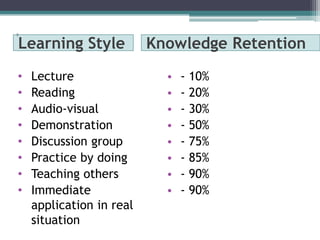
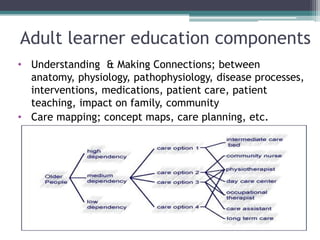
This document outlines objectives and content for a nursing education study. It describes the shift in nursing education from a traditional to collaborative approach. External forces like global issues and internal factors like new degrees are driving changes. Learning theories like Kolb's learning cycle and teaching approaches like problem-based learning are discussed. The document also covers curriculum development, teaching styles, and trends like increased interprofessional collaboration and distance learning.