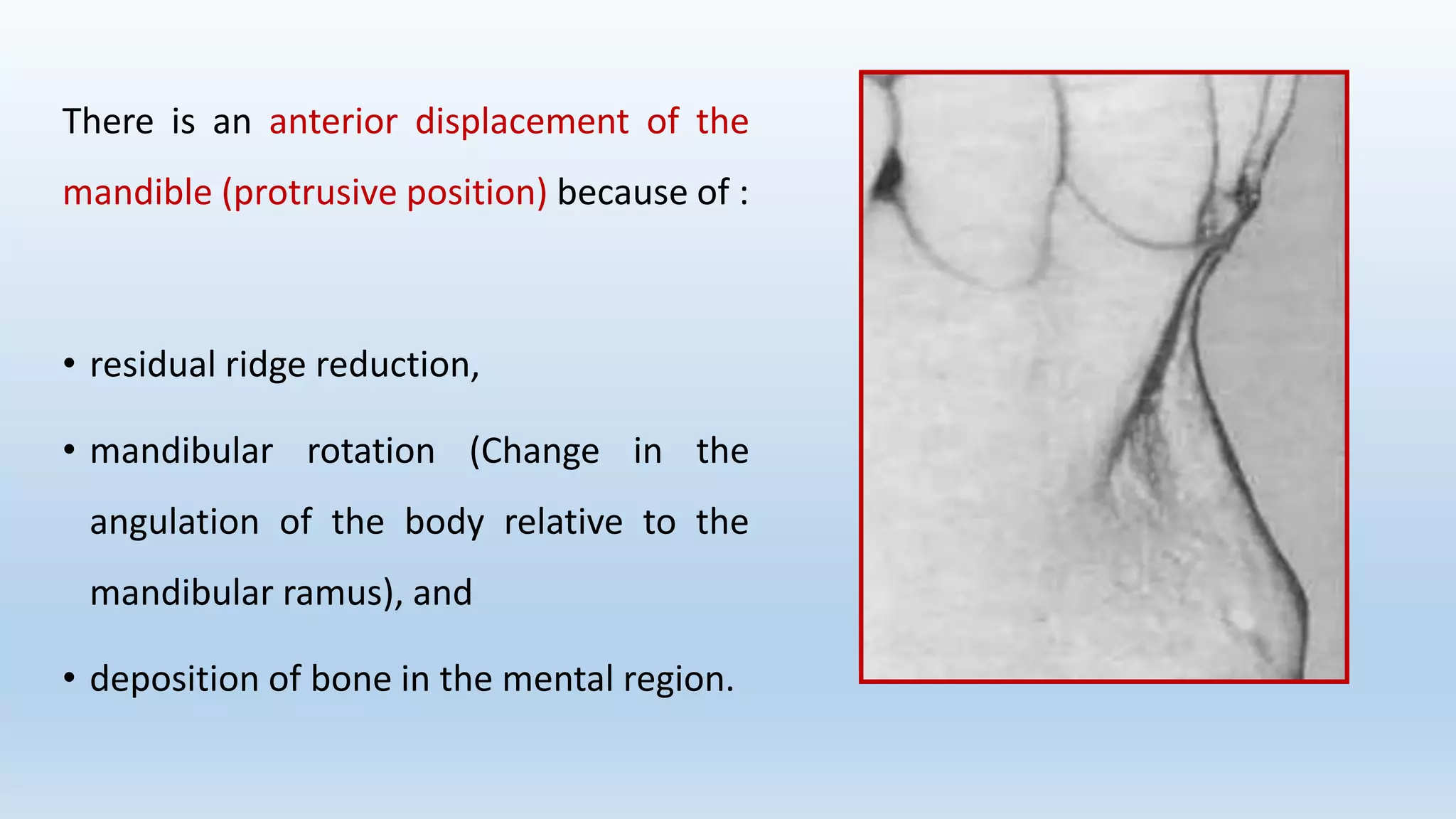
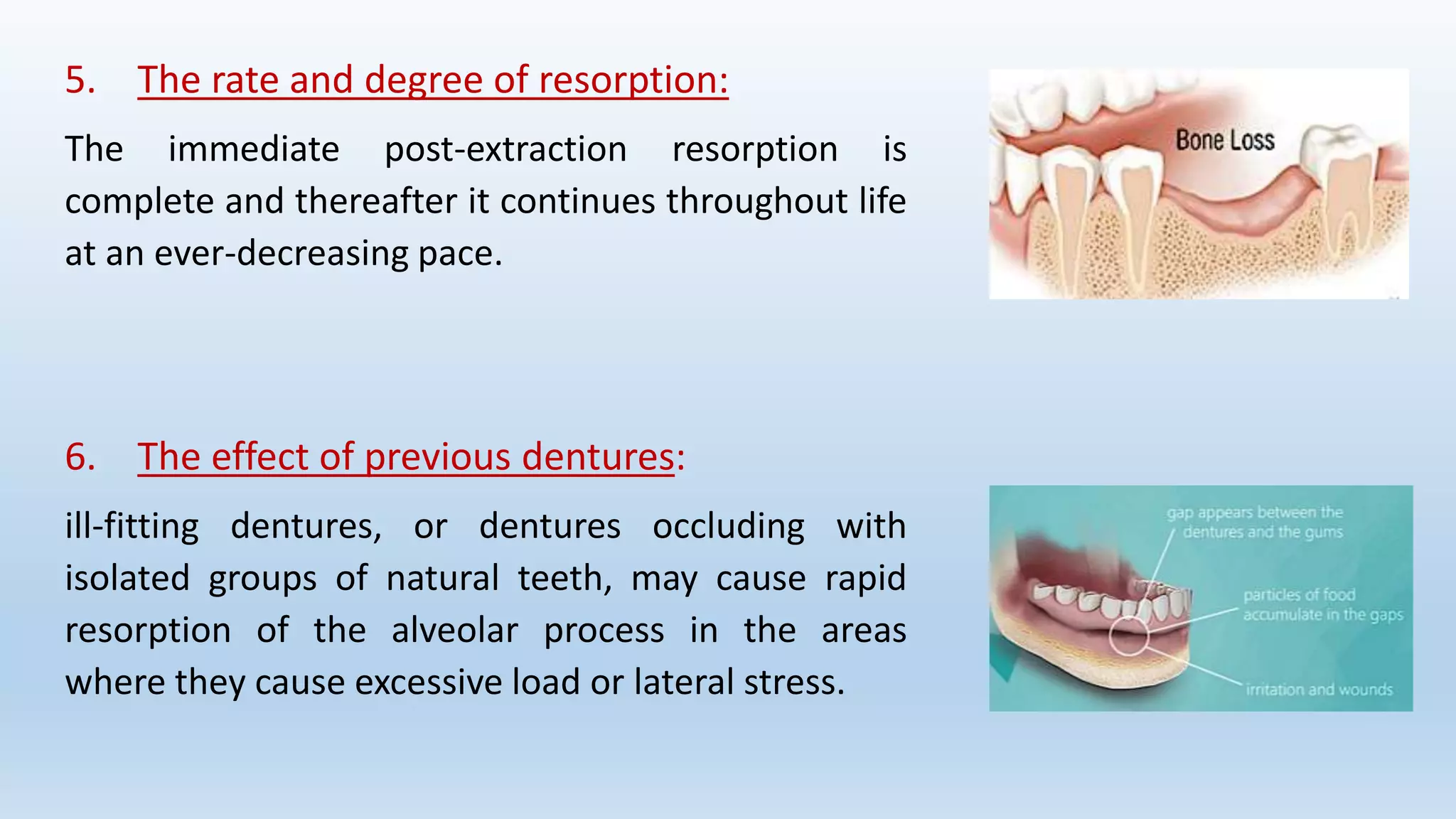
The document discusses alveolar bone and its relevance in prosthodontics. It defines alveolar bone and related terms, and describes the functions, composition, cells, classification, anatomy, development, histological structure, and influence of systemic diseases, vitamins, hormones, and drugs on alveolar bone. Alveolar bone supports teeth, distributes forces, provides attachment for muscles, acts as a reservoir for minerals, and works to maintain pH balance. Its microscopic structure consists of concentric lamellae that form Haversian systems. Conditions like hyperparathyroidism and diabetes can negatively impact alveolar bone through increased resorption.





































































![Fabricating the fixed dentures :
• The fabrication of FPD should follow treatment of osteoporosis rather
than preceding it since fabricating fixed partial denture in
periodontally compromised abutments it may accelerate the bone
loss in osteoporotic patients
• Refer patient for bone density screenings .
Von Wowern N. General and oral aspects of osteoporosis: a review. Clin Oral Investig. 2001;5:71–
82. [PubMed]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alveolarboneinprosthodontics-200418085810/75/Alveolar-bone-in-prosthodontics-76-2048.jpg)







