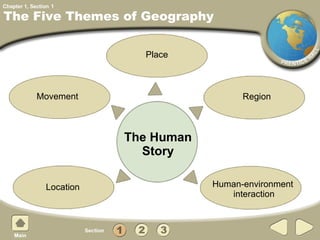
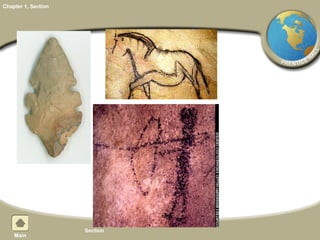
The document provides an overview of world history from prehistory to 3000 BC. It discusses how geography is linked to history and how anthropologists and archaeologists study early peoples. It describes advances made in the Old Stone Age and the religious beliefs of early humans. It explains how the Neolithic Agricultural Revolution led to permanent settlements and civilization near rivers. Key features that distinguish civilizations are also outlined, and how cultures spread and changed over time through interactions.