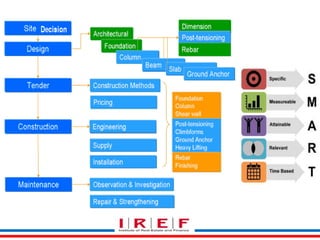
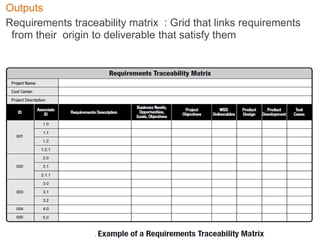
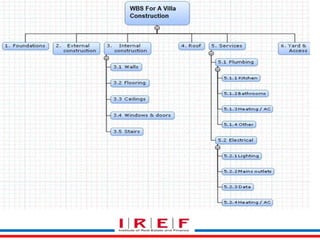
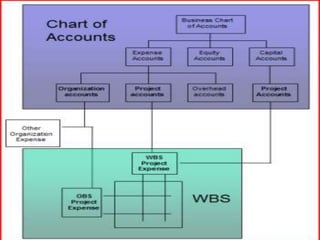
This document discusses project scope management for construction projects. It defines project scope as ensuring a project contains all required work and only the required work. The key processes are: collecting requirements, defining the scope statement, creating a work breakdown structure (WBS), validating the scope, and controlling scope. Requirements are gathered from stakeholders using techniques like interviews and workshops. The scope statement and WBS break the project scope into manageable components. Scope validation obtains customer acceptance, while scope control compares work to the baseline to ensure all approved scope is delivered.