10319264.ppt
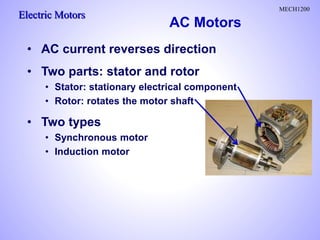
- 1. Electric Motors MECH1200 • AC current reverses direction • Two parts: stator and rotor • Stator: stationary electrical component • Rotor: rotates the motor shaft • Two types • Synchronous motor • Induction motor AC Motors
- 5. Electric Motors MECH1200 • Most common motors in industry • Advantages: • Simple design • Inexpensive • High power to weight ratio • Easy to maintain • Direct connection to AC power source AC – Induction motor
- 6. Electric Motors MECH1200 AC – Induction motor How induction motors work • Electricity supplied to stator • Magnetic field generated that moves around rotor • Current induced in rotor Electromagnetics Stator Rotor • Rotor produces second magnetic field that opposes stator magnetic field • Rotor begins to rotate
- 7. Electric Motors MECH1200 • Single-phase induction motor • One stator winding • Single-phase power supply • Squirrel cage rotor • Require device to start motor • Up to 3 to 4 HP • Household appliances: fans, washing machines, dryers AC – Induction motor
- 8. Electric Motors MECH1200 Shaded-pole motor • The shaded pole delays the creation of the magnetic field in that portion of the stator poles. • This produces a magnetic field in the shaded portion that is approximately 90° apart from the magnetic field produced in the main portion of the pole. • Considered a nonreversible motor.
- 9. Electric Motors MECH1200 Split-phase motor • Start winding – Many turns of heavy-gauge wire • Centrifugal switch opens after start-up removing the start winding from the circuit. • Reverse direction of rotation by interchanging run winding or start winding connections (preferred).
- 10. Electric Motors MECH1200 Three Types of Capacitor Start Motors 1. Capacitor Start (disconnects capacitor after motor speed picks up) 2. Capacitor Run (Keeps the capacitor connected during the operation of the motor, in order to keep the electric power consumption low) 3. Capacitor Start-Run (uses two capacitors, one for starting and one for running. This further improves Power Consumption)
- 11. Electric Motors MECH1200 Capacitor-start motor • Start circuit has: – Centrifugal switch – Start winding – Start capacitor • This produces higher starting torque. • Run winding • Reverse direction of rotation by interchanging run winding or start winding connections (preferred).
- 12. Electric Motors MECH1200 Capacitor-run motor • The capacitor shifts the phase on one of the windings so that the voltage across the winding is at 90° from the other winding • Run capacitor produces higher running torque. • Start winding stays as part of the circuit • Run winding • Reverse direction of rotation by interchanging run winding or start winding connections (preferred).
- 13. Electric Motors MECH1200 Capacitor-start/capacitor-run motor • Start circuit: – Start winding – Centrifugal switch – Start capacitor • Larger value produces higher starting torque. • Run winding • Run capacitor – Smaller value produces higher running torque. • Reverse direction of rotation by interchanging run winding or start winding connections (preferred).
- 14. Electric Motors MECH1200 Capacitor start-run reverse connections
- 15. Electric Motors MECH1200 •Winding(s) which produce the magnetic field(s) necessary to cause the rotor to turn. 3 Phase; 2 Pole Motor What are Poles in a Motor?
