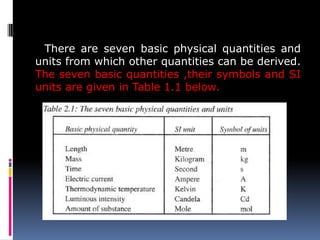
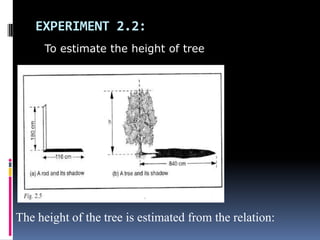
1. The document discusses various concepts related to measurement including length, area, volume, mass, density, and time. It describes the fundamental International System of Units (SI units) used to measure these physical quantities.
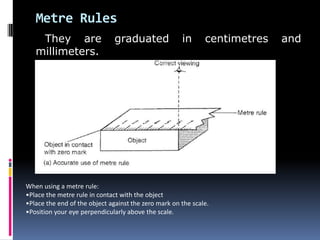
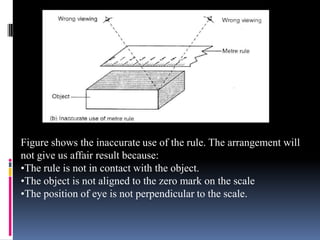
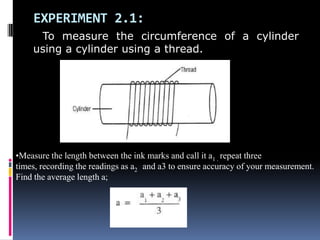
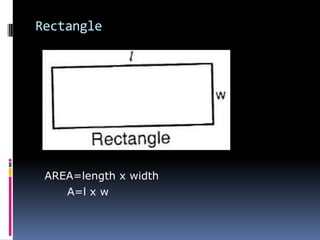
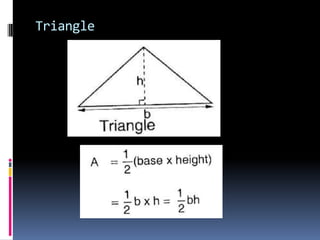
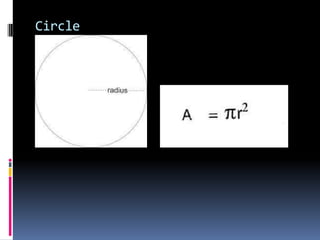
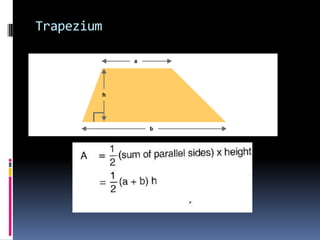
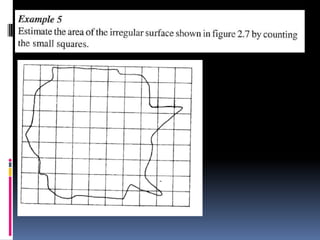
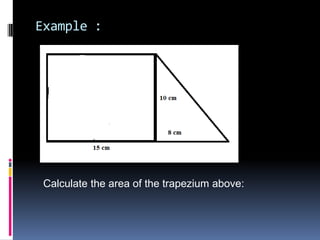
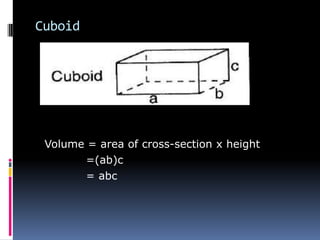
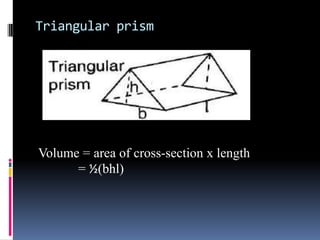
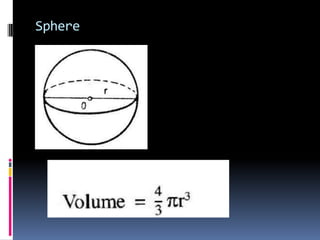
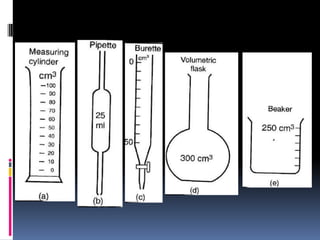
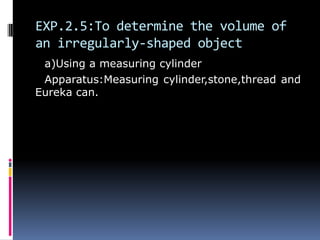
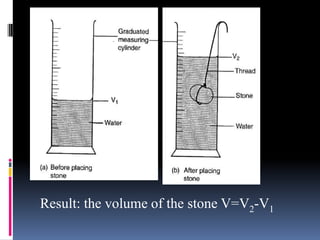
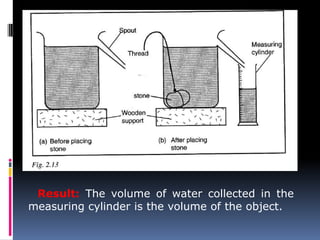
2. Methods for measuring length include using metre rules, tape measures, and estimating techniques. Area can be measured for regular shapes using formulas and irregular shapes can be divided into regular portions. Volume is measured using formulas for regular solids and displacement methods for irregular solids.
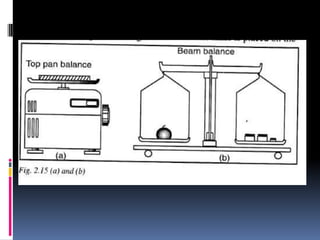
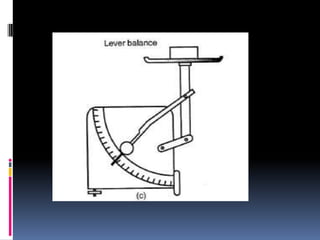
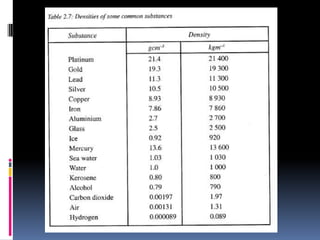
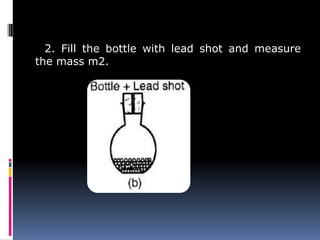
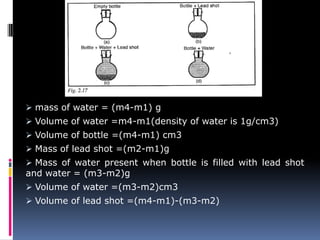
3. Mass is measured using balances, density is a ratio of mass to volume, and time intervals are recorded using stopwatches or clocks depending on the needed accuracy. Standardizing measurement systems and defining base SI units has allowed