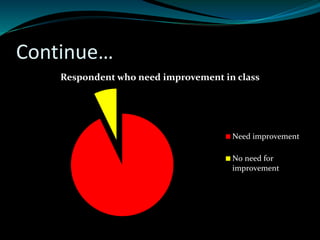
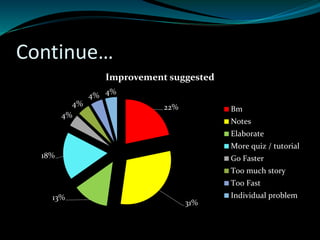
Here are some suggestions for improvement:
- Provide more examples and real-life case studies to help illustrate concepts. Stories and examples help cement understanding.
- Consider breaking lessons into smaller, more digestible chunks. The material may be too dense at times.
- Incorporate more interactive elements like polls, quizzes and group discussions to keep students engaged. Active learning is more effective than passive listening.
- Vary teaching methods - lectures, videos, group work etc. to cater to different learning styles and keep lessons interesting.
- Solicit feedback regularly to ensure the pace and content meets students' needs. Adjust based on feedback.
- Be available for individual help to address specific problems students may