- 16. Electric Motors MECH1200 • Requires DC voltage for starting excitation • Has low starting torque • Suited for low load applications • Rotor of the synchronous motor travels at the same speed as the rotating magnetic field AC - Synchronous motor
- 17. Electric Motors MECH1200 Synchronous motor Three-Phase Motors • Parts – Rotor with single winding – Slip rings and brushes – Three-phase stator windings
- 18. Electric Motors MECH1200 • Constant speed fixed by system frequency • Used where there is a need to improve the power factor • Synchronous speed (Ns): AC - Synchronous motor F = frequency of the voltage source supplied P = number of poles P F NS * 120 5252 * ) ( ) ( ) ( RPM lbs ft Speed Torque HP Power
- 19. Electric Motors MECH1200 Synchronous speed P 50 Hz 60 Hz 2 3000 3600 4 1500 1800 6 1000 1200 8 750 900 10 600 720 12 500 600
- 20. Electric Motors MECH1200 4-Pole stator winding • Each AC phase has 4 stator windings • Each winding is in opposite direction from preceding winding, making a N-S-N-S field • Field strength rotates with AC current of each phase
- 21. Electric Motors MECH1200 • Three-phase induction motor • Three-phase supply produces magnetic field • Squirrel cage or wound rotor • Self-starting • High power capabilities • Fractional to 100’s of HP • Applications: pumps, compressors, conveyor belts, grinders • 70% of motors in industry! AC – Induction motor
- 22. Electric Motors MECH1200 • Aka: Asynchronous motor • The induction ac motor is a common form of an asynchronous motor • Is basically an AC transformer with a rotating secondary AC – Induction motor
- 23. Electric Motors MECH1200 Components • Rotor •Squirrel cage: conducting bars in parallel slots •Wound rotor: 3- phase, double-layer, distributed winding AC – Induction motor • Stator • Stampings with slots to carry 3-phase windings • Wound for definite number of poles
- 24. Electric Motors MECH1200 3-phase Induction Motor Operation • Arrows shows stator magnetic field vector • Stator field precedes the rotor’s induction field http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:3phase-rmf-noadd-60f- airopt.gif
- 25. Electric Motors MECH1200 • Interchange any two of the three stator leads. – The industry standard is to switch T1 and T3 . • The wound-rotor induction motor is considered to be a variable-speed motor. • Initial cost is higher and maintenance costs are higher than for a squirrel-cage induction motor. Reversing Direction of a 3 Phase Motor
- 26. Electric Motors MECH1200 Reversing Direction of a 3 Phase Motor A B C
- 27. Electric Motors MECH1200 Changing AC Motor Speed • Voltage – Hertz Ratio: – Operating motor in a range different from rated frequency and voltage affects both torque and current . Hertz Voltage Ratio Hz V AC
- 28. Electric Motors MECH1200 Changing AC Motor Speed • Voltage – Hertz Ratio: – Maintaining the ratio gives a constant torque range Hertz Voltage Ratio Hz V AC For a synchronous motor rated for 3 phase, 460 volts, 60 Hz and 3600 rpm, what will be the operating frequency and voltage if the motor controller commands the motor to run at 2750 rpm? 60 460 Ratio Hz V 7.67 P f NS * 120 3600 60 * 120 P 2 poles P f NS * 120 2750 * 120 2 2750rpm at f 45.83 Hz 83 . 45 67 . 7 V 351.52 volts
- 29. Electric Motors MECH1200 Squirrel-cage induction motor • Parts: – Rotor – Stator • The squirrel-cage induction motor is considered to be a fixed- speed motor.
- 30. Electric Motors MECH1200 Speed and slip • Motor never runs at synchronous speed but lower actual rotor speed • Difference is “slip” • Install slip ring to avoid this • Calculate % slip: Ns = synchronous speed in RPM NR = rotor speed in RPM AC – Induction motor 100 * % S R S N N N Slip
- 31. Electric Motors MECH1200 Wound-rotor induction motor • The rotor contains windings. • Slip rings and brushes provide an electrical connection to the rotor windings. • The wound-rotor induction motor is considered to be a variable-speed motor. • Initial cost is higher and maintenance costs are higher than for a squirrel- cage induction motor.
