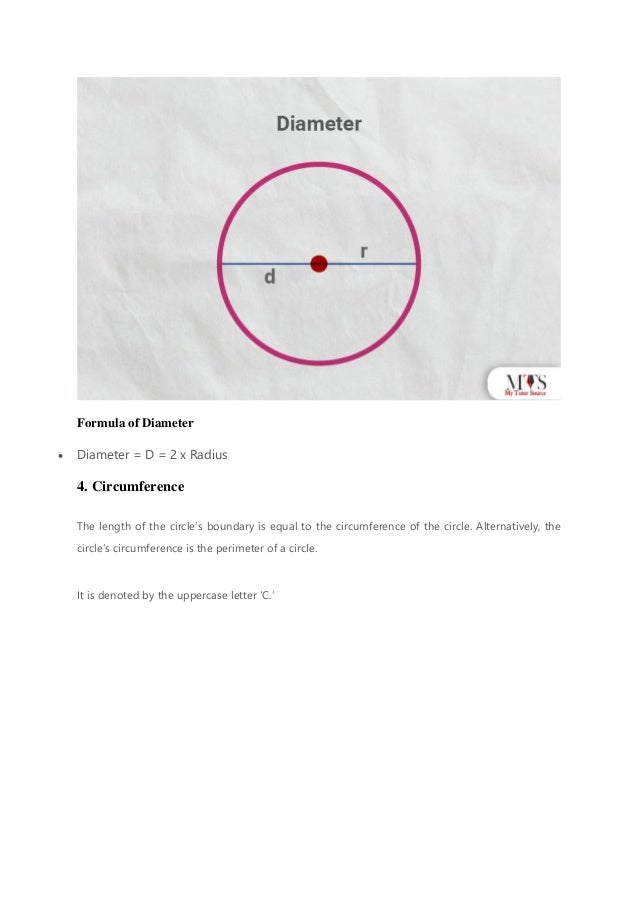
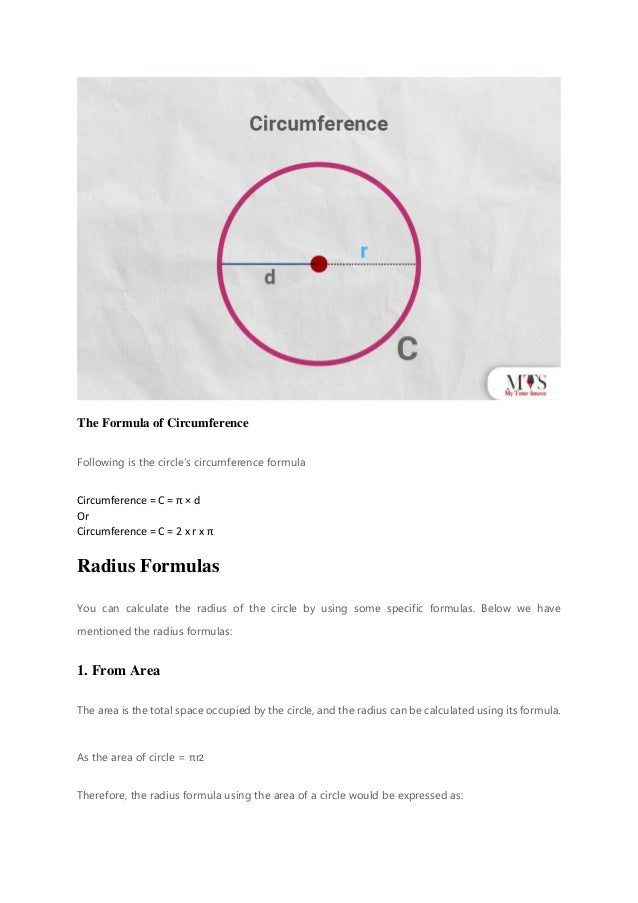
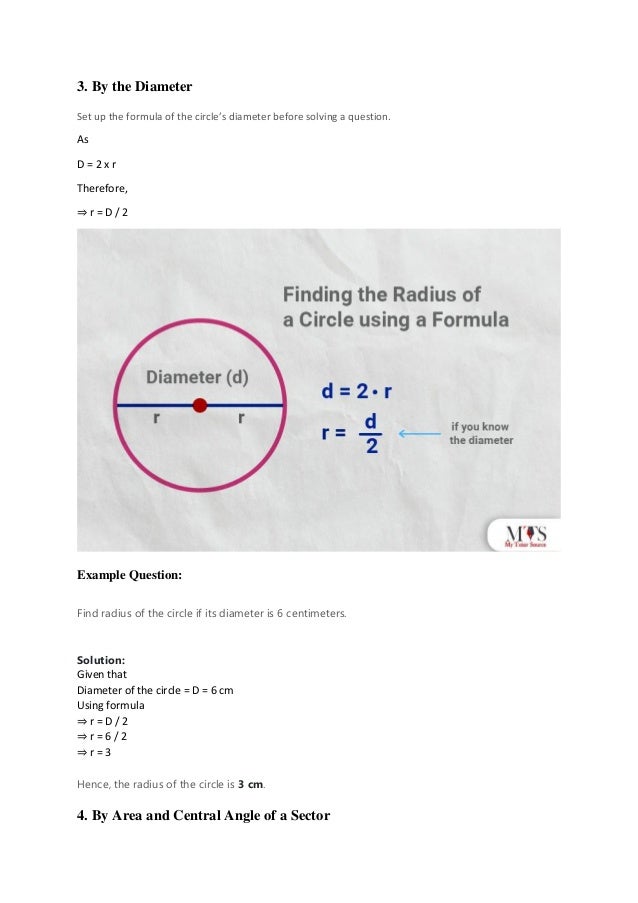
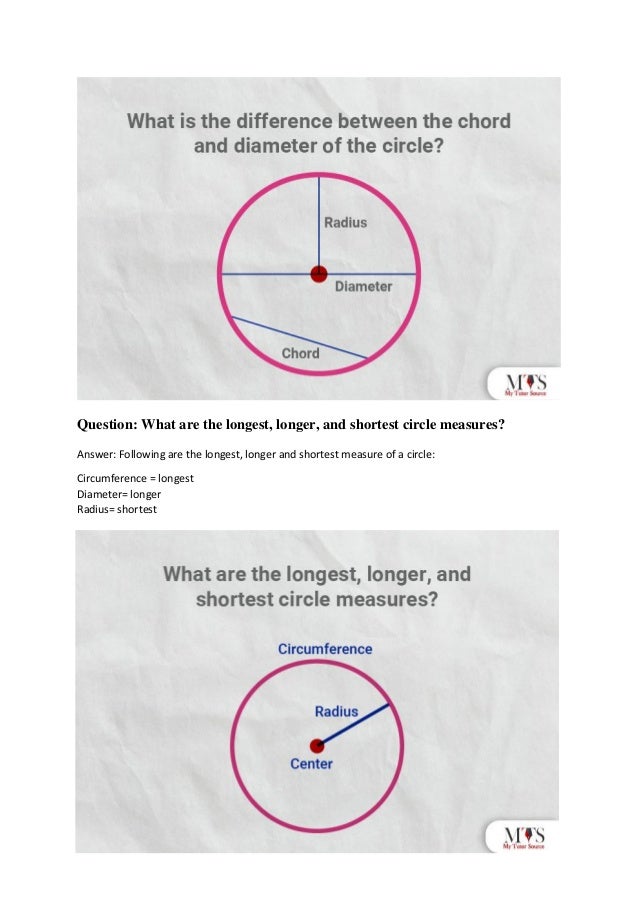
The document provides an overview of the radius of a circle, defining it as a line segment from the center to the outer edge, and outlines various methods for calculating it using area, diameter, and circumference. Key formulas include radius = diameter / 2, area = πr², and circumference = 2πr. Practical examples and frequently asked questions illustrate the concepts and applications of these measurements in geometry.