The document discusses mathematical analysis of algorithms, including both non-recursive and recursive algorithms. For non-recursive algorithms, it describes identifying the input size, basic operation, complexity case, and setting up a summation or recurrence relation to solve. For recursive algorithms, it similarly identifies these elements and sets up a recurrence relation to solve. It provides examples of analyzing algorithms for finding the largest array element, element uniqueness, matrix multiplication, factorial, Tower of Hanoi, and calculating number of bits to store a decimal number.


![Finding largest element in array
Algorithm max_element(A,n)
maxval=A[0]
for i=1 to n-1
if A[i]>maxval
maxval=A[i]
Return maxval](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-mathematicalanaylsis-150601060826-lva1-app6891/85/03-mathematical-anaylsis-3-320.jpg)
![Element uniqueness problem
Algorithm element_unique(A,n)
for i=0 to n-2
for j=i+1 to n-1
if A[i]==A[j]
return false
return true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-mathematicalanaylsis-150601060826-lva1-app6891/85/03-mathematical-anaylsis-5-320.jpg)
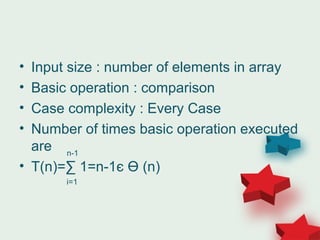
![• Input size : number of elements in array
• Basic operation : comparison of element of
Array
• Case complexity : Worst Case
• Number of times basic operation executed
are
T(n)=∑ ∑ 1 = ∑ [(n-1)-(i+1)+1]
=n(n-1)/2
i=0
n-2
j=i+1
n-1
i=0
n-2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-mathematicalanaylsis-150601060826-lva1-app6891/85/03-mathematical-anaylsis-6-320.jpg)
![Matrix Multiplication
Algorithm matrix_mul(A,B,C)
for i=1 to n
for j=1 to n
C[i,j]=0
for k=1 to n
C[i,j]=C[i,j]+A[i,k ]*B[k,j]
return C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-mathematicalanaylsis-150601060826-lva1-app6891/85/03-mathematical-anaylsis-7-320.jpg)