- 32. Electric Motors MECH1200 Relationship: load, speed and torque Starting Torque (aka LRT): high torque and low speed “Pull-up” torque: lower torque and increasing speed “Breakdown” torque: 75% speed and highest torque = 178.6 ft-#’S Full load torque: motor operates at rated voltage, frequency and load and stator current are zero 30 HP 1765 RPM
- 33. Electric Motors MECH1200 Torque Curve Calculate: Speed at 100% full load current % Slip 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 98 100 % Full Load Current % Synchorous Speed Torque Curve For Asychronous Induction Motor with a synchronous speed of 1800 RPM
- 34. Electric Motors MECH1200 AC Motor Data Plate
- 35. Electric Motors MECH1200 Types of Motor Enclosures • ODP – Open Drip Proof – Air flows through motor (fan blades help flow) – Used in environments free from contaminants
- 36. Electric Motors MECH1200 Types of Motor Enclosures • TENV – Totally Enclosed Non-Ventilating – Protect motor from corrosive and harmful elements – Frame fins help to dissipate heat
- 37. Electric Motors MECH1200 Types of Motor Enclosures • TEFC – Totally enclosed Fan Cooled – Similar to TENV except has external fan for cooling
- 38. Electric Motors MECH1200 Types of Motor Enclosures • XP – Explosion Proof – Similar to TEFC but enclosures are cast iron
- 39. Electric Motors MECH1200 Hazardous Locations Division I – Hazardous material present in the air as a norm Division II - Hazardous material present in the air as an abnormal event
- 40. Electric Motors MECH1200 Summary • DC motors are: – permanent magnet – series-wound, – shunt-wound, – compound-wound • AC single phase motors are: – the shaded-pole, – split-phase, – capacitor-start, – capacitor-run, – capacitor-start/ capacitor-run
- 41. Electric Motors MECH1200 Questions • Name two motors that do not need brushes for their rotor windings. • Which motor supplies the highest output torque to weight ratio? • Why is it not recommended to use dc motors in artificial hearts? • In an environment that contains explosive gases, such as in mines, which motor do you recommend using: a) series dc motor b) shunt dc motor c) induction motor d) universal motor
Editor's Notes
- Alternating current (AC) motors use an electrical current, which reverses its direction at regular intervals. An AC motor has two basic electrical parts: a "stator" and a "rotor". The stator is in the stationary electrical component. The rotor is the rotating electrical component, which in turn rotates the motor shaft. The main advantage of DC motors over AC motors is that speed is more difficult to control for AC motors. To compensate for this, AC motors can be equipped with variable frequency drives but the improved speed control comes together with a reduced power quality. There are two types of AC motors: synchronous (see figure) and induction. The main difference between the synchronous motor and the induction motor is that the rotor of the synchronous motor travels at the same speed as the rotating magnetic field.
- Alternating current (AC) motors use an electrical current, which reverses its direction at regular intervals. An AC motor has two basic electrical parts: a "stator" and a "rotor". The stator is in the stationary electrical component. The rotor is the rotating electrical component, which in turn rotates the motor shaft. The main advantage of DC motors over AC motors is that speed is more difficult to control for AC motors. To compensate for this, AC motors can be equipped with variable frequency drives but the improved speed control comes together with a reduced power quality. There are two types of AC motors: synchronous (see figure) and induction. The main difference between the synchronous motor and the induction motor is that the rotor of the synchronous motor travels at the same speed as the rotating magnetic field.
- Induction motors are the most common motors used for various equipments in industry. Their popularity is due to their simple design, they are inexpensive (half or less of the cost of a DC motor) High power to weight ratio (about twice that of a DC motor) easy to maintain can be directly connected to an AC power source
- Induction motors work as follows: Electricity is supplied to the stator, which generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field moves at synchronous speed around the rotor, which in turn induces a current in the rotor. The rotor current produces a second magnetic field, which tries to oppose the stator magnetic field, and this causes the rotor to rotate.
- Induction motors can be classified into two main groups: single-phase and three-phase induction motors Single-phase induction motors. These only have one stator winding, operate with a single-phase power supply, have a squirrel cage rotor, and require a device to get the motor started. This is by far the most common type of motor used in household appliances, such as fans, washing machines and clothes dryers, and for applications for up to 3 to 4 horsepower.
