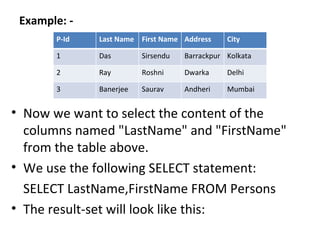
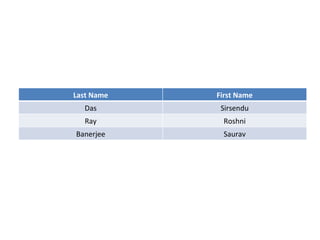
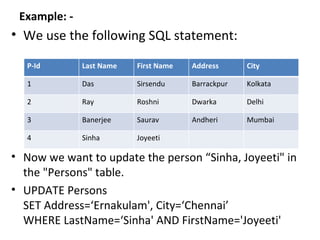
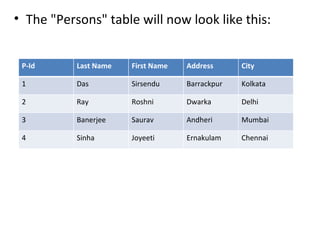
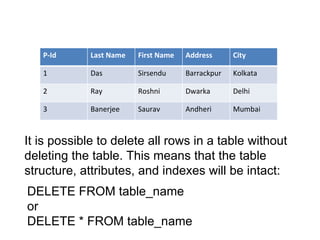
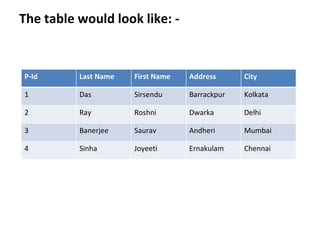
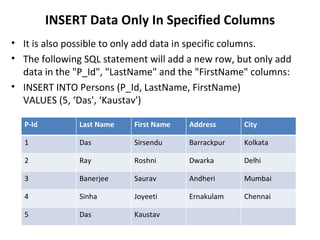
This document provides an overview of SQL (Structured Query Language) including what it is, what it can do, and some key SQL statements. SQL is a standard language for accessing and manipulating databases and allows users to retrieve, insert, update, and delete data. The document describes common statements like SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT and provides examples of basic usage.