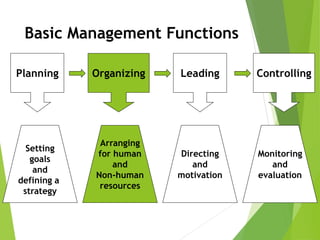
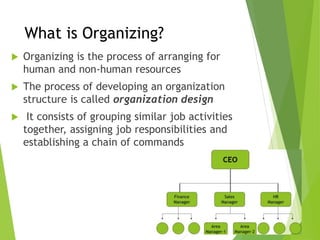
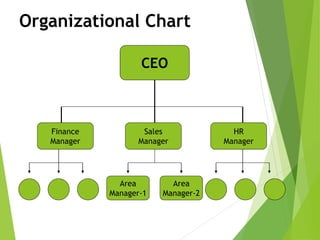
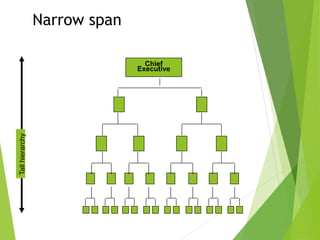
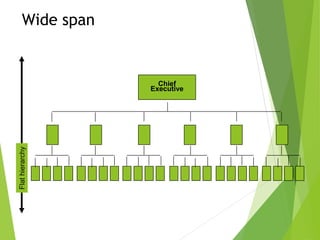
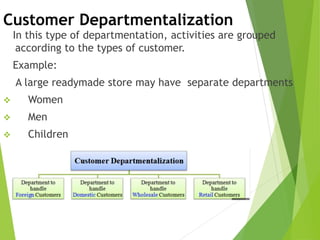
The organizing function of management involves arranging human and non-human resources and establishing an organizational structure. This includes grouping similar job activities, assigning responsibilities, and establishing reporting relationships. There are different types of organizational structures such as functional, product, process, and customer-based departmentalization. An organizational chart illustrates the structure by showing reporting relationships and positions. Key aspects of organizing include span of control, authority, responsibility, accountability, and delegation. Organizational culture refers to shared behaviors, beliefs, and values within an organization that influence how work is performed.