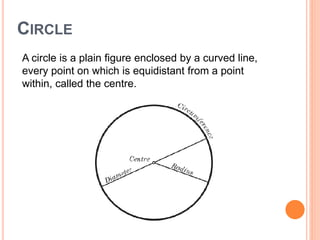
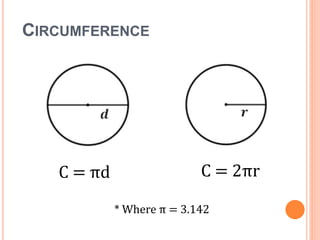
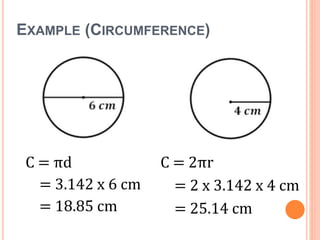
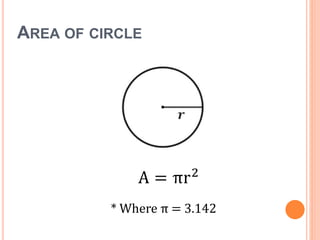
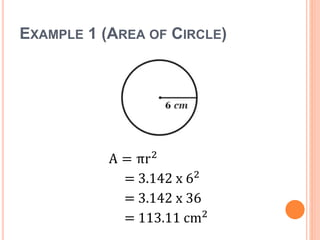
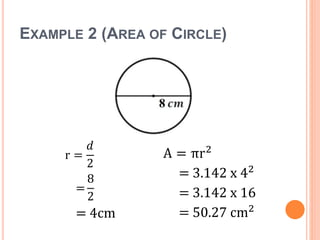
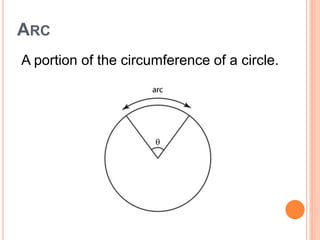
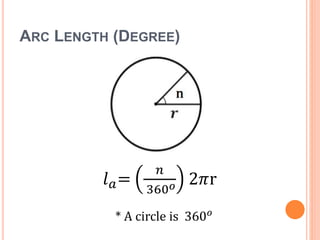
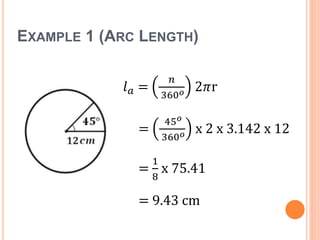
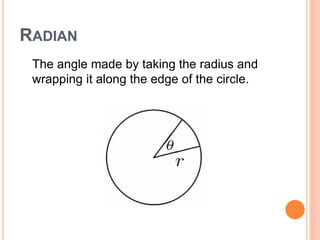
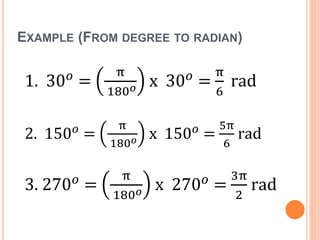
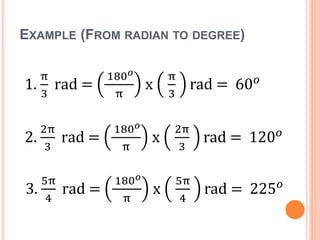
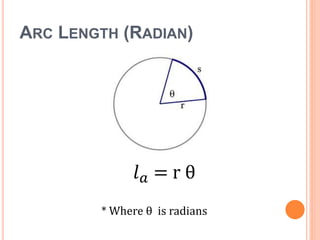
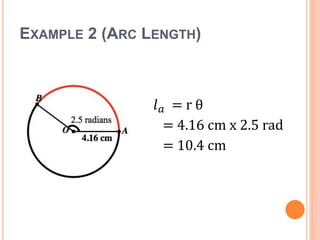
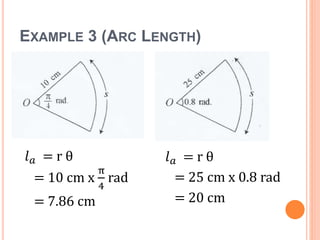
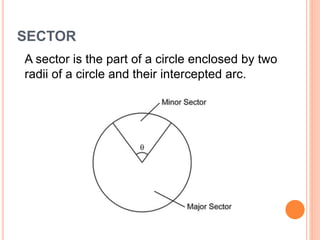
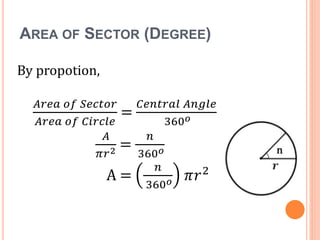
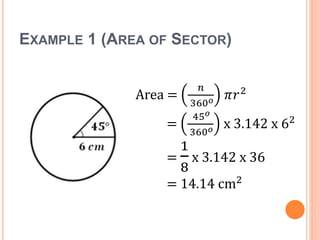
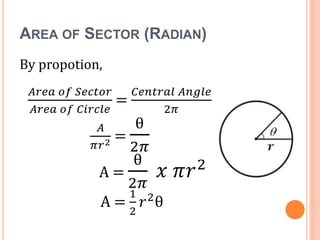
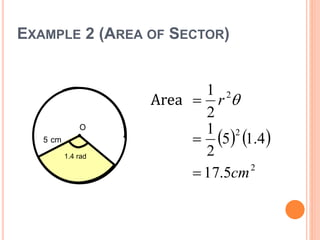
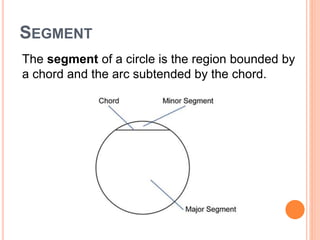
