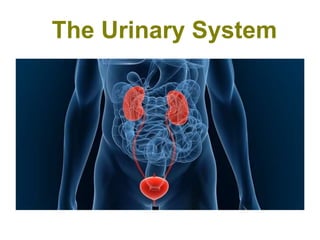
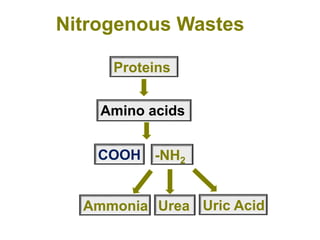
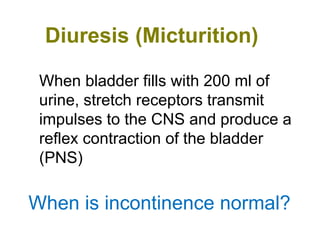
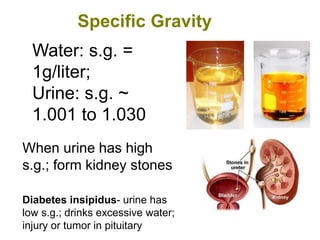
The urinary system functions to remove waste from the blood, regulate fluid and electrolyte balance, and produce hormones. It is composed of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter the blood to form urine, reabsorbing useful molecules while collecting waste to be excreted. Through intricate tubular transport, the nephron precisely regulates fluid and solute levels in the blood and produces concentrated urine for excretion.