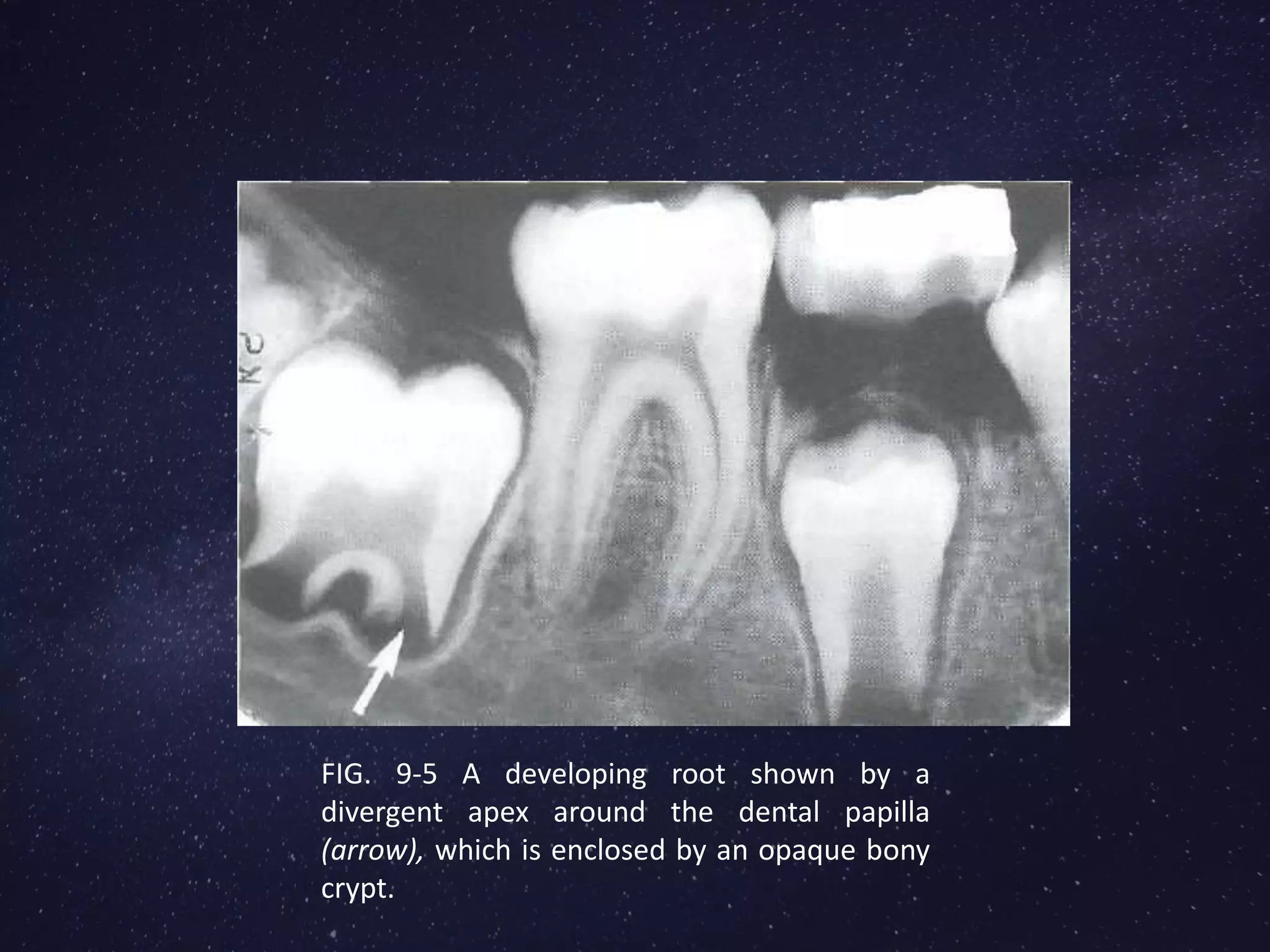
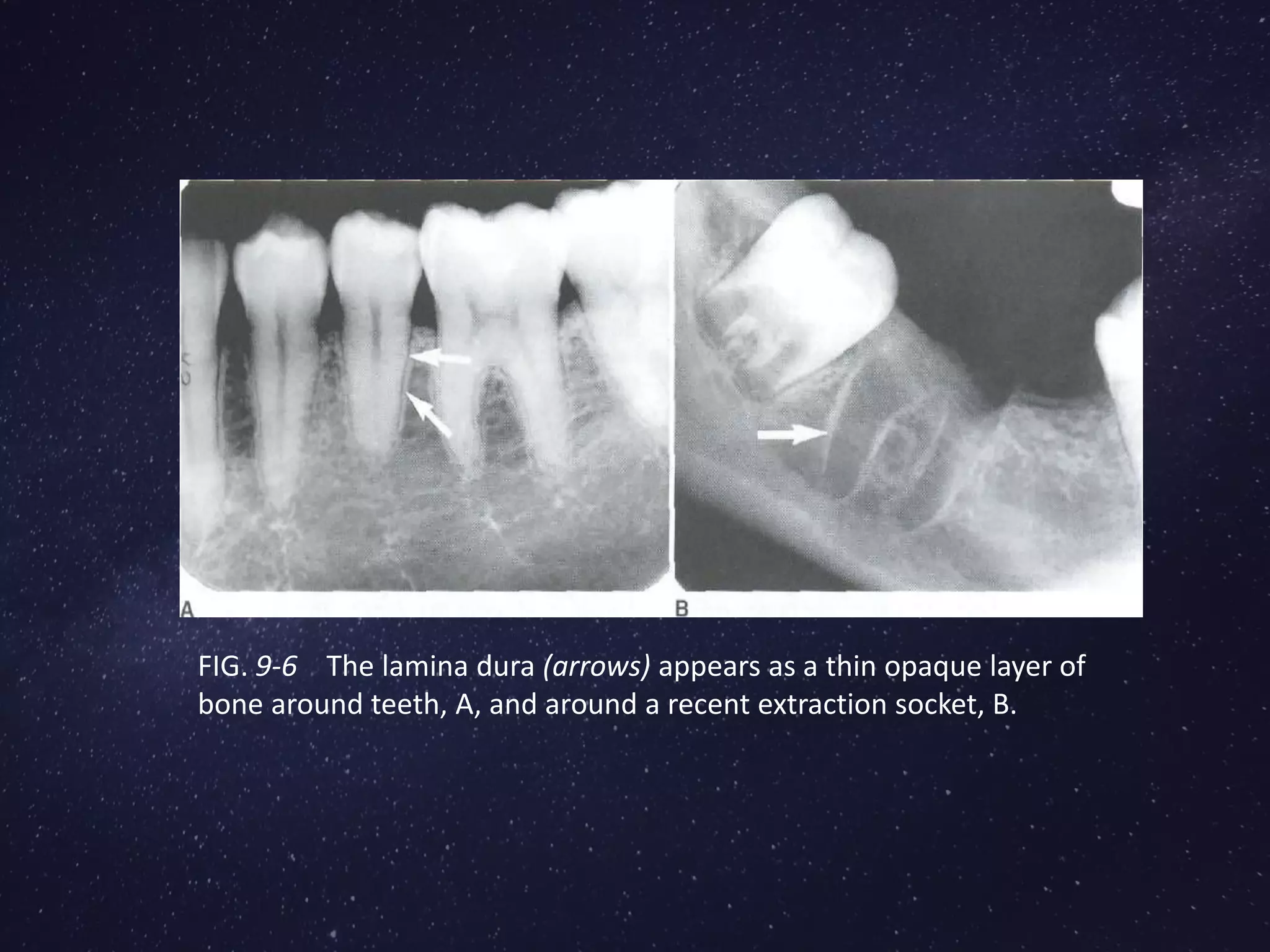
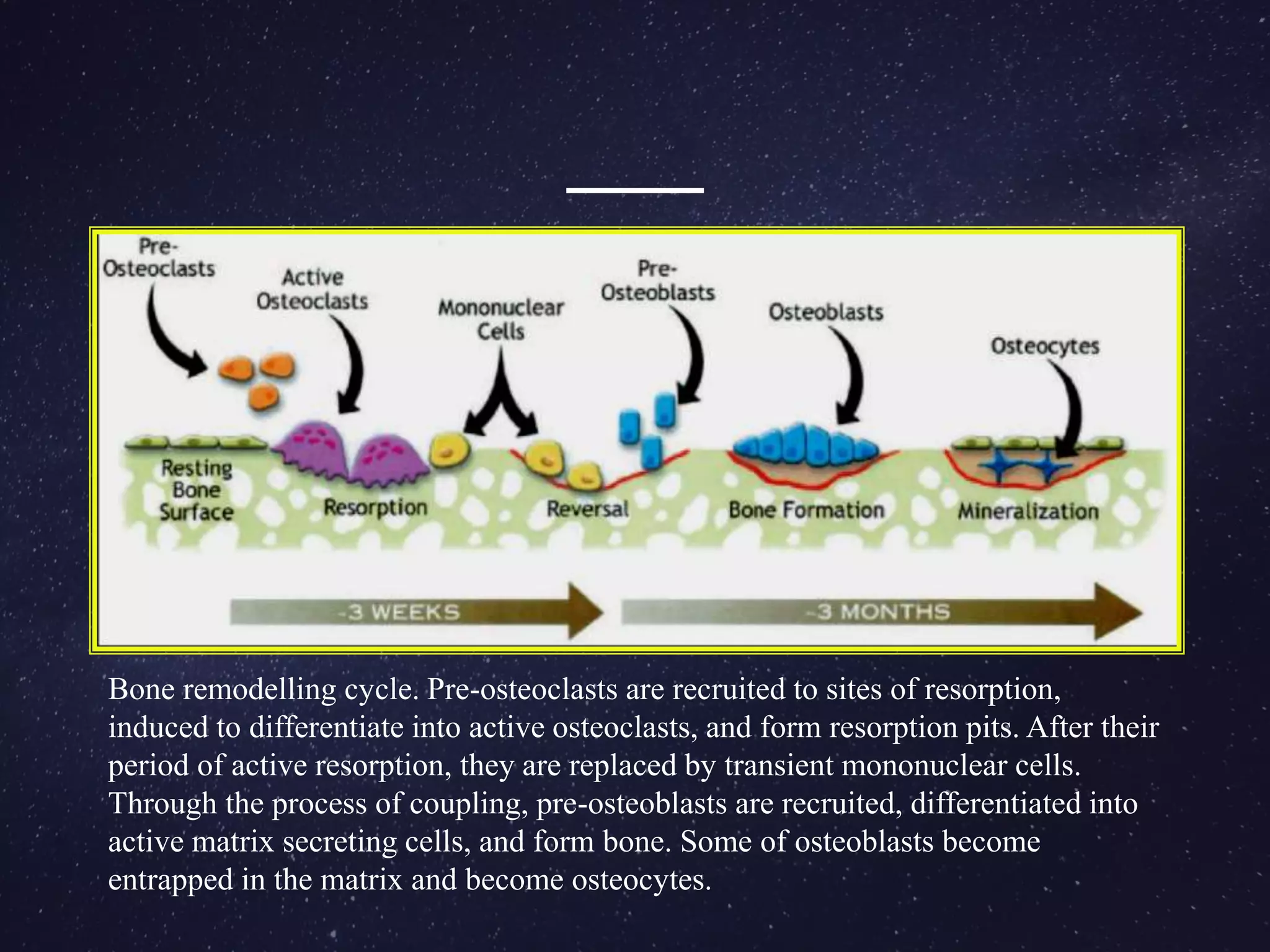
The alveolar process is the portion of the maxilla or mandible that supports and protects the tooth sockets (alveoli). It is formed during tooth eruption to provide bony attachment for the periodontal ligament. The alveolar process has two parts - the alveolar bone proper surrounding each tooth root, and the supporting alveolar bone of the rest of the process. The structure and remodelling of the alveolar bone is dependent on the presence of teeth. Bone is continually broken down by osteoclasts and rebuilt by osteoblasts to maintain levels. Loss of alveolar bone from periodontal disease is difficult to regenerate fully.