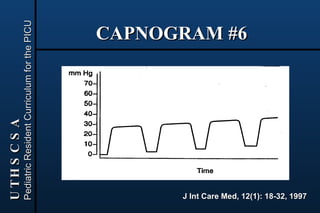
Capnography and pulse oximetry are noninvasive methods to monitor carbon dioxide and oxygen levels in patients. Capnography uses infrared absorption to measure exhaled carbon dioxide levels by detecting the absorption of infrared light as it passes through gas samples. It provides a capnogram that can be used to assess ventilation and detect abnormalities. Pulse oximetry uses spectrophotometry to differentiate oxyhemoglobin from deoxyhemoglobin and estimates functional hemoglobin saturation and heart rate by measuring light absorption at different wavelengths through tissues like the finger or ear. Both methods have sources of error and limitations, but provide useful respiratory and perfusion monitoring when applied and interpreted appropriately.