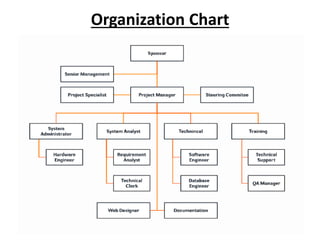
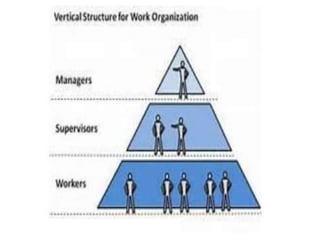
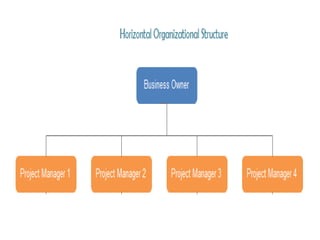
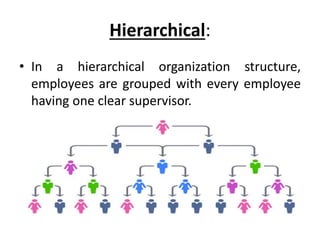
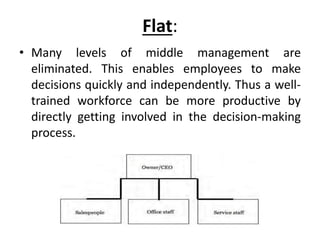
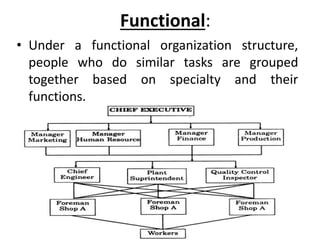
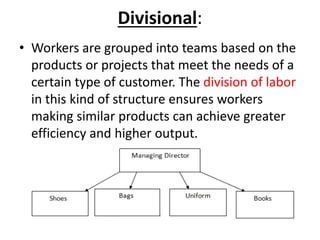
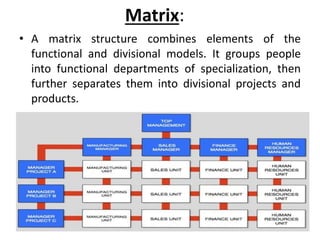
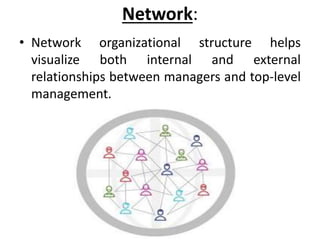
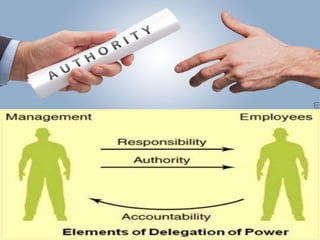
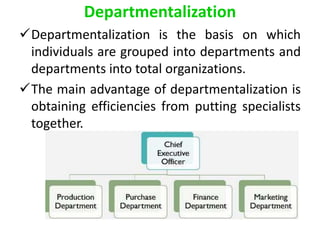
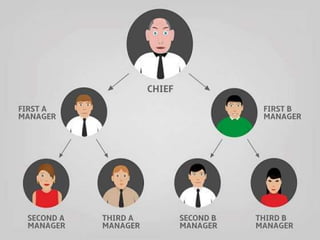
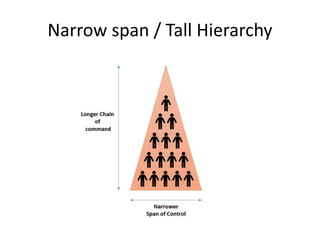
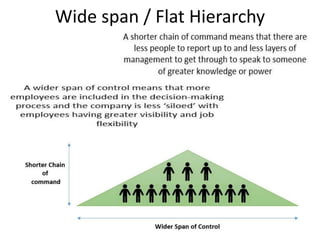
This document discusses key concepts related to organizing as a management function. It defines organizing and explains that it involves developing an organizational structure and allocating resources to achieve objectives. Some key elements of organizing discussed include departmentalization, the span of management, centralization vs decentralization, and defining reporting relationships and delegating responsibilities through an organization chart. The document also outlines different types of organizational structures like functional, divisional, and matrix structures.