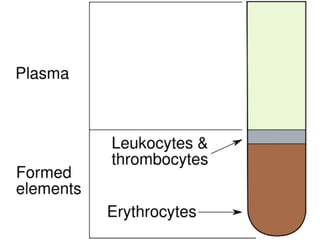
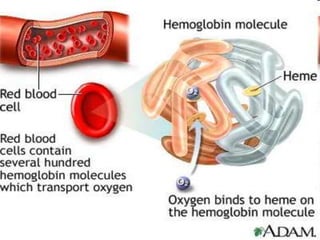
The circulatory system transports blood throughout the body, which contains both living and nonliving components to deliver nutrients and remove waste. Blood is made up of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells carry oxygen using hemoglobin, while white blood cells defend against infection through mechanisms like phagocytosis and releasing chemicals to respond to pathogens. Platelets initiate clotting to repair damaged blood vessels. Key disorders like anemia occur when red blood cells are deficient in number or hemoglobin, reducing oxygen delivery in the body.