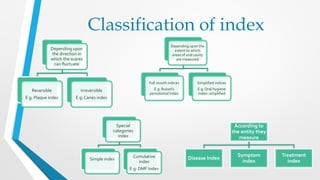
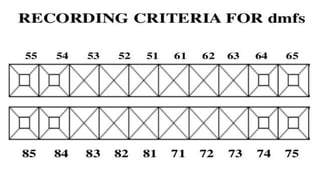
The document provides information on various oral health indices, including the CPITN (Community Periodontal Index of Treatment Needs), DMFT (Decayed Missing Filled Teeth), and DMFS (Decayed Missing Filled Surface) indices.
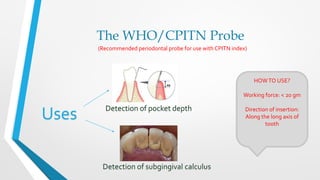
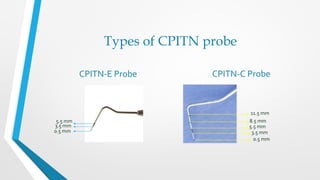
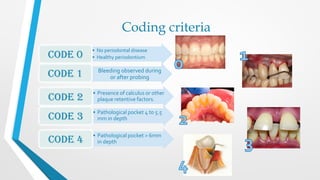
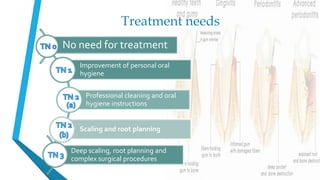
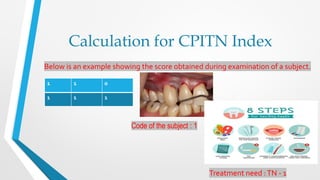
The CPITN index involves examining six index teeth in each sextant of the mouth to determine a code from 0-4 representing the periodontal treatment need. A score is given to each sextant and used to assess the periodontal treatment needs of communities.
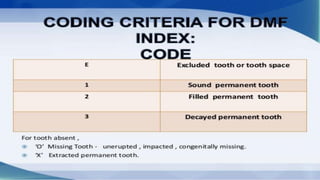
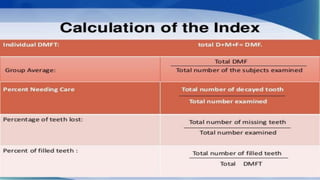
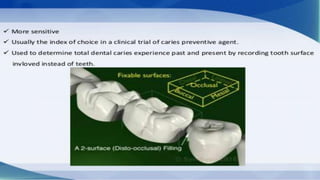
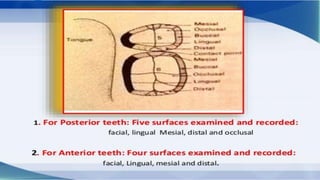
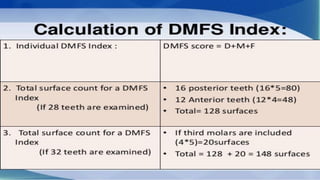
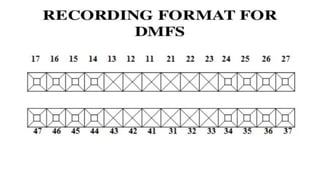
The DMFT index quantifies the number of decayed, missing, and filled teeth in a person or population. The DMFS index is similar but quantifies these values at the tooth surface