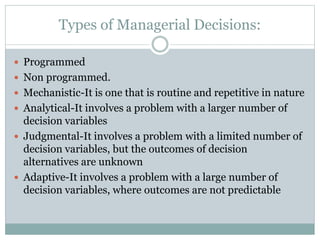
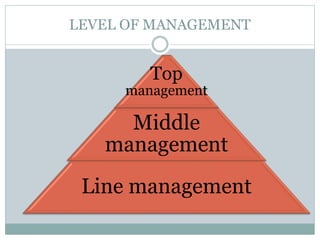
This document provides an introduction to management. It defines management as the attainment of organizational goals through planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling resources. It discusses the key functions of management, including planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. It also outlines the different levels of management in an organization and their core functions.