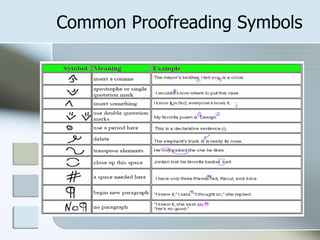
Proofreading is the final step of the editing process to identify and correct external errors such as spelling mistakes, grammar errors, and punctuation issues. The document outlines various proofreading tools like dictionaries and style sheets, techniques such as reading aloud and one word at a time, common symbols used in proofreading, and tips to double check for typical errors and formatting issues that spellcheck may miss. Proofreaders are advised to use standard marks and abbreviations to clearly communicate needed changes to the writer.