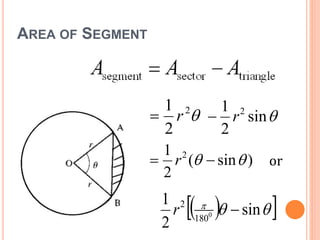
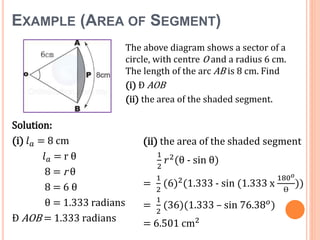
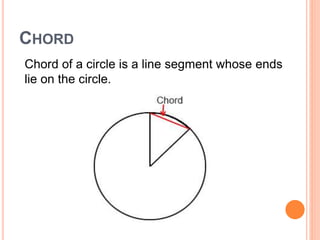
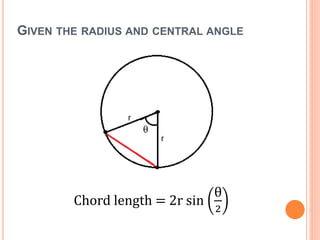
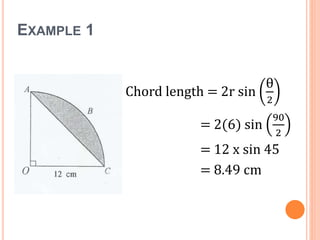
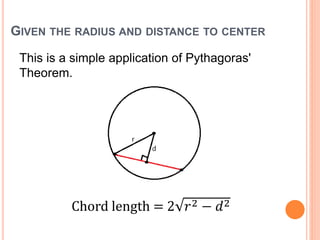
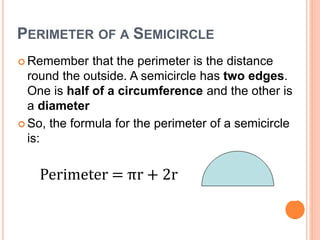
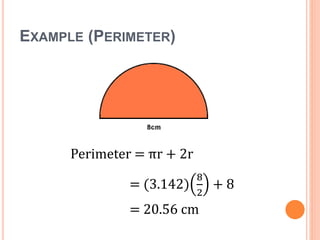
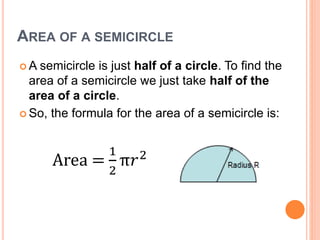
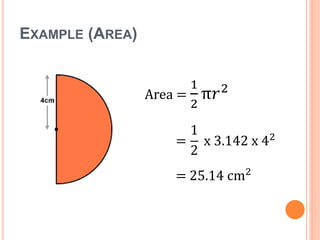
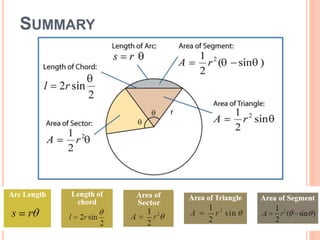
This document defines key terms and formulas related to circles, including circumference, diameter, radius, area, arcs, sectors, segments, chords, and semicircles. It provides formulas for calculating the circumference, area, arc length, area of sectors and segments, chord length, perimeter and area of semicircles. Examples are included to demonstrate how to apply the formulas to solve geometry problems involving circles.