- A synchronous motor is an AC motor, which runs at constant speed fixed by frequency of the system. It requires direct current (DC) for excitation and has low starting torque, and synchronous motors are therefore suited for applications that start with a low load, such as air compressors, frequency changes and motor generators. Synchronous motors are able to improve the power factor of a system, which is why they are often used in systems that use a lot of electricity. This motor rotates at a synchronous speed, which is given by the following equation Ns = 120 f / P Where: f = frequency of the supply frequency P= number of poles
- A synchronous motor is an AC motor, which runs at constant speed fixed by frequency of the system. It requires direct current (DC) for excitation and has low starting torque, and synchronous motors are therefore suited for applications that start with a low load, such as air compressors, frequency changes and motor generators. Synchronous motors are able to improve the power factor of a system, which is why they are often used in systems that use a lot of electricity. This motor rotates at a synchronous speed, which is given by the following equation Ns = 120 f / P Where: f = frequency of the supply frequency P= number of poles
- Arrow in stator depicts magnetic field of windings according to the left hand rule. X is out of plane; dot is into plane.
- Induction motors can be classified into two main groups: Single-phase induction motors. These only have one stator winding, operate with a single-phase power supply, have a squirrel cage rotor, and require a device to get the motor started. This is by far the most common type of motor used in household appliances, such as fans, washing machines and clothes dryers, and for applications for up to 3 to 4 horsepower. Three-phase induction motors. The rotating magnetic field is produced by the balanced three-phase supply. These motors have high power capabilities, can have squirrel cage or wound rotors (although 90% have a squirrel cage rotor), and are self-starting. It is estimated that about 70% of motors in industry are of this type, are used in, for example, pumps, compressors, conveyor belts, heavy-duty electrical networks, and grinders. They are available in 1/3 to hundreds of horsepower ratings.
- An induction motor has two main electrical components as shown in the figure Rotor. Induction motors use two types of rotors: A squirrel-cage rotor consists of thick conducting bars embedded in parallel slots. These bars are short-circuited at both ends by means of short-circuiting rings. A wound rotor has a three-phase, double-layer, distributed winding. It is wound for as many poles as the stator. The three phases are wired internally and the other ends are connected to slip-rings mounted on a shaft with brushes resting on them. Stator. The stator is made up of a number of stampings with slots to carry three-phase windings. It is wound for a definite number of poles. The windings are geometrically spaced 120 degrees apart
- From wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:3phase-rmf-noadd-60f-airopt.gif WARNING Animation shows flaws when GIF is resized. The reason for this behavior is unclear, but it is common both to Mozilla and Konqueror on Linux. Any advice welcome (mtodorov3_69@yahoo.com). Note: IE 7.0 does not seem to share this deficiency. (The error seems to affect Chrome on Windows XP too) Model of 3 phase synchronous electric motor with animated vector adding of stator coil magnetic fields. Stator phases R, S and T have sine current shifted by 120 degrees between each. Magnetic field is proportional to current in linear approximation. Magnetic field vectors of the phases add up on the axis of the motor as vectors, combining into single rotating vector according to parallelogram law, which is clearly visible. Rotor has a constant current and hence constant magnetic field, which shows the inclination to follow rotating magnetic field of the stator coils, causing rotor to rotate. This particular image shows phase vectors change in time, the other one sums them using parallelogram theorem.
- In practice however, the motor never runs at synchronous speed but at a lower “base speed”. The difference between these two speeds is the “slip”, which increases with higher loads. Slip only occurs in all induction motors. To avoid slip, a slip ring can be installed, and these motors are called “slip ring motors”. The following equation can be used to calculate the percentage slip % Slip = Ns – Nb x 100 Ns Where: Ns = synchronous speed in RPM Nb = base speed in RPM
- The figure shows the typical torque-speed curve of a three-phase AC induction motor with a fixed current. When the motor: (Click once) Starts there is a high starting current and low torque (“pull-up torque”). (Click once) Reaches 80% of the full speed, the torque is at its highest level (“pull-out torque”) and the current begins to drop. (Click once) Is at full speed, or synchronous speed, the torque and stator current drop to zero.
- More questions: How does the rotor of a dc motor maintain electrical contact with its commutation circuit? Name two motors that do not need brushes for their rotor windings.