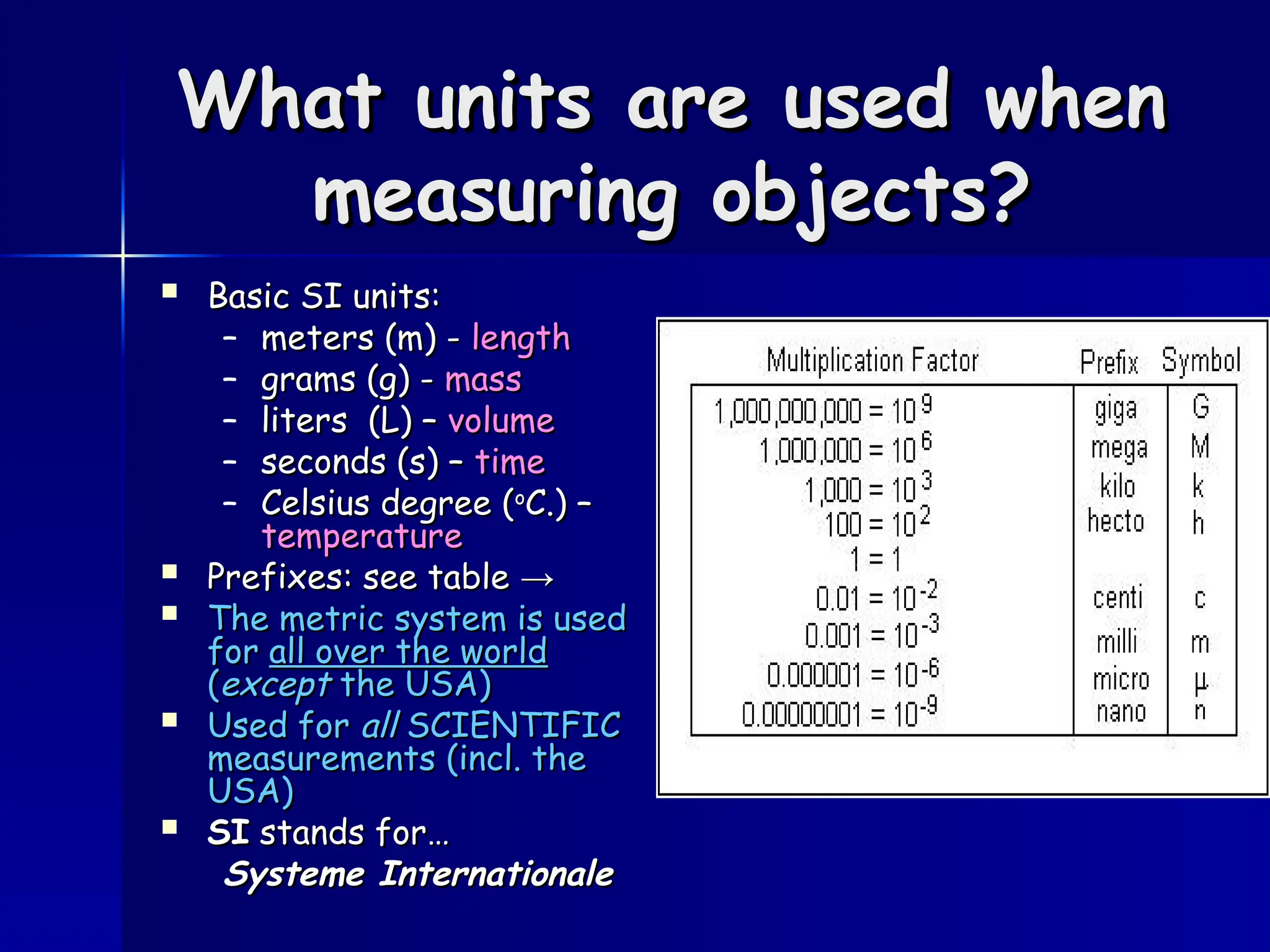
The document provides an overview of the International System of Units (SI) used in scientific measurements worldwide, highlighting its basic units such as meters, grams, liters, and seconds, along with common prefixes. It explains the method for converting between metric units and includes explanation for various temperature scales and methods for measuring mass and volume. Additionally, the document outlines practical exercises and temperature comparisons to reinforce these concepts.
![SCIENTIFIC
SCIENTIFIC
MEASUREMENT
MEASUREMENT
International System of Units
International System of Units (SI) -
(SI) -
measurement system used by scientists
measurement system used by scientists
around the world to express
around the world to express
measurements made in scientific
measurements made in scientific
investigations [the Metric System].
investigations [the Metric System].
[THE METRIC SYSTEM]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01-04bmetricsystem-240822085427-14365ed6/75/Scientific-measurement_metric_system-ppt-1-2048.jpg)