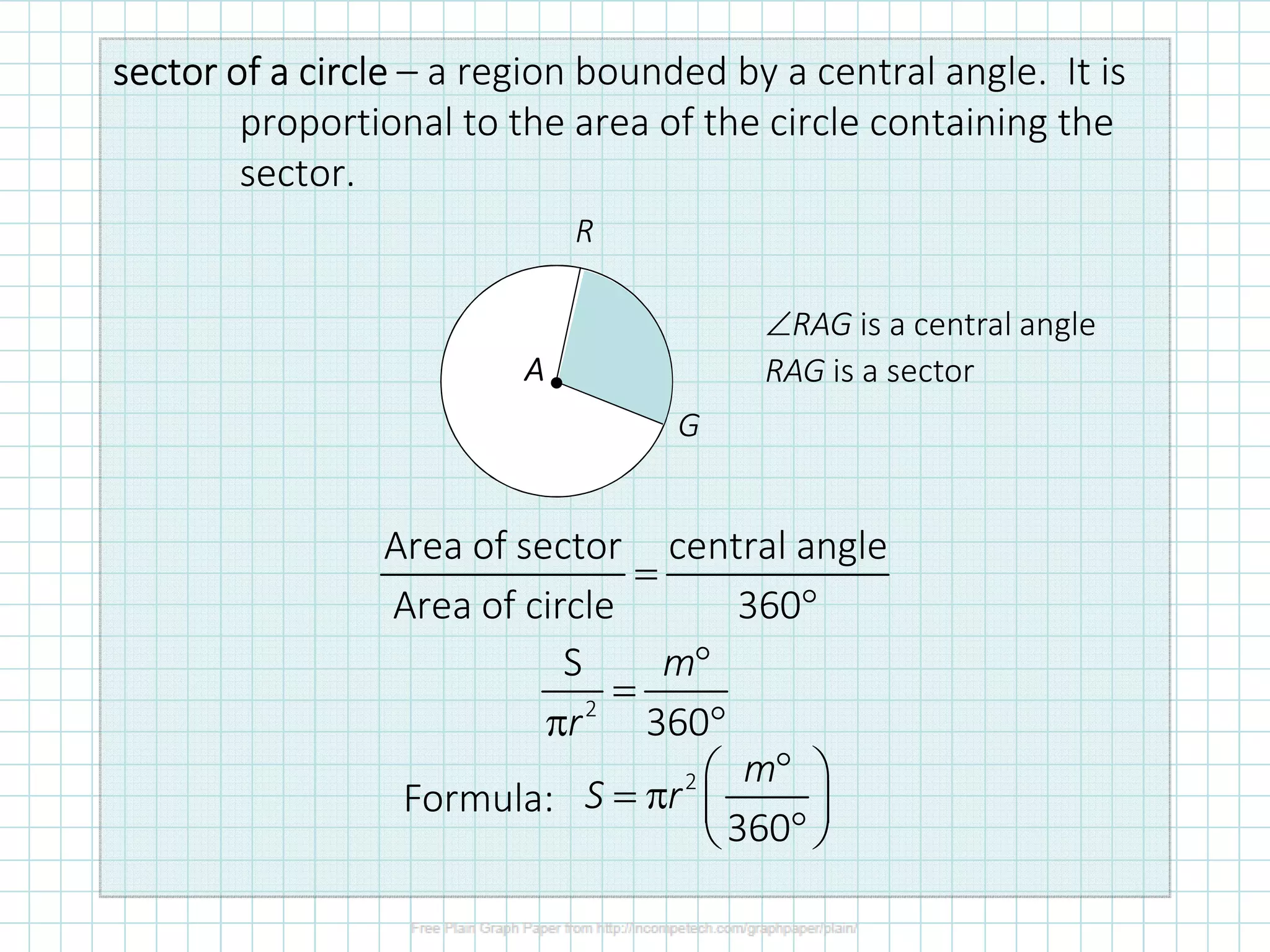
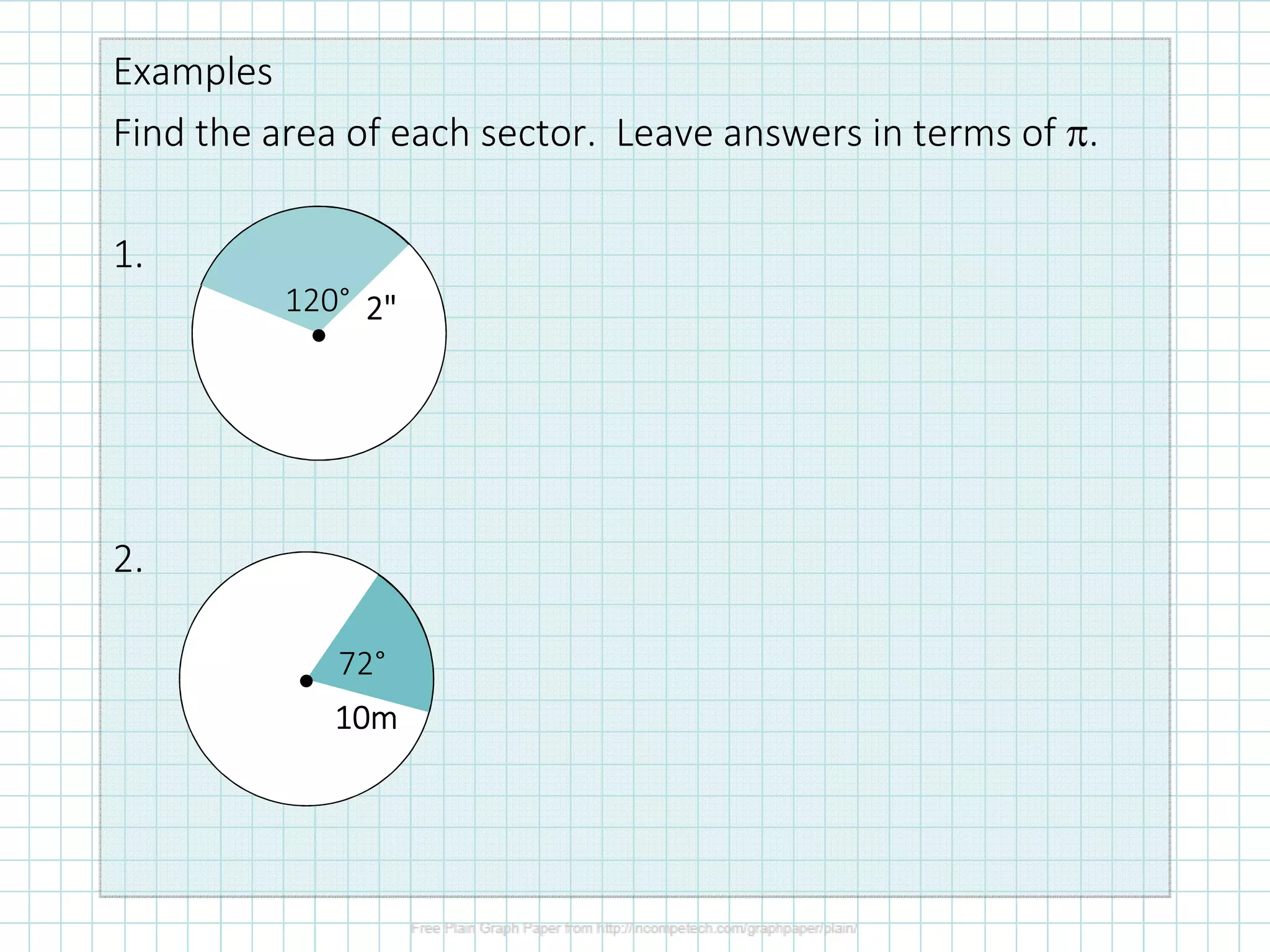
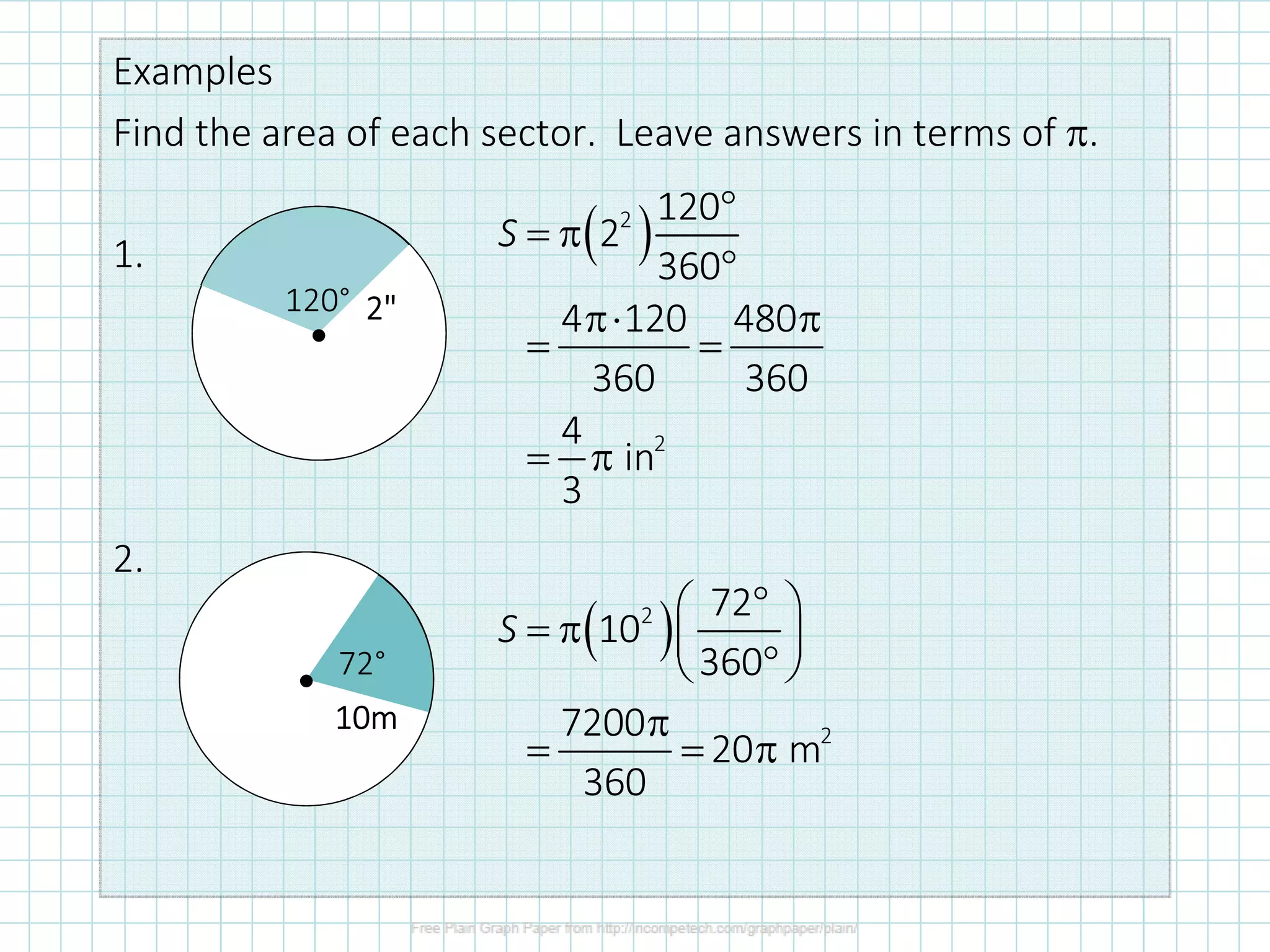
The document discusses formulas for calculating properties of circles such as circumference, area, arc length, and sector area. It defines pi (π) and shows formulas for calculating the circumference and area of a circle using its diameter or radius. Examples are provided for calculating the circumference, diameter, area, radius, arc length, and sector area of various